Introduction
A solar dryer is a sustainable innovation that leverages solar energy to effectively dehydrate materials especially food items like fruits and vegetables. Unlike traditional sun-drying methods that expose food directly to the elements, solar dryers offer a cleaner and faster alternative. The device captures sunlight, converts it into thermal energy, and traps this heat within a controlled environment. This enclosed chamber circulates warm air around the food, speeding up moisture evaporation while maintaining hygiene and protecting it from dust, insects, and unpredictable weather.
Type of Solar Dryers:
On the basis of shape it divided into three types are as follows :
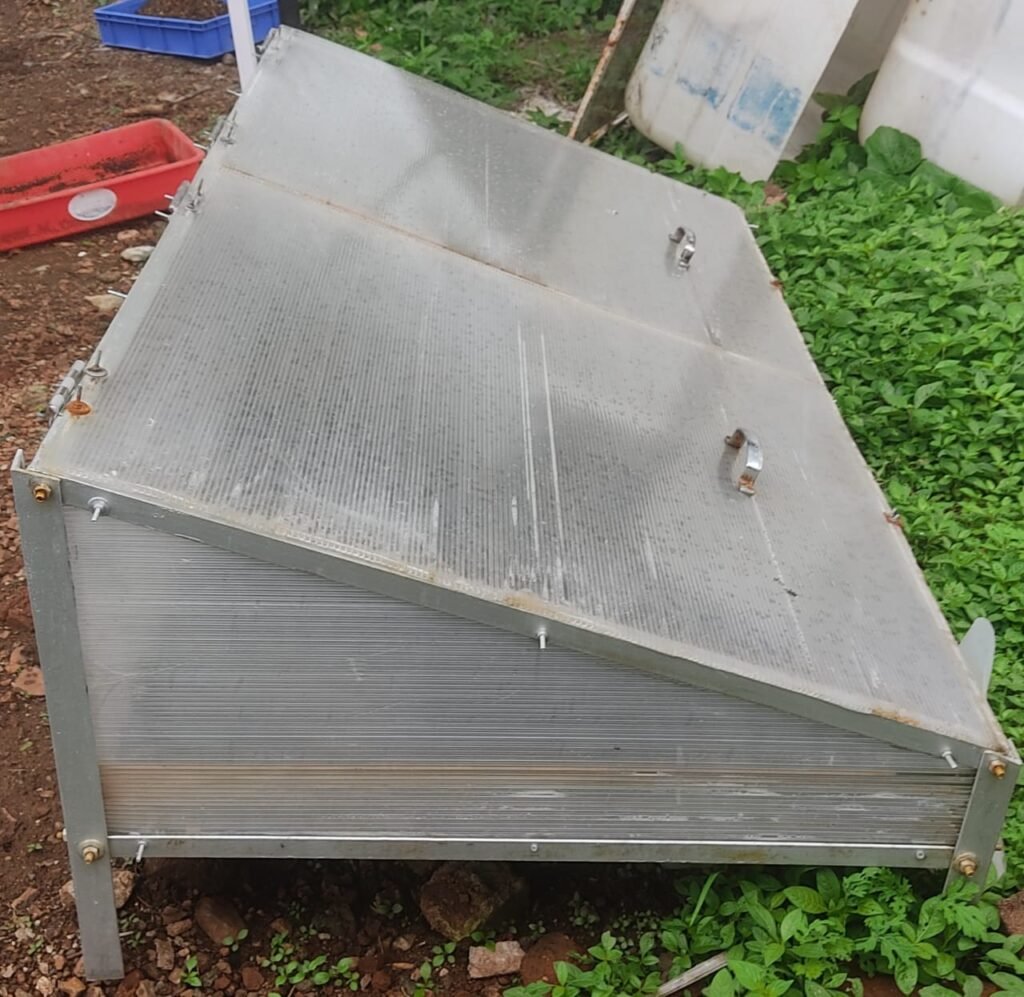
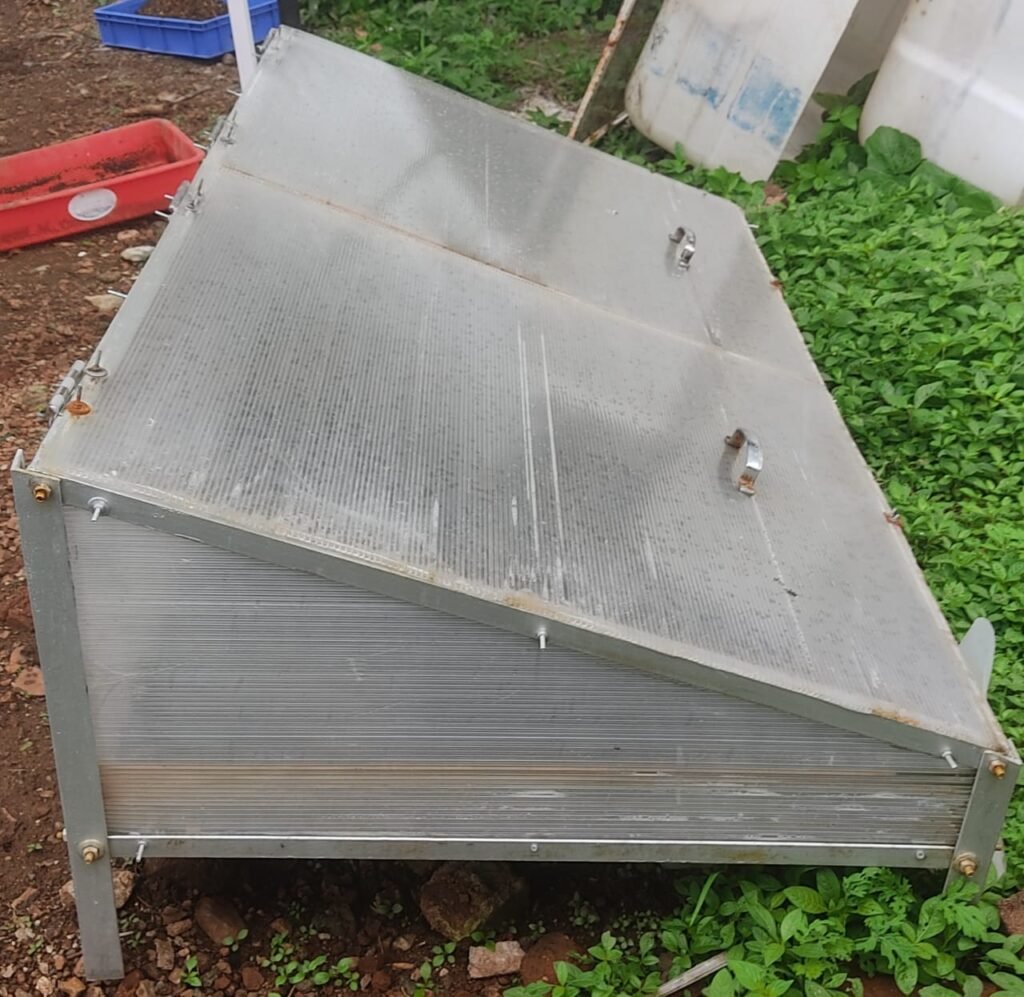
1. Flat Dryer
- Shape & Volume: Box type, 0.5026 m³
- Drying Capacity: 2 kg
- Drying Time: 2 days
- Air Circulation: Natural air circulation
- Energy Used: Solar illumination
- Absorber Plate Area: 1.64 m²
- Materials Used:
- Base: MS L frames
- Bed walls: Polycarbonate sheet
- Absorber plate: Polycarbonate sheet

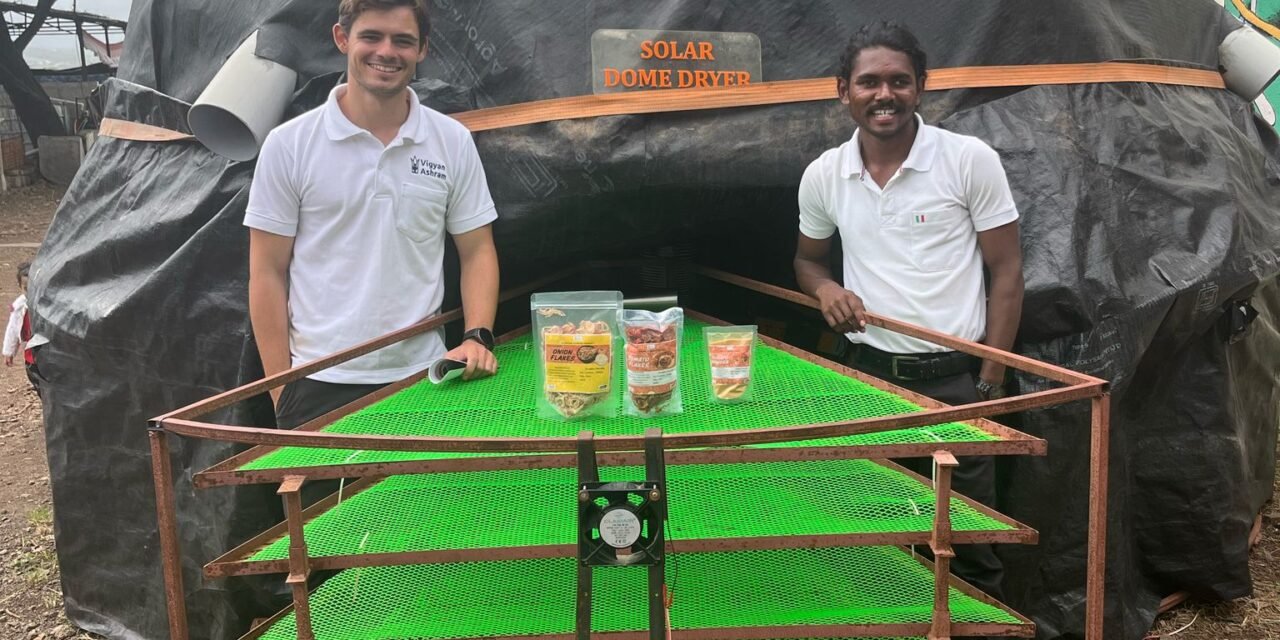
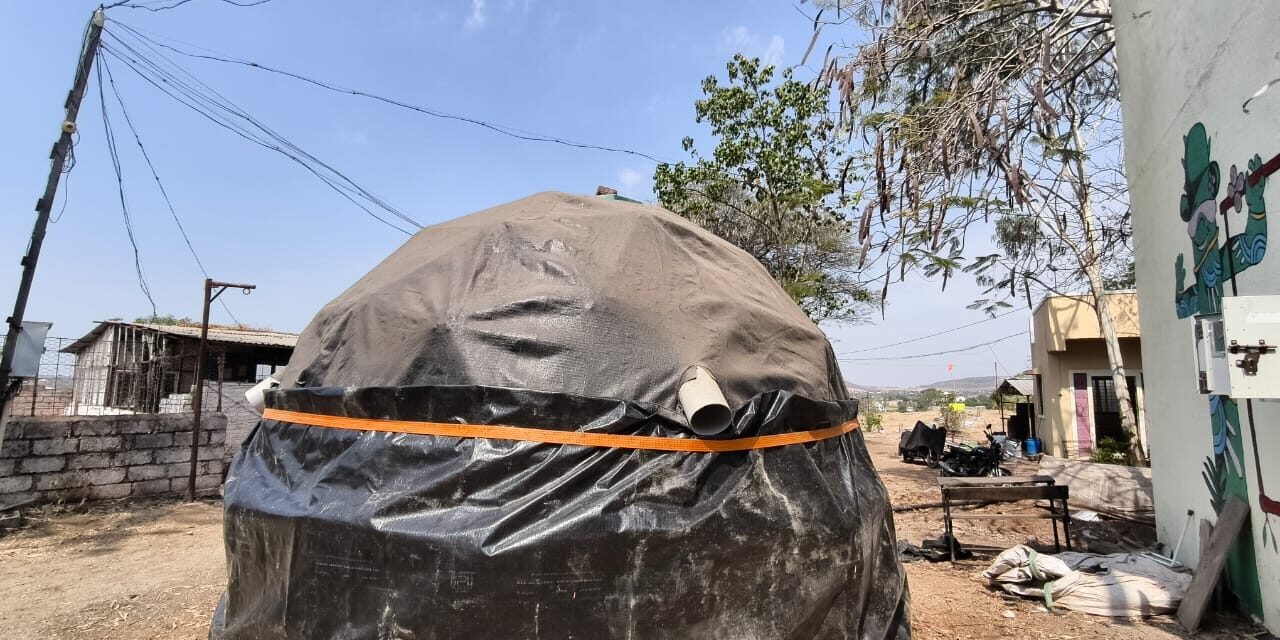
2. Dome Dryer
- Shape & Volume: Dome-shaped, 0.78345 m³
- Drying Capacity: 100kg
- Drying Time: 2 day
- Air Circulation: Forced air circulation
- Energy Used: Electricity / Solar illumination
- Absorber Plate Area: m²
- Materials Used:
- Base: Plywood circular plate
- Stand and tray: MS tubes
- Dome: Made from sheet metal

