Date:23/07/202
Azolla
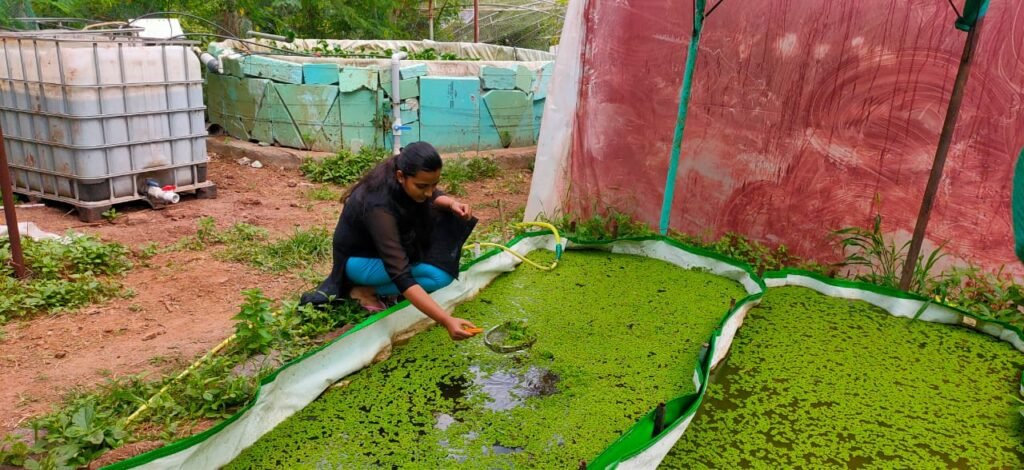
Azolla bed were plantation was done.3 azolla beds were made ready for plantation.
Azolla is fastest growing plant. Azolla is generally grow best in less than full sunlight. Water is a basic requirement for the growth and multiplication of Azolla. Azolla is highly productive plant. It doubles in 3-8 days.
It is reach in proteins hence we are trying to bring azolla in our food chain . We can use this Azolla as fodder for cow, buffalos, hens ,sheep and etc.We dry Azolla by sun drying to feed hens.


Date:31/07/2021
Soil Testing:
Tested 6 soil samples by using Prerana lab. kit Ph., EC ,Nitrogen, Sodium, Potassium, OC was determine. Soil testing was done and parameter are determine.
Soil analysis is a valuable tool it determines the input required for efficient and economic production.
A soil test is important to optimize crop production to protect the environment from contamination by runoff and leaching of excess fertilizer.
A proper soil test will help to ensure the application of enough fertilizer to meet the requirement of crop while taking advantage of the nutrient already present in soil .
Range
In soil highest range of organic carbon is above 1%.
In soil highest range of nitrogen is above 700 Kg/Ha.
In soil highest range of potassium is over 300 Kg/Ha.
In soil highest range of phosphorous is above 35 Kgs/Ha.
In soil highest range of PH is 8.
In soil highest range of Ec is 2000.

Date:04/08/2021
Soil Testing:
Tested 4 soil samples by using Prerana lab. kit Ph., EC ,Nitrogen, Sodium, Potassium, Oc was determine. Soil testing was done and parameter are determine.
- If there is deficiency of Nitrogen then we can suggest fertilizers like urea and ammonium sulfate.
- If there is deficiency of phosphorus so we use DAP .
- If there is deficiency of Potassium then we can use mined rock powders and wood ash.