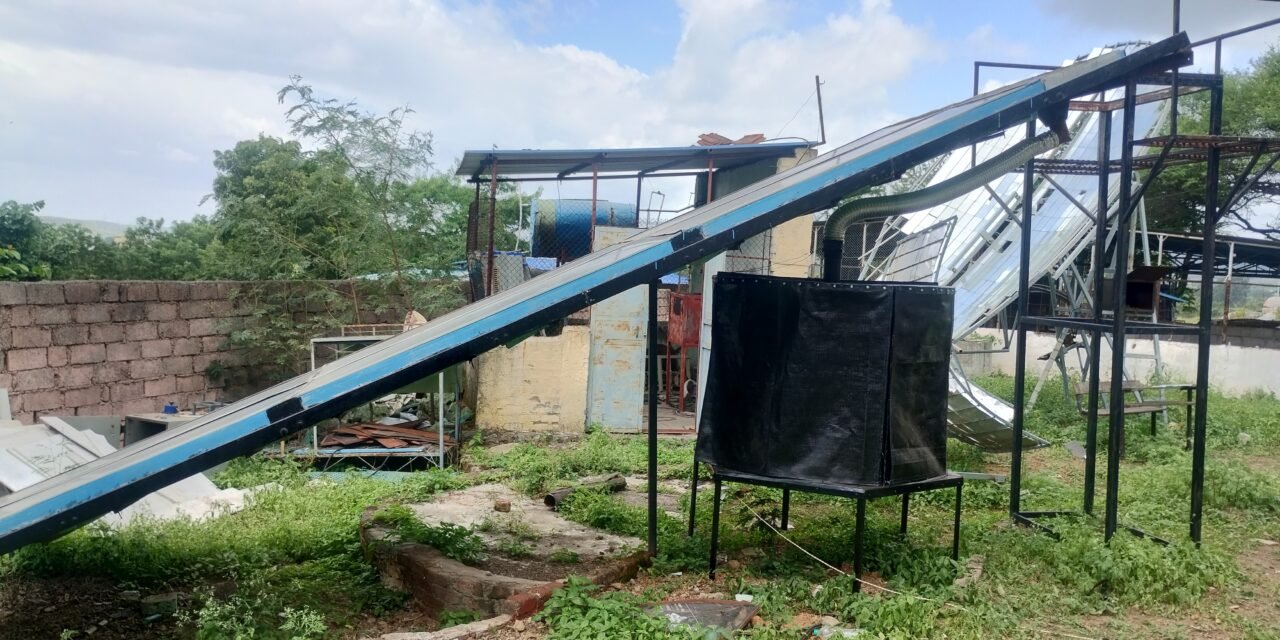
3. Inclined Dryer
- Shape & Volume: Inclined plane, 2.2 m³
- Drying Capacity: 7.3 kg
- Drying Time: 1 day
- Air Circulation: Forced air circulation
- Energy Used: Electricity
- Efficiency: 41.39%
- Absorber Plate Area: 11.97 m²
- Materials Used:
- Surface: Sheet metal with black paint coating
- Chamber walls: PVC sheets with black cloth paper
- Components: Absorber box, air circulation box, insulating foam

Factor Affecting drying
1. Temperature
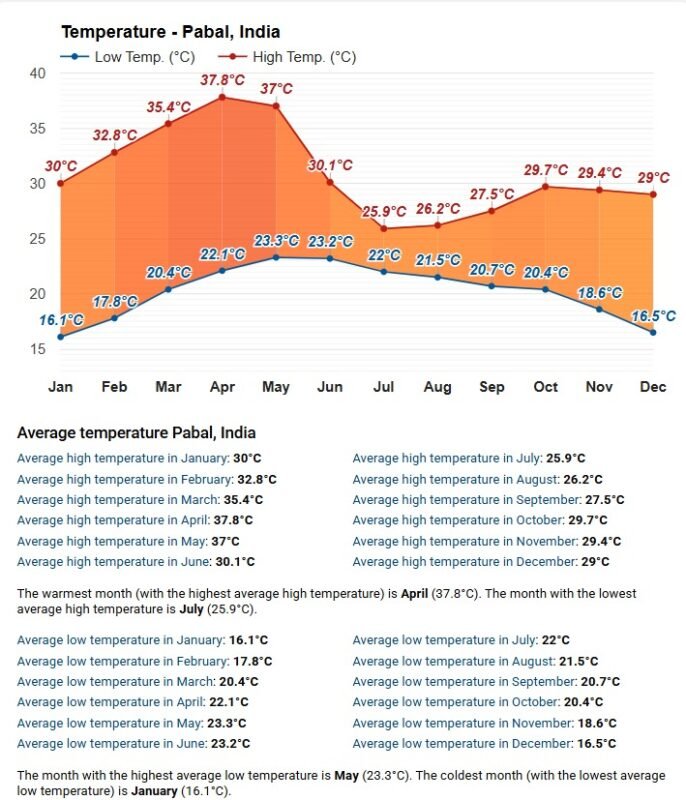
Higher temperature = faster drying
- Warmer air holds more moisture.
- It increases the rate of evaporation from the wet surface.
Lower temperature slows evaporation because the air can’t hold as much moisture.
2.Humidity
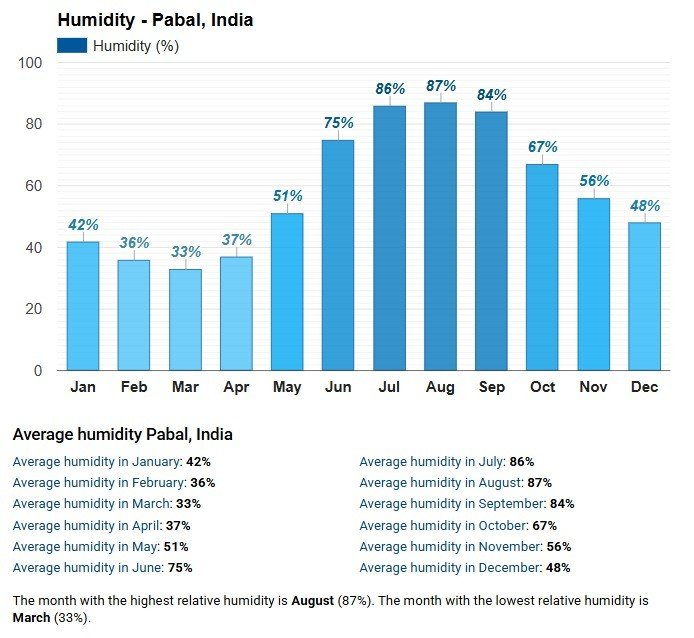
Low humidity = dry air = absorbs more moisture from the surface = fast drying.
High humidity = air is already full of moisture = evaporation slows down
3. Air Flow ( wind )
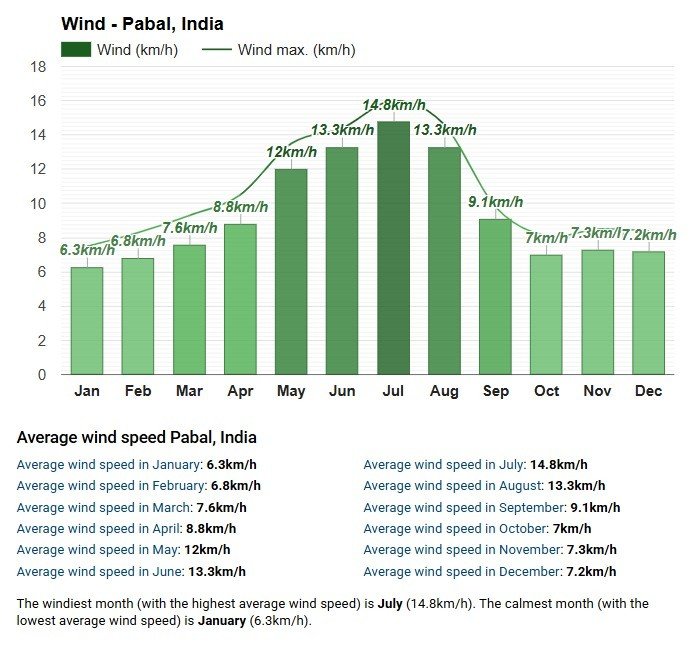
Increased wind removes the moist air layer above the drying surface.
It keeps replacing humid air with dry air, boosting evaporation.
No wind = stagnant humid air near the surface = slower drying
4. Substrate;
Every substrate has its own value of losing water from its core and from the surface of the substrate .
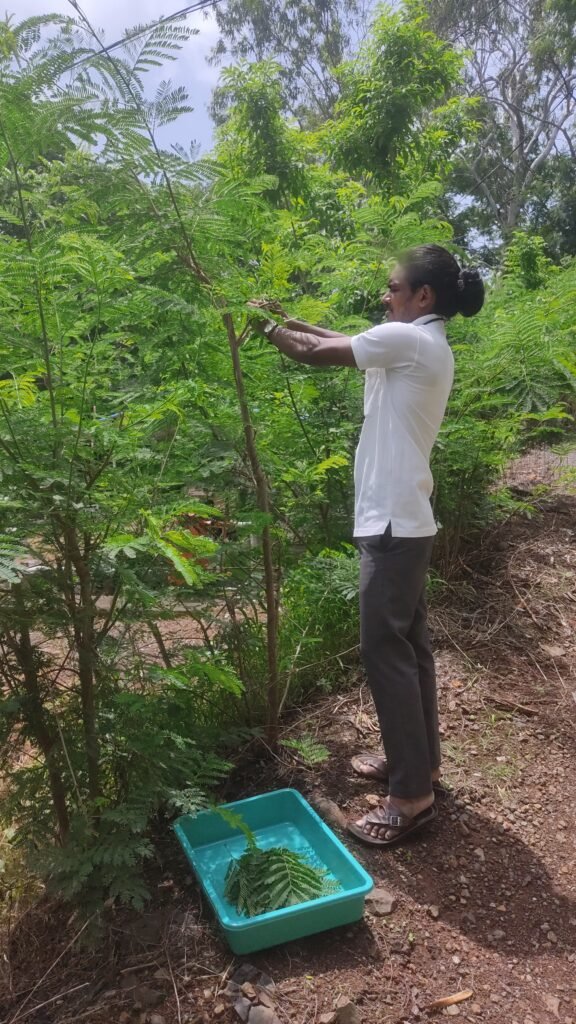
First trial on SUBABUL in Flat bed dryer
On first trial we consider readily available plants leaves SUBABUL. In Vigyan Ashram compass abundance of Subabul is available. To make it useful for drying process we cut the leaves of subabul plant measurably to fit in the flat bed dryer.
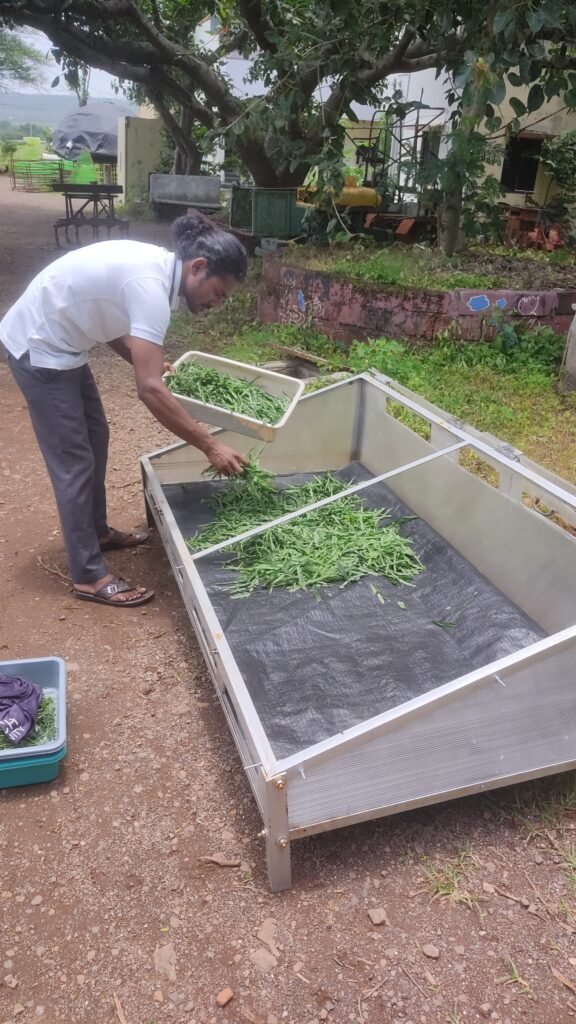


Calculations
- Initial weight of subabul leaves = 1.5 kg = 1500 g
- Final (dry) weight (day 1) = 622 g
- Drying time = From 12:50 PM to 5:30 PM = 4 hours 40 minutes = 4.67 hours ≈ 16,800 seconds
1. Moisture Removed:
Moisture Removed=1500 g−622 g=878 g
2. Moisture Content (Wet Basis %):
MC wb=Initial Weight Moisture Removed /initial weight ×100
=878/1500×100=58.53%
3.Moisture Content (Dry Basis %):
MC db=Moisture Removed /Final Dry Weight×100
=878/622×100=141.13%
4. Drying Rate (g water removed per second):
Drying Rate=878 g/16,800 s≈0.0523 g/s
Or in per hour:
=878/4.67≈188.01 g/hr
17th June – Arrival at Vigyan Ashram
Today marked the beginning of my journey at Vigyan Ashram, Pabal, as part of the IIT Bombay – TUM SEED Internship Program. Arriving at this rural innovation hub was both humbling and inspiring. The campus, surrounded by a serene landscape, reflects its mission—to blend science and rural life for meaningful innovation.
I spent the day settling into the environment, meeting fellow interns and the staff, and getting a basic idea of the various domains in which the ashram functions—from fabrication and electronics to agriculture and energy. I also got an initial glimpse of the solar dryers set up on campus, which would later become central to my project.
18th June – Orientation & Observations
The day began with an orientation that introduced us to the philosophy and working model of Vigyan Ashram. We learned how the ashram uses learning-by-doing as its core pedagogy. I got familiar with the daily schedule and the hands-on nature of projects here.
In the second half, I walked around the premises, carefully observing different types of dryers being used—especially the inclined dryer, dome dryer, and flat-bed dryer. I began noting initial thoughts on how airflow, sunlight direction, and material loading might affect drying performance—forming early ideas for the experimental phase.
19th June – Exploring Existing Setups
My third day was dedicated to deep exploration of the existing infrastructure. I took closer looks at how different types of solar dryers are positioned and how they’re performing in real conditions. I noted variables like sunlight exposure during various times of the day, fan arrangements, airflow patterns, and the design of trays.
I also reviewed previous data from earlier interns and staff, which gave me context about moisture loss patterns and drying times across various materials—like herbs, leaves, and even BSF larvae. These observations helped me understand what improvements or trials might be relevant during my project phase.
20th June – Self-Study and Preparation
Today was focused on preparing myself with technical knowledge for the project. I studied research papers and documentation related to solar drying technologies, particularly for drying vegetables and fruits. I also learned about energy loss mechanisms, airflow optimization techniques, and drying kinetics.
In the field, I cross-verified existing designs with those I’d read about, trying to visualize how design modification could lead to performance improvement. These studies formed the backbone of my initial project approach.
21st June – First Official Project Meeting
A major milestone today was my first project discussion with Dixit Sir and Prasad Sir. I formally introduced the project topic: “Performance Investigation of Solar Dryer for Vegetables and Fruits Drying.”
During the meeting, we discussed:
- Main Objective: To improve the efficiency of existing solar dryers at Vigyan Ashram.
- Identified Problems: Uneven drying, poor airflow control, difficulty in material placement/removal, and lack of data for certain conditions.
- Expected Outcomes: A detailed performance comparison of different dryers, technical suggestions for design improvements, and real drying efficiency tests on selected materials.
They appreciated my groundwork and gave me guidance on approaching the trials methodically—suggesting that I start by interacting with Akshay dada, who had hands-on experience with previous solar drying and product sales.
22nd June – Expert Consultation with Akshay Dada
Today I had a very informative and practical discussion with Akshay Dada, who has been working extensively on the solar drying systems at Vigyan Ashram and is also involved in marketing dried products.
Key Insights from the Meeting:
| Topic | Notes |
|---|---|
| Solar Dryer Types Used | Inclined Dryer, Dome Dryer, Flat Bed Dryer |
| Existing Issues | Tray net damage, uneven airflow, long drying hours in humid climate |
| Sales Challenges | Quality consistency, appearance of dried products, hygiene |
| Marketing Channels | Local farmers’ markets, tie-ups with self-help groups, small shops |
Akshay Dada recommended I observe past trials on Lemon Grass (Gavati Chaha) and BSF larvae, which face drying inconsistency. His field knowledge added real-world perspective to my technical planning.
23rd June – DBRT Students’ Farewell & Inspiration
Today was a heartfelt day as the DBRT (Diploma in Basic Rural Technology) students had their send-off ceremony. Watching these students talk about their journey was deeply motivating.
They spoke about:
- Learning practical life skills: plumbing, wiring, food processing
- Personal transformations and confidence boost
- How the ashram gave them purpose and self-reliance
Reflection:
This made me realize that scientific interventions like my project on solar drying are not just technical tasks—they have the power to uplift rural livelihoods when applied meaningfully.
24th June – Measurement and Site Visit to Heat Pump Dryer
Today, I began formally collecting dimensions and technical parameters of all three dryers.
Dryer Measurement Table:
| Dryer Type | Tray Area (per tray) | No. of Trays | Total Tray Area | Fan Support | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dome Dryer | 0.5 m² | 3 | 1.5 m² | 8 | Passive type |
| Inclined Dryer | 0.4 m² | 4 | 1.6 m² | 2 fans | Needs net replacement |
| Flat Bed Dryer | 1.0 m² | 2 | 2.0 m² | ✅ | Higher loading capacity |
In the afternoon, I visited Dhamari village to examine a heat pump dryer installed by a local farmer. Unlike solar dryers, this system:
- Works independent of weather
- Has precise temperature control
- Is more energy-intensive but gives uniform drying
I documented its build and working system with pictures and sketches for possible benchmarking.