Date:24/07/2021
Flame photometer
Calibrition of sodium, potassium filter in flame photometer by using standard stock solution.
Preparation of standard and stack solutions.
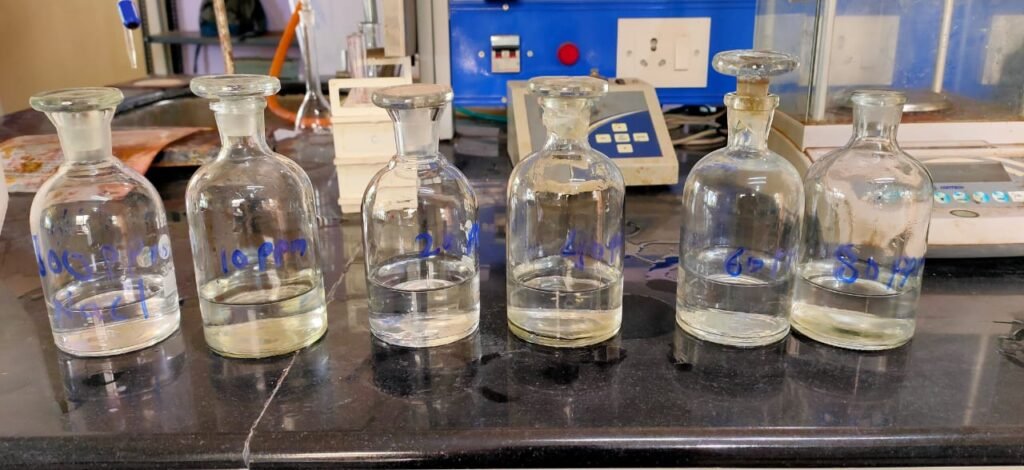

Sodium (Na) – 300 ppm
Prepare by dissolving 0.75g NaCl in 300 of glass distilled water
pippet out 10, 20, 40, 60, 80 ml of NaCl sample into 100 ml volumetric flask and make volume by adding distilled water to prepare 10, 20, 40, 60, 80 ppm sodium chloride (NaCl) solution. Calibrate the flame photometer by using this solution. When a flame photometer detects sodium (Na) flame colour changes blue to dark red.
.

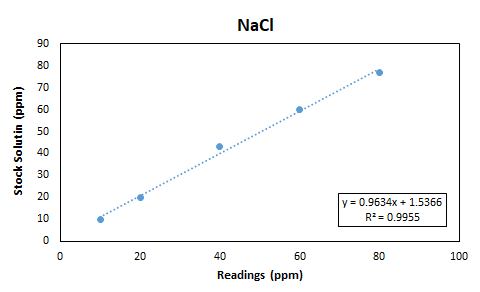
| Stock Solution | R1 | R2 | Avg |
| 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| 40 | 42 | 44 | 43 |
| 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 |
| 80 | 76 | 78 | 77 |

Preparation of standard and stack solutions.
Potassium – 300 ppm
300 ppm calcium solution prepared by dissolving 0.75g of KNO3 in one 300 ml of glass distilled water.Pippet out 10, 20, 40, 60, 80 ml of KNO3 sample into 100 ml volumetric flask and make volume by adding distilled water to prepare 10, 20, 40, 60, 80 ppm KNO3 solution. Calibrate the flame photometer by using this solution. When a flame photometer detects flame colour changes blue to red.
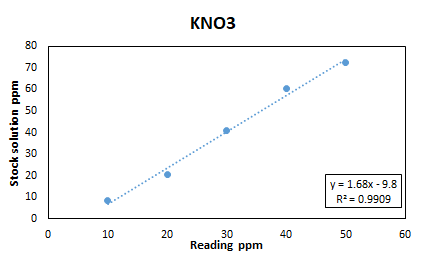
| Stock Solution | R1 | R2 | Avg |
| 10 | 9 | 8 | 8.5 |
| 20 | 21 | 20 | 20.5 |
| 30 | 42 | 40 | 41 |
| 40 | 61 | 60 | 60.5 |
| 50 | 70 | 75 | 72.5 |

Date:16/08/2021
Soil Sample:
Tested 23 soil samples by using Prerana lab. kit Ph., EC ,Nitrogen, Sodium, Potassium, Oc was determine. Soil testing was done and parameter are determine.
Farmer Name: Ganesh Kale
Soil Report
| N | P | K | O.c | pH | EC |
| 140 | 0 | 350 | 1.0 | 6.6 | 406 |
In this soil phosphorus is very less. I suggested him apply DAP in farm to enrich phosphorus level.