25th June – Material Procurement at Manchar
Today I traveled to Manchar City, around 20 km from Vigyan Ashram, to procure the net material required for the trays of the Inclined Solar Dryer. The previous net had worn out, causing difficulties in placing or removing drying material.
I evaluated different types of nets:
- Plastic Mesh (Low cost, less durable)
- Stainless Steel Mesh (High cost, highly durable)
- Fiber-Coated Nylon (Mid-range option, heat resistant)
After cost-benefit comparison, I selected fiber-coated nylon for initial replacement.
26th June – Holiday (Pune Visit)
Today was a scheduled holiday, and I visited Pune with fellow interns for a short break. The city visit helped me refresh and reflect on the past week’s learning.
Reflection:
In just a few days, I’ve gone from exploring ideas to defining a concrete action plan. The interplay between fieldwork and technical thinking has made this internship one of the most enriching experiences so far.
27th June – Fan Installation & Consultation with Abhijit Sir
Today, I had a fruitful consultation with Abhijit Sir regarding the progress of my solar dryer project. He reviewed my understanding and gave practical suggestions to improve the Inclined Dryer efficiency.
Major Tasks:
- Installed two fans (top and bottom) inside the Inclined Dryer
- Connected both to a timer circuit to control airflow duration and reduce overheating during peak sun
Key Learning:
Fan-assisted airflow increases moisture removal speed and ensures more uniform drying of leafy materials like Subabul and Gavati Chaha.
28th June – First Trial: Subabul Drying
My first official experimental trial began today using Subabul leaves in the Inclined Dryer.
Subabul Drying Trial
| Time | Weight (g) |
|---|---|
| 11:00 AM | 1500 g |
| 6:00 PM | 622 g |
Weight Reduction:
1500g → 622g
That’s a loss of 878g, or 58.5% moisture loss in one day.
Subabul Drying – Line Chart
Subabul Drying Progress – 28th June
|
| ● 1500g
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ● 622g
|_______________________________
11:00 AM 6:00 PM
Modification:
I also installed a timer for both fans (top and bottom) of the Inclined Dryer to automate airflow for 2 hours ON / 1 hour OFF cycles.
29th June – Review and Maintenance
Today was a review and maintenance day. I:
- Revisited the Subabul trial data with Abhijit Sir
- Checked the net condition in Inclined Dryer
- Scheduled repairs for the tray frame and insulation cracks
I also prepared for the next trial with Gavati Chaha, known for its high essential oil and moisture conten
30th June – Trial 2: Gavati Chaha
Started trial on Gavati Chaha (Lemon Grass) in the Inclined Dryer.
Gavati Chaha Drying Trial – Day 1
| Time | Weight (g) |
|---|---|
| 11:30 AM | 930 g |
| 6:00 PM | 722 g |
Day 1 Moisture Loss:
22.4% moisture loss in 6.5 hours
Gavati Chaha – Day 1 Line Chart
plaintextCopy codeGavati Chaha Drying Progress – 30th June
|
| ● 930g
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ● 722g
|_______________________________
11:30 AM 6:00 PM
Observation:
- Moderate drying rate due to weather fluctuation
- Essential oils may slow down moisture evaporation
- Leaf stacking could reduce surface area exposure — tray modification may be needed
Summary Table – Drying Trials (28th–30th June)
| Date | Material | Initial Weight | Final Weight | Moisture Loss (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 28th June | Subabul Leaves | 1500 g | 622 g | 58.5% |
| 30th June | Gavati Chaha | 930 g | 722 g | 22.4% |
1st July – Final Weighing of Gavati Chaha & BSF Trial Begins
Today marked the second day of drying for Gavati Chaha and a new trial on Black Soldier Fly larvae (BSF alli) in the Inclined Dryer.
Gavati Chaha – Final Readings
| Time | Weight (g) |
|---|---|
| 10:00 AM | 385 g |
| 6:00 PM | 265 g |
Total Moisture Loss (from 930g):
- Final weight: 265 g
- Moisture loss: 930g – 265g = 665g
- Moisture loss %: 71.5%
BSF Alli – Trial in Inclined Dryer
| Time | Weight (g) |
|---|---|
| 10:00 AM | 90 g |
| 6:00 PM | 60 g |
Moisture Loss: 33.3%
Observation: BSF larvae are rich in proteins and fats, so they retain internal moisture longer and need high, consistent heat + airflow.
1st July – Final Weighing of Gavati Chaha & BSF Trial Begins
Today marked the second day of drying for Gavati Chaha and a new trial on Black Soldier Fly larvae (BSF alli) in the Inclined Dryer.
Gavati Chaha – Final Readings
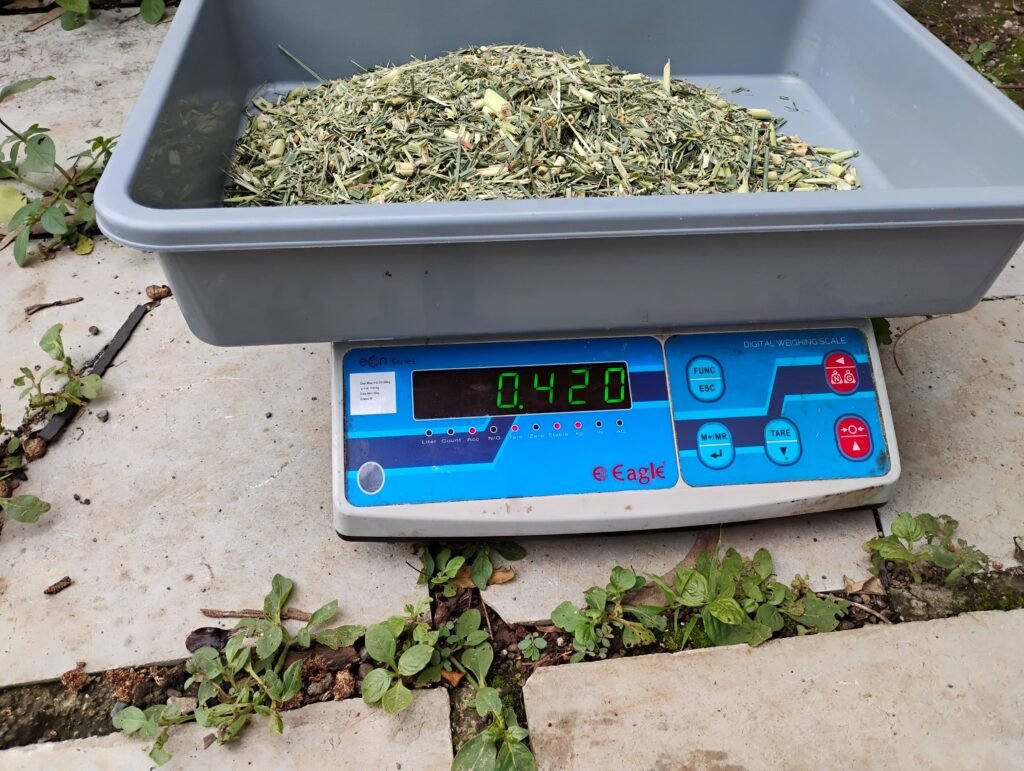

| Time | Weight (g) |
|---|---|
| 10:00 AM | 385 g |
| 6:00 PM | 265 g |
Total Moisture Loss (from 930g):
- Final weight: 265 g
- Moisture loss: 930g – 265g = 665g
- Moisture loss %: 71.5%
BSF Alli – Trial in Inclined Dryer
| Time | Weight (g) |
|---|---|
| 10:00 AM | 90 g |
| 6:00 PM | 60 g |
Moisture Loss: 33.3%
Observation: BSF larvae are rich in proteins and fats, so they retain internal moisture longer and need high, consistent heat + airflow.
2nd July – Gavati Chaha in Flat Bed Dryer & Dome Dryer Prep
- Transferred remaining Gavati Chaha into the Flat Bed Dryer to study comparison between inclined and flat drying techniques.
- Cleaned the Dome Dryer thoroughly for upcoming BSF larvae trials.
Cleaning Checklist:
| Dryer | Task Performed |
|---|---|
| Dome Dryer | Tray scrubbing, vent clearing |
| Flat Bed | Fan mesh cleaned, surface swept |
3rd July – Final Dome Dryer Clean-Up
Completed final dust and debris removal from Dome Dryer and ensured all trays are leveled. This will ensure more uniform drying and accurate LOD results.
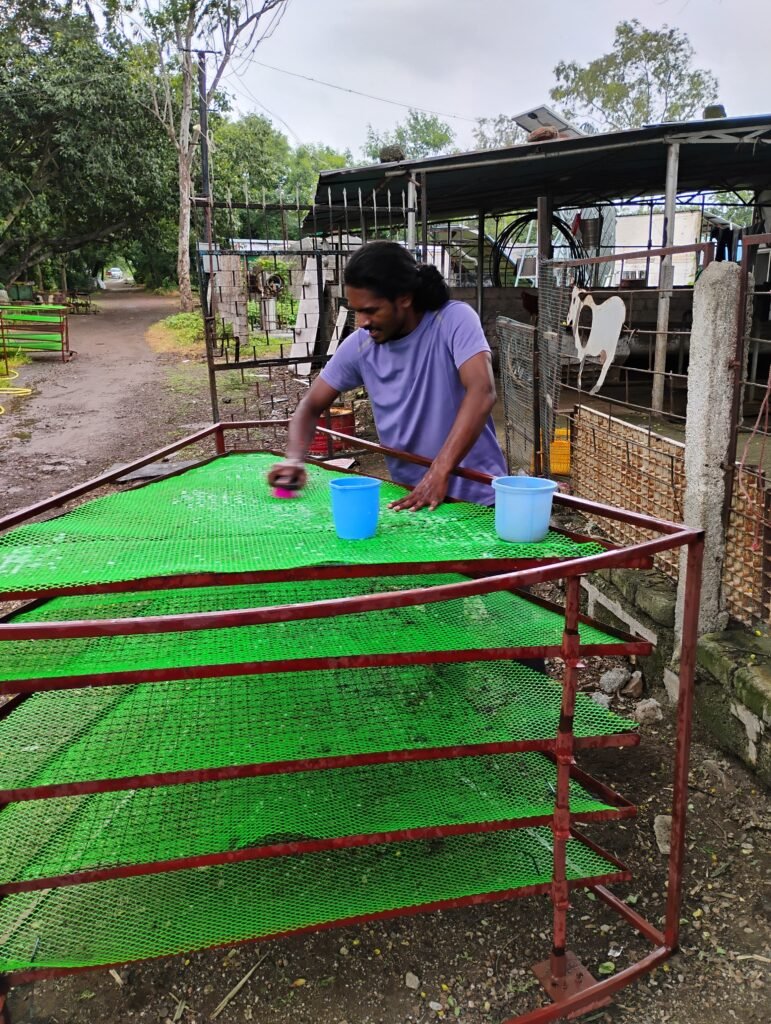

4th July – LOD Calculation for BSF Alli
Today, I conducted a Loss on Drying (LOD) test for BSF larvae using an oven to get precise moisture vs. solid content.
LOD Result Table
| Sample | Initial Wt (g) | Dried Wt (g) | Moisture Content (%) | Solid Content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BSF Alli | 5.00 g | 2.49 g | 50.2% | 49.8% |
Learning: Even though the outer layer dries quickly, inner core retains water, so it’s important to have airflow from below too.
BSF Capacity per Square Foot
I tested how much BSF larvae can be placed per sq. foot for optimal drying.
| Tray Size (sq. ft) | Max Load (g) |
|---|---|
| 1.0 | 140 g |
Conclusion: Loading more than this causes stacking, which traps moisture and slows drying.
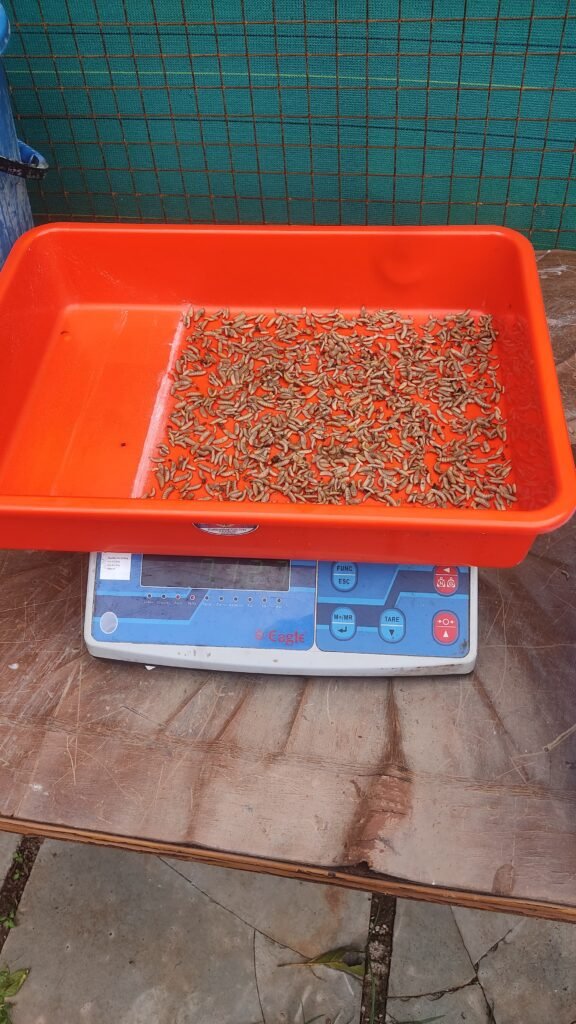

Trial on Flat Bed Dryer with BSF (360g)
| Time | Initial Wt | Final Wt | Loss |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10:00 AM | 360 g | 320 g | 40 g |
Moisture Loss: 11.1%
Observation: Less loss than expected → may require increased airflow and temperature.
5th July – Oven Area & Capacity Calculation
Today, I calculated total oven tray area and how much BSF alli it can accommodate.
Tray Area Calculation:
| Dimension (ft) | Formula | Result |
|---|---|---|
| a = b = 1.4 ft | Area = a × b | 1.96 sq. ft |
Capacity in Oven
| Tray Count | Area/Tray | BSF Capacity/tray | Total Capacity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 trays | 1.96 sq.ft | 140g × 1.96 = 274g | 548.8 g |
Result: One oven can accommodate 548.8g of BSF larvae evenly.
6th July 2025 – BSF Larvae Drying Trial
Today, I performed a drying trial using Black Soldier Fly (BSF) larvae. I placed 280g of larvae into three trays and an additional 512g in a fourth tray, resulting in a total of 1352g. The drying was conducted using an oven from 3:15 PM to 6:15 PM. Weight measurements were taken hourly to monitor moisture reduction.
Drying Data Table (BSF Ali):
| Time | Weight (g) |
|---|---|
| 3:15 PM | 1352 |
| 4:15 PM | 600 |
| 5:15 PM | 528 |
| 6:15 PM | 501 |
Total moisture loss after three hours of drying was 851g, indicating significant dehydration.
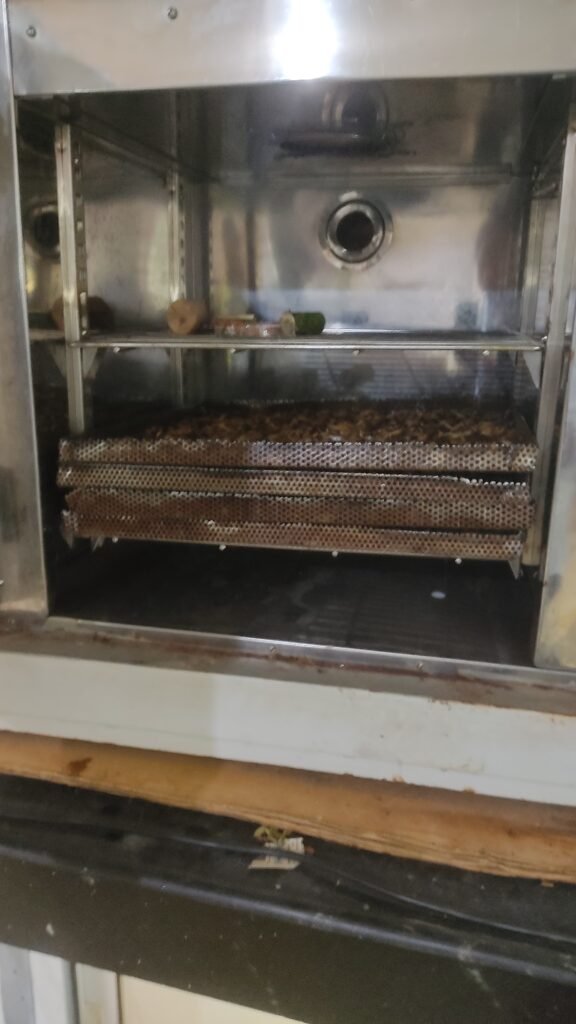

7th July 2025 – Adhri Track and Outdoor Activity
We participated in an outdoor trek to Adhri. It was a refreshing and energetic break that helped build team spirit and mental clarity.
8th to 10th July 2025 – Visit to IIT Bombay
Over the next three days, we visited IIT Bombay as part of the internship. This educational tour allowed us to observe cutting-edge research infrastructure and interact with scholars in the field of science and engineering.
11th July 2025 – Drying Process Discussion and Field Visit
I had a detailed interaction with Dixit Sir and Prasad Sir to review the progress and future steps of the drying experiments. A new member, Juvencio from MIT Sloan School of Management, joined our team. Later in the day, I accompanied Rudra Bhau to Dhamari where we installed an electricity meter to track the power consumption of the heat pump dryer.
12th July 2025 – First Trial of Subabul Leaves in Inclined Dryer
We initiated a new trial by placing Subabul leaves into the inclined dryer. A total of 945g was distributed across six trays (five trays with 175g each and one tray with 70g). The trial began at 2 PM. We also calculated the dryer area based on side dimensions (108cm, 60cm, 60cm, and 15cm), converting to square feet for analysis.
13th July 2025 – Mid-Trial Measurement and Review
On the second day of the Subabul trial, I measured the weight of each tray at 10 AM to monitor drying progress.
Subabul Leaf Trial – Interim Weight (13th July, 10 AM):
| Tray No. | Weight (g) |
|---|---|
| Tray 1 | 97 |
| Tray 2 | 87 |
| Tray 3 | 85 |
| Tray 4 | 83 |
| Tray 5 | 40 |
| Total | 392g |
We also conducted a weekly review to assess the project’s development and challenges.
Solar illuminence Data of 13th July.
| Time | Illuminance (lux) | Irradiance (W/m²) | Temp (°C) | Humidity (%) | Wind (m/s) | Cloud (%) | Rainfall (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12:00pm | 38,000 | 301.59 | 25 | 78 | 8.89 | 80 | 21 |
| 12:30pm | 10,800 | 85.71 | 25 | 78 | 8.89 | 80 | 21 |
| 1:00pm | 43,800 | 347.62 | 23 | 78 | 8.89 | 85 | 21 |
| 1:30pm | 35,200 | 279.37 | 25 | 78 | 8.89 | 85 | 21 |
| 2:00pm | 65,200 | 517.46 | 25 | 78 | 8.89 | 90 | 21 |
| 2:30pm | 65,500 | 519.84 | 25 | 78 | 8.89 | 90 | 21 |
| 3:00pm | 45,600 | 361.90 | 25 | 78 | 8.89 | 90 | 21 |
| 3:30pm | 19,200 | 152.38 | 25 | 78 | 8.89 | 90 | 21 |
| 4:00pm | 10,600 | 84.13 | 25 | 78 | 8.89 | 95 | 21 |
| 4:30pm | 10,600 | 84.13 | 24 | 78 | 8.89 | 95 | 21 |
| 5:00pm | 36,100 | 286.51 | 24 | 78 | 8.89 | 95 | 21 |
| 5:30pm | 25,600 | 203.17 | 23 | 78 | 8.89 | 98 | 21 |
| 6:00pm | 3,100 | 24.60 | 23 | 78 | 8.89 | 98 | 21 |
14th July 2025 – Oven Tray Fabrication and Dhamari Manual Work
Today, I worked with Mahesh Sir to fabricate new trays for the oven. The oven was thoroughly cleaned for upcoming BSF trials. In the afternoon, I visited Dhamari with Juvencio to collect data and document drying practices. Throughout the day, I recorded illuminance data at 30-minute intervals.