Date:19/08/2021
Determination of nitrogen content from azolla by Kjeldahl Method
Introduction:
As we know azolla is high protein compound so it was necessary to estimate nitrogen content in azolla.
Reagents:
- Sulfuric acid , 95% , reagent grade
- Catalyst (copper sulphate and potassium sulphate ):- Add 5 g of potassium sulphate and 2 g copper sulphate
- Glycine powder
- Sodium hydroxide 50% :- Dissolve 50 g sodium hydroxide in 50 ml DW
- Sulphuric acid solution 0.5 M:- Dissolve 2.4 ml of 98% Sulphuric acid in 10 ml distilled water and make volume 100 ml .
- Hydrochloric acid 0.25 N :-Dissolve 2.17 ml of HCl in 100 ml DW
- Sodium carbonate solution :- For standardization of HCl solution

Procedure:
- Weigh around 1 grams of dry glycine in the digestion flask and add 2 grams of catalyst and add 20 ml sulphuric acid (95%).Add glass beads in the flask to avoid excess heating .
- Digest the content in flask for 30-40 mins until the temp raises up to 160 degree Celsius .
- Color changes from blue to colourless
- 4.After cooling add 100 ml D.W then add 50% NaOH
- Then start distillation process and trap the ammonia in sulphuric acid.
- After distillation proceed for back titration to remove excess acid from trapping solution.
- Now titrate the distillate with 0.25 molar HCl solution .By adding 5-6 drops tashiro indicator and end point is blue to slight voilet.
Result :Nitrogen content azolla is 8.7.
Date:17/08/2021
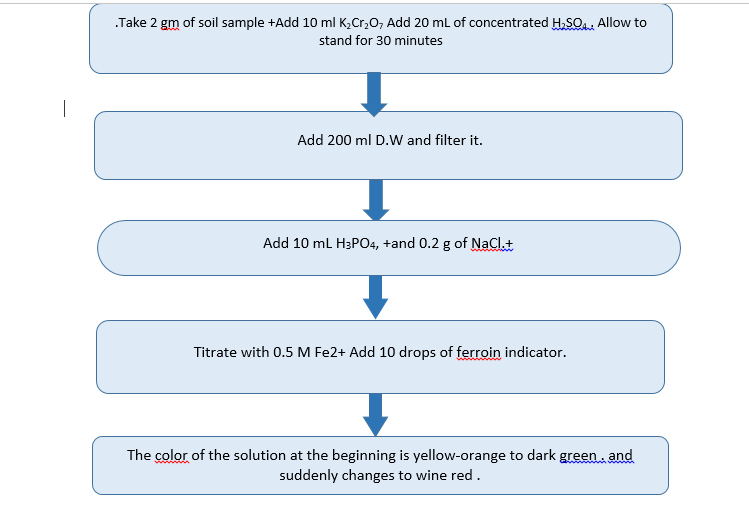
Determination of Organic Carbon from soil by Walkey Black Method
Farmer Name: Umesh sandbhor
H3PO4, 85%.
2. H2SO4, concentrated (96%)
3. NaCl , solid.
4. Standard 0.167M K2Cr2O7:- Dissolve 49.04 g of dried (105oC) K2Cr2O7 in water and dilute to 1 L.
5. 0.5M Fe2+ solution: Dissolve 196.1 g of Fe(NH4)2(SO4)•6H2O in 800 mL of water containing 20 mL of concentrated H2SO4 and dilute to 1 L. The Fe2+ in this solution oxidizes slowly on exposure to air so it must be standardized against the dichromate.
6. Ferroine indicator: Slowly dissolve 3.71 g of o-phenanthroline and 1.74 g of FeSO4•7H2O in 250 mL of water.
Procedure:


Calculation:
18-8×0.5x12x100/4000 x 2
Where:
B = mL of Fe2+ solution used to titrate blank
S = mL of Fe2+ solution used to titrate sample
12/4000 = Milliequivalent weight of C in sample
C = (B-S) x M of Fe2+ x 12 x 100g soil /4000 x 2
17-7.9×0.5x12x100/4000 x 2
5460/8000
0.64
Result: Organic carbon in given soil is 0.68
Date:- 24/08/2021
Estimation of organic carbon by walkey black method.
2 sample were checked for organic carbon.