Solar Illuminance Data of 14th July
| Time | Illuminance (lux) | Irradiance (W/m²) | Temp (°C) | Humidity (%) | Wind (m/s) | Cloud (%) | Rainfall (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10:00am | 10,300 | 81.75 | 23 | 86 | 5.83 | 85 | 30.5 |
| 10:30am | 7,400 | 58.73 | 24 | 86 | 5.83 | 85 | 30.5 |
| 11:00am | 120,100 | 953.17 | 25 | 86 | 5.83 | 85 | 30.5 |
| 11:30am | 33,700 | 267.46 | 25 | 86 | 5.83 | 85 | 30.5 |
| 12:30pm | 42,300 | 335.71 | 25 | 86 | 5.83 | 85 | 30.5 |
| 1:00pm | 48,700 | 386.51 | 25 | 86 | 5.83 | 90 | 30.5 |
| 1:30pm | 40,900 | 324.60 | 25 | 86 | 5.83 | 90 | 30.5 |
| 2:00pm | 45,000 | 357.14 | 25 | 86 | 5.83 | 90 | 30.5 |
| 2:30pm | 11,400 | 90.48 | 25 | 86 | 5.83 | 90 | 30.5 |
| 3:00pm | 34,800 | 276.19 | 24 | 86 | 5.83 | 92 | 30.5 |
| 3:30pm | 24,800 | 196.83 | 24 | 86 | 5.83 | 92 | 30.5 |
| 4:00pm | 4,300 | 34.13 | 24 | 86 | 5.83 | 92 | 30.5 |
| 4:30pm | 26,200 | 207.94 | 24 | 86 | 5.83 | 95 | 30.5 |
| 5:00pm | 29,000 | 230.16 | 23 | 86 | 5.83 | 95 | 30.5 |
| 5:30pm | 19,800 | 157.14 | 23 | 86 | 5.83 | 98 | 30.5 |
| 6:00pm | 14,000 | 111.11 | 23 | 86 | 5.83 | 98 | 30.5 |
15th July 2025 – Final Subabul Drying Data and Logger Setup
We continued the illuminance measurements and I consulted with Pranit Sir regarding the setup and functionality of the data logger. Below is the complete data for the drying process of the Subabul leaves:

Subabul Drying Trial Data (12th to 15th July):
| Batch | Initial | 12 Jul 6PM | 13 Jul 10AM | 13 Jul 6PM | 14 Jul 10AM | 14 Jul 6PM | 15 Jul 10AM | 15 Jul 2PM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 175g | 90g | 95g | 71g | 72g | 68g | 74g | 65g |
| 2 | 175g | 92g | 94g | 62g | 73g | 60g | 67g | 49g |
| 3 | 175g | 78g | 82g | 63g | 72g | 62g | 65g | 52g |
| 4 | 175g | 80g | 83g | 62g | 72g | 66g | 65g | 52g |
| 5 | 175g | 84g | 86g | 66g | 74g | 66g | 62g | 49g |
| 6 | 70g | 38g | 40g | 29g | 30g | 27g | 23g | 20g |
Solar illuminence Data of 15th July
| Time | Illuminance (lux) | Irradiance (W/m²) | Temp (°C) | Humidity (%) | Wind Speed (m/s) | Cloud Cover (%) | Rainfall (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10:00am | 16,200 | 128.57 | 24.5 | 70 | 4.46 | 96 | 0 |
| 10:30am | 15,600 | 123.81 | 24.5 | 70 | 4.46 | 96 | 0 |
| 11:00am | 8,500 | 67.46 | 24.5 | 70 | 4.46 | 96 | 0 |
| 11:30am | 28,200 | 223.81 | 24.5 | 70 | 4.46 | 96 | 0 |
| 12:00pm | 39,000 | 309.52 | 24.5 | 70 | 4.46 | 96 | 0 |
| 12:30pm | 25,200 | 200.00 | 24.5 | 70 | 4.46 | 96 | 0 |
| 1:00pm | 26,700 | 211.90 | 24.5 | 70 | 4.46 | 96 | 0 |
| 1:30pm | 28,300 | 224.60 | 24.5 | 70 | 4.46 | 96 | 0 |
| 2:00pm | 36,300 | 288.10 | 24.5 | 70 | 4.46 | 96 | 0 |
| 2:30pm | 37,600 | 298.41 | 24.5 | 70 | 4.46 | 96 | 0 |
| 3:00pm | 25,300 | 200.79 | 24.5 | 70 | 4.46 | 96 | 0 |
| 3:30pm | 17,400 | 138.10 | 24.5 | 70 | 4.46 | 96 | 0 |
| 4:00pm | 22,500 | 178.57 | 24.5 | 70 | 4.46 | 96 | 0 |
| 4:30pm | 22,200 | 176.19 | 24.5 | 70 | 4.46 | 96 | 0 |
| 5:00pm | 14,500 | 115.08 | 24.5 | 70 | 4.46 | 96 | 0 |
| 5:30pm | 23,000 | 182.54 | 24.5 | 70 | 4.46 | 96 | 0 |
| 6:00pm | 12,400 | 98.41 | 24.5 | 70 | 4.46 | 96 | 0 |
16th July 2025 – Carrot Drying at Dhamari
I continued the regular illuminance measurements and traveled to Dhamari to supervise the carrot drying trial involving 38kg of fresh carrots. I stayed on-site to collect data from the heat pump dryer during the drying process.
Solar illuminence Data of 16th July.
| Time | Illuminance (lux) | Irradiance (W/m²) | Temp (°C) | Humidity (%) | Cloud Cover (%) | Wind Speed (m/s) | Rainfall (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10:00 | 18,000 | 142.86 | 24.0 | 85 | 95 | 4.0 | 0 |
| 10:30 | 20,000 | 158.73 | 24.4 | 81 | 90 | 4.1 | 0 |
| 11:00 | 22,000 | 174.60 | 25.0 | 77 | 87 | 4.3 | 0 |
| 11:30 | 24,000 | 190.48 | 25.7 | 73 | 85 | 4.3 | 0 |
| 12:00 | 25,300 | 200.79 | 26.5 | 70 | 80 | 4.4 | 0 |
| 12:30 | 26,000 | 206.35 | 27.0 | 68 | 75 | 4.5 | 0 |
| 1:00 | 25,800 | 204.76 | 27.3 | 68 | 78 | 4.6 | 0 |
| 1:30 | 25,500 | 202.38 | 27.7 | 69 | 81 | 4.7 | 0 |
| 2:00 | 25,300 | 200.79 | 28.0 | 71 | 84 | 4.6 | 0 |
| 2:30 | 25,300 | 200.79 | 27.8 | 73 | 89 | 4.6 | 0 |
| 3:00 | 25,300 | 200.79 | 27.2 | 76 | 92 | 4.5 | 0 |
| 3:30 | 24,500 | 194.44 | 26.8 | 79 | 95 | 4.4 | 0 |
| 4:00 | 23,000 | 182.54 | 26.2 | 81 | 97 | 4.2 | 0 |
| 4:30 | 21,000 | 166.67 | 25.8 | 83 | 99 | 4.2 | 0.6 |
| 5:00 | 19,000 | 150.79 | 25.4 | 85 | 99 | 4.1 | 1.4 |
| 5:30 | 17,000 | 134.92 | 25.0 | 87 | 100 | 4.0 | 2 |
| 6:00 | 15,000 | 119.05 | 24.7 | 89 | 100 | 3.9 | 2.8 |
17th July 2025 – Solar Data and Carrot Dry Mass Collection
Today, I recorded solar illuminance data and visited Dhamari again to collect the final dried mass of the carrots from the ongoing trial.

Solar illuminence Data of 17th July
| Time | Illuminance (lux) | Irradiance (W/m²) | Temp (°C) | Humidity (%) | Cloud Cover (%) | Wind Speed (m/s) | Rainfall (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10:00 | 32,100 | 255 | 25.2 | 88 | 93 | 2.1 | 0 |
| 10:30 | 54,800 | 436 | 25.8 | 86 | 92 | 2.3 | 0 |
| 11:00 | 65,900 | 524 | 26.6 | 83 | 89 | 2.5 | 0 |
| 11:30 | 39,900 | 317 | 27.2 | 81 | 87 | 2.6 | 0 |
| 12:00 | 35,200 | 280 | 27.9 | 80 | 85 | 2.4 | 0 |
| 12:30 | 42,800 | 341 | 28.3 | 79 | 82 | 2.7 | 0 |
| 1:00PM | 41,200 | 328 | 28.6 | 78 | 81 | 2.9 | 0 |
| 1:30PM | 53,800 | 428 | 28.8 | 77 | 83 | 2.8 | 0 |
| 2:00PM | 52,700 | 419 | 29.0 | 78 | 86 | 2.8 | 0.2 |
| 2:30PM | 34,400 | 274 | 28.7 | 80 | 90 | 2.4 | 0.5 |
| 3:00PM | 38,900 | 310 | 28.2 | 83 | 93 | 2.1 | 0.7 |
| 3:30PM | 47,100 | 376 | 27.8 | 85 | 95 | 2.0 | 1 |
| 4:00PM | 29,800 | 238 | 27.1 | 88 | 98 | 1.8 | 1.3 |
| 4:30PM | 32,800 | 262 | 26.5 | 90 | 99 | 1.6 | 1 |
| 5:00PM | 38,000 | 304 | 26.0 | 92 | 100 | 1.5 | 0.8 |
18th July 2025 – Dome Dryer Evaluation and Logger Progress
Illuminance measurement was maintained every 30 minutes. I checked the functionality of fans in the dome dryer and found that 14 out of 16 were operational. I also discussed the progress of our data logging system with Pranit Sir.
19th July 2025 – Ali Drying Preparation and Equipment Repair
Preparations were made for the next round of BSF larvae drying. I consulted with Mahesh Sir and repaired the data logger system, restoring 9 sensors to working condition. The fans were properly positioned and adjusted in the dome dryer for optimal air circulation.
20th July 2025 – Project Review and Dhamari Visit
On Sunday, 20th July, I spent the day reviewing the earlier BSF larvae drying experiments and consolidating observations from the Dhamari visit on heat pump drying. During this review I was assigned a new responsibility: to record and analyze meter readings for the electric heat pump dryer so that the team can quantify its electricity consumption for future comparisons with solar-based systems.
21st July 2025 – Dome Dryer Check and Evening Lecture
On the 21st of July I inspected the dome dryer fans and verified the installation points of the data logger within the dome. The hardware inspection was followed by an evening lecture on moths, where I learned about their role in pollination and broader environmental importance. The lecture reinforced how biological understanding supports better design decisions in agricultural post-harvest processing.
22nd July 2025 – Second BSF Oven Trial and Illuminance Measurements
On 22nd July I initiated the second drying trial of BSF larvae in the oven with an initial load of 2.910 kg. After three hours of drying, the remaining mass was 1.080 kg. On the same day I began systematic measurement of solar illuminance to support comparisons between passive solar and active heat-pump/oven drying systems.
23rd July 2025 – Pyramid Dryer Refurbishment and Illuminance Monitoring
On 23rd July, our team began a refurbishment project to restore the pyramid-shaped dryer ahead of a demonstration prepared for Dr. Kalbagh Sir’s death anniversary. The initial work focused on grinding rusted iron from the structure. Illuminance measurements were continued throughout the day to document solar conditions during the refurbishment.

24th July 2025 – Painting and Finishing Work
At the end of the grinding process on 24th July we discovered a loss of the original black finish on the dryer frame. I traveled to Pabal to procure paint and then applied the coating to the metal surface. Solar illuminance monitoring continued in parallel to keep the environmental record consistent.

25th to 28th July 2025 – Preparation for the Open House and New Projects
Between 25th and 28th July, preparations intensified for the Open House on 30th July. I was assigned the dome dryer project with a new partner, Juvencio from MIT Boston, and we coordinated a bilingual presentation: I would present in Marathi while Juvencio would cover the same material in English. Concurrently, the team started fabrication of two new flat-bed dryers intended for sale to consumers; Rudra Bhau provided a frame, which I cleaned with a three-in-one solution to prepare it for powder coating. During these days, I also participated in cleaning the techno park and held multiple discussions with Juvencio to finalize our script and demonstration flow.
29th July 2025 – Open House Rehearsal
On 29th July, the final rehearsal and presentation of the dome dryer specifications took place. I explained the technical details and operation of the dome dryer in Marathi, while Juvencio explained the same in English. The bilingual delivery was well received and showed the value of presenting technical work in both local and international contexts.
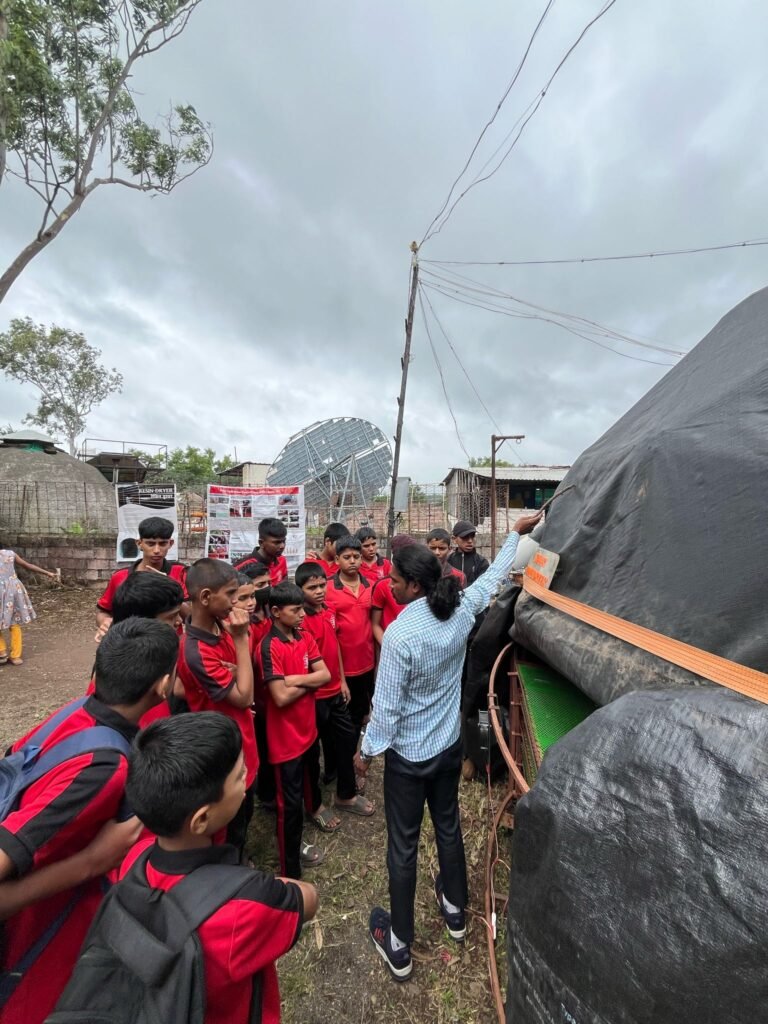

30th July 2025 – Open House Exhibition
The Open House on 30th July was an intense and formative experience. Presenting the dome dryer to visitors helped me refine my own understanding of the system. Juvencio proved to be an exceptional co-presenter; visitors showed great interest in him, and many asked for photographs with him. The two days of exhibition underscored how demonstrations can bridge science and society.
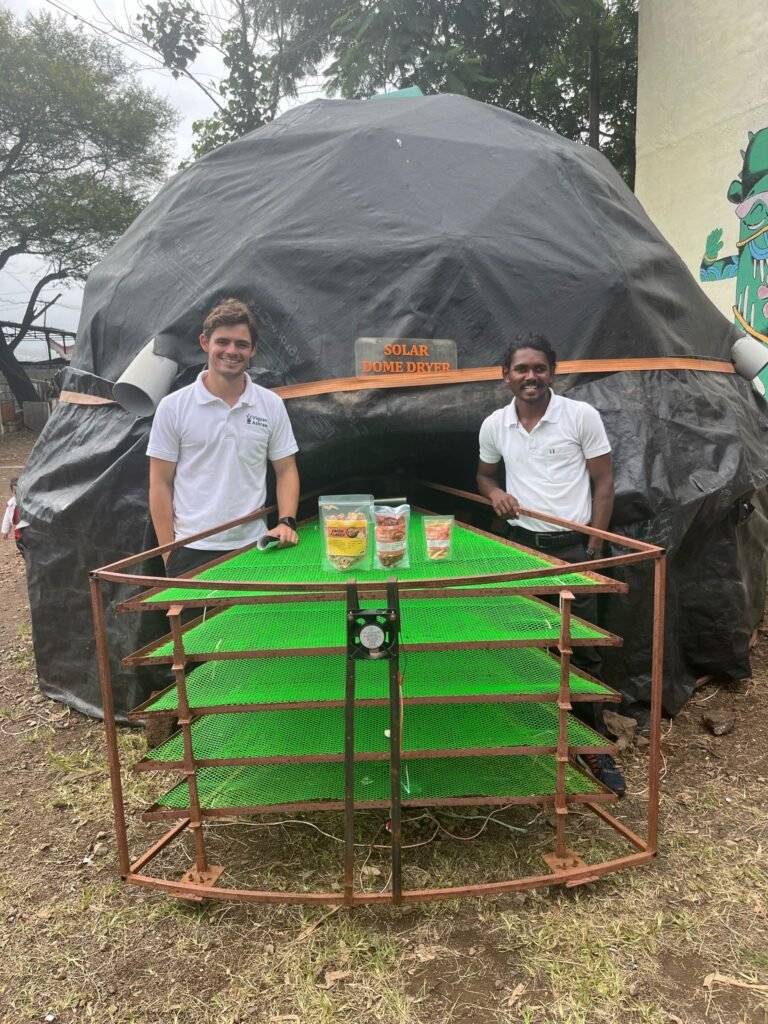

1st August 2025 – Local Reading and Context Building
On 1st August I began reading “Kahani Pabalchya Vigyan Ashramchi” in Marathi to better understand the history and community context of the ashram. This reading helped frame our technical work within the institution’s long-term social mission.
2nd August 2025 – Ginger Trial on Inclined Dryer
On 2nd August I ran a trial on the inclined dryer using 770 g of ginger. After two days of drying the sample mass had reduced to 60 g.
3rd August 2025 – Review with Dixit Sir
Sunday, 3rd August, was a review day; I consulted with Dixit Sir on ongoing trials across the three dryer types: inclined dryer, flat bed dryer, and dome dryer. The discussion focused on trial consistency, data logging status, and next steps for comparative analysis.
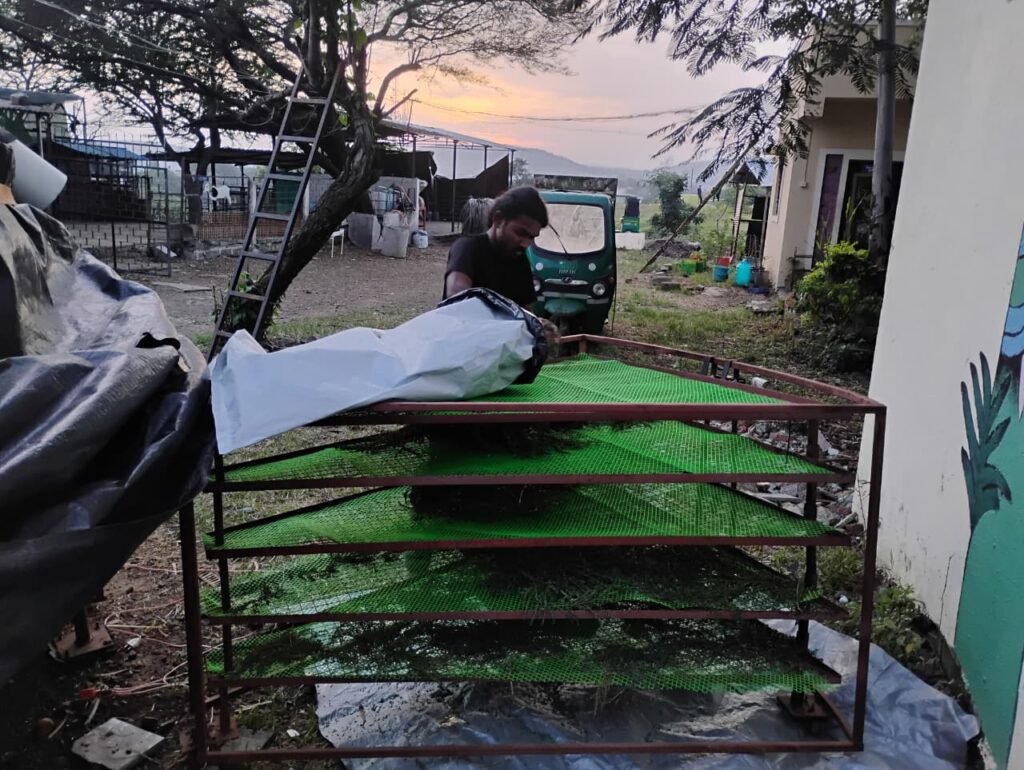
4th to 6th August 2025 – Large-Scale Subabul Trial Across Three Dryers
From 4th to 6th August, we conducted a coordinated trial of Subabul leaves across the dome dryer, flat bed dryer, and inclined dryer. Each tray received 520 g of material and, with 40 trays in total, the full sample amounted to 20.800 kg. To measure local drying rates within trays, we placed 40 g samples in one square foot areas: two samples near the centre and one sample near the peripheral exhaust for each of five trays, which gave 10 samples per section. Readings were taken in the early morning and in the evening on consecutive days to capture diurnal drying behaviour.
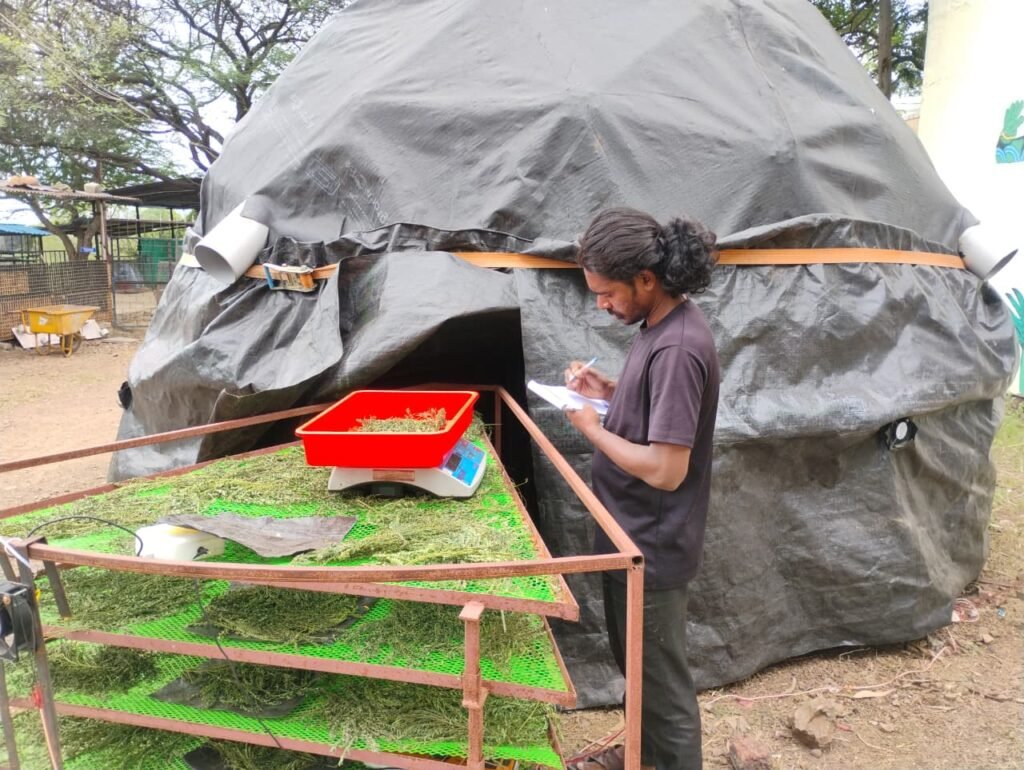

Reading of dome dryer

| Date & Time | Tray | Nearby Centre (g) | Nearby Exhaust Fan (g) | Water Loss % Centre | Water Loss % Exhaust |
| 4/8/25 morning | 1 | 40 | 40 | 0 | 0 |
| 4/8/25 morning | 2 | 40 | 40 | 0 | 0 |
| 4/8/25 morning | 3 | 40 | 40 | 0 | 0 |
| 4/8/25 morning | 4 | 40 | 40 | 0 | 0 |
| 4/8/25 morning | 5 | 40 | 40 | 0 | 0 |
| 4/8/25 evening | 1 | 24 | 24 | 40% | 40% |
| 4/8/25 evening | 2 | 24 | 25 | 40% | 37.50% |
| 4/8/25 evening | 3 | 34 | 28 | 15% | 30% |
| 4/8/25 evening | 4 | 23 | 35 | 42.50% | 12.50% |
| 4/8/25 evening | 5 | 26 | 21 | 35% | 47.50% |
| 5/8/25 morning | 1 | 19 | 23 | 20.83% | 4.17% |
| 5/8/25 morning | 2 | 20 | 21 | 16.67% | 16% |
| 5/8/25 morning | 3 | 26 | 16 | 23.53% | 42.86% |
| 5/8/25 morning | 4 | 17 | 25 | 26.09% | 28.57% |
| 5/8/25 morning | 5 | 21 | 20 | 19.23% | 4.76% |
| 5/8/25 evening | 1 | 14 | 18 | 26.32% | 21.74% |
| 5/8/25 evening | 2 | 16 | 16 | 20% | 23.81% |
| 5/8/25 evening | 3 | 17 | 12 | 34.62% | 25% |
| 5/8/25 evening | 4 | 13 | 18 | 23.53% | 28% |
| 5/8/25 evening | 5 | 20 | 11 | 4.76% | 45% |
| 6/8/25 morning | 1 | 15 | 20 | -7.14% | -11.11% |
| 6/8/25 morning | 2 | 20 | 19 | 25% | 18.75% |
| 6/8/25 morning | 3 | 21 | 19 | -23.53% | 36.36% |
| 6/8/25 morning | 4 | 17 | 23 | 30.77% | 27.78% |
| 6/8/25 morning | 5 | 19 | 17 | -5% | 54.55% |
| 6/8/25 evening | 1 | 14 | 18 | 6.67% | 10% |
| 6/8/25 evening | 2 | 14 | 11 | 30% | 57.89% |
| 6/8/25 evening | 3 | 16 | 12 | 23.81% | 36.84% |
| 6/8/25 evening | 4 | 13 | 19 | 23.53% | 17.39% |
| 6/8/25 evening | 5 | 18 | 15 | 5.26% | 11.76% |
Reading of flat bed dryer
| Date | Weight (g) | Water Loss % |
| 4/8/25 Afternoon | 720 | — |
| 4/8/25 Evening | 460 | 36.11% |
| 5/8/25 Morning | 286 | 37.83% |
| 5/8/25 Evening | 237 | 17.13% |
| 6/8/25 Morning | 236 | 0.42% |
| evening | 230 | 2.54% |
Reading of inclind dryer
| Date | Tray Upside (g) | Tray Downside (g) | Water Loss % Upside | Water Loss % Downside |
| 4/8/25 Afternoon | 40 | 40 | — | — |
| 4/8/25 Evening | 38 | 34 | 5.00% | 15.00% |
| 5/8/25 Morning | 40 | 36 | -5.26% | 5.88% |
| 5/8/25 Evening | 21 | 15 | 47.50% | 58.33% |
| 6/8/25 Morning | 21 | 15 | 0.00% | 0.00% |
| Date | Time | Illuminance (lux) | Illuminance/126 | Ambient Temp (°C) | Humidity (%) | Wind Speed (m/s) | Cloud Cover (%) |
| 4-Aug | 10.00am | 18,000 | 143 | 23 | 90 | 7 | 85 |
| 4-Aug | 10.30am | 20,000 | 159 | 24 | 89 | 7 | 85 |
| 4-Aug | 11.00am | 25,000 | 198 | 25 | 88 | 7 | 80 |
| 4-Aug | 11.30am | 27,000 | 214 | 26 | 85 | 7 | 75 |
| 4-Aug | 12.30pm | 29,000 | 230 | 26 | 85 | 7 | 75 |
| 4-Aug | 1.00pm | 28,000 | 222 | 27 | 82 | 7 | 80 |
| 4-Aug | 1.30pm | 25,000 | 198 | 27 | 82 | 7 | 80 |
| 4-Aug | 2.00pm | 22,000 | 175 | 26 | 85 | 7 | 85 |
| 4-Aug | 2.30pm | 20,000 | 159 | 26 | 86 | 7 | 85 |
| 4-Aug | 3.00pm | 18,000 | 143 | 25 | 86 | 7 | 90 |
| 4-Aug | 3.30pm | 16,000 | 127 | 24 | 87 | 7 | 92 |
| 4-Aug | 4.00pm | 12,000 | 95 | 23 | 89 | 7 | 96 |
| 4-Aug | 4.30pm | 10,000 | 79 | 23 | 90 | 7 | 98 |
| 4-Aug | 5.00pm | 8,000 | 63 | 22 | 92 | 6 | 98 |
| 4-Aug | 5.30pm | 5,000 | 40 | 22 | 94 | 6 | 99 |
| 4-Aug | 6.00pm | 3,500 | 28 | 22 | 96 | 6 | 99 |
| 5-Aug | 10:00am | 19,000 | 150 | 25 | 85 | 6 | 75 |
| 5-Aug | 10:30am | 21,000 | 166 | 26 | 85 | 6 | 75 |
| 5-Aug | 11:00am | 25,000 | 198 | 27 | 82 | 6 | 70 |
| 5-Aug | 11:30am | 27,000 | 214 | 28 | 80 | 6 | 70 |
| 5-Aug | 12:30pm | 31,000 | 246 | 28 | 78 | 6 | 65 |
| 5-Aug | 1:00pm | 32,000 | 253 | 29 | 75 | 6 | 60 |
| 5-Aug | 1:30pm | 30,000 | 238 | 29 | 75 | 6 | 65 |
| 5-Aug | 2:00pm | 28,000 | 222 | 28 | 78 | 6 | 70 |
| 5-Aug | 2:30pm | 24,000 | 190 | 27 | 80 | 6 | 75 |
| 5-Aug | 3:00pm | 21,000 | 166 | 27 | 83 | 6 | 80 |
| 5-Aug | 3:30pm | 19,000 | 150 | 26 | 85 | 6 | 85 |
| 5-Aug | 4:00pm | 15,000 | 119 | 25 | 87 | 6 | 90 |
| 5-Aug | 4:30pm | 10,000 | 79 | 24 | 90 | 6 | 95 |
| 5-Aug | 5:00pm | 7,000 | 55 | 24 | 92 | 6 | 98 |
| 5-Aug | 5:30pm | 4,000 | 31 | 23 | 95 | 6 | 99 |
| 5-Aug | 6:00pm | 2,000 | 15 | 23 | 96 | 6 | 99 |
| 6-Aug | 10:00am | 17,000 | 134 | 24 | 90 | 5 | 80 |
| 6-Aug | 10:30am | 18,000 | 142 | 25 | 88 | 5 | 80 |
| 6-Aug | 11:00am | 22,000 | 174 | 26 | 85 | 5 | 75 |
| 6-Aug | 11:30am | 24,000 | 190 | 27 | 83 | 5 | 75 |
| 6-Aug | 12:30pm | 28,000 | 222 | 27 | 80 | 5 | 70 |
| 6-Aug | 1:00pm | 29,000 | 230 | 28 | 78 | 5 | 65 |
| 6-Aug | 1:30pm | 27,000 | 214 | 28 | 78 | 5 | 70 |
| 6-Aug | 2:00pm | 25,000 | 198 | 27 | 80 | 5 | 75 |
| 6-Aug | 2:30pm | 21,000 | 166 | 27 | 83 | 5 | 80 |
| 6-Aug | 3:00pm | 18,000 | 142 | 25 | 85 | 5 | 85 |
| 6-Aug | 3:30pm | 16,000 | 126 | 24 | 87 | 5 | 90 |
| 6-Aug | 4:00pm | 13,000 | 103 | 23 | 88 | 5 | 95 |
| 6-Aug | 4:30pm | 8,000 | 63 | 23 | 90 | 5 | 98 |
| 6-Aug | 5:00pm | 5,000 | 39 | 22 | 92 | 5 | 99 |
| 6-Aug | 5:30pm | 3,000 | 23 | 22 | 94 | 5 | 100 |
| 6-Aug | 6:00pm | 1,500 | 11 | 22 | 95 | 5 | 100 |
In a dome dryer, the loss of 65.88% moisture, while for a flat bed is 67.08% and for an inclined dryer is 69.26% in three days