Date:06/09/2021
Determination of nitrogen content from kale sample by Kjeldahl Method :-
Reagents:
- Sulfuric acid , 95% , reagent grade
- Catalyst (copper sulphate and potassium sulphate ):- Add 5 g of potassium sulphate and 2 g copper sulphate
- Glycine powder
- Sodium hydroxide 50% :- Dissolve 50 g sodium hydroxide in 50 ml DW
- Sulphuric acid solution 0.5 M:- Dissolve 2.4 ml of 98% Sulphuric acid in 10 ml distilled water and make volume 100 ml .
- Hydrochloric acid 0.25 N :-Dissolve 2.17 ml of HCl in 100 ml DW
- Sodium carbonate solution :- For standardization of HCl solution

Procedure:
- Weigh around 1 grams of dry glycine in the digestion flask and add 2 grams of catalyst and add 20 ml sulphuric acid (95%).Add glass beads in the flask to avoid excess heating .
- Digest the content in flask for 30-40 mins until the temp raises up to 160 degree Celsius .
- Color changes from blue to colorless
- 4.After cooling add 100 ml D.W then add 50% Noah
- Then start distillation process and trap the ammonia in sulphuric acid.
- After distillation proceed for back titration to remove excess acid from trapping solution.
- Now titrate the distillate with 0.25 molar HCl solution .By adding 5-6 drops Tashiro indicator and end point is blue to slight violet.
Date :- 09/09/2021
koi fish feeding :-

koi are a type of carp, a common fish that can be found all over the world, but what makes Koi so special is their coloring and lineage.
There are regular competitions to name the top koi and just like prized dog breeds, Japanese people take koi breeding very seriously.
we want to bring Azolla in food chain , but Azolla is heavy to digest because of high lignin content .
Date:20/09/2021
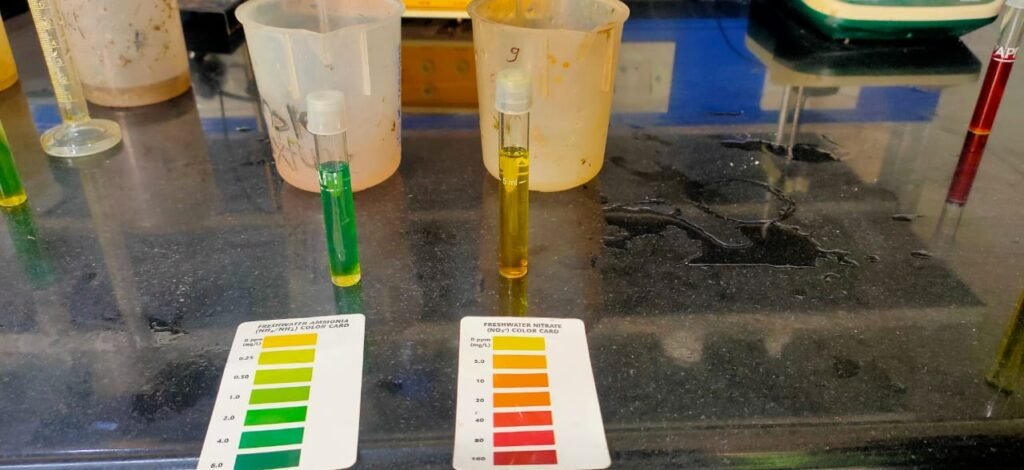
Estimating concentration of Nitrates and Ammonia in fish water :- Ammonia is toxic to fish if allowed to accumulate in fish production systems. When ammonia accumulates to toxic levels, fish can not extract energy from feed efficiently.

If the ammonia concentration gets high enough, the fish will become lethargic and eventually fall into a coma and die.
Result:
Ammonia : 20 ppm
Nitrate: 40 ppm

Date:-17/09/2021
Estimation calcium and magnesium from given water sample by EDTA method
A. Buffer Solution (NH4Cl-NH4OH) :-Dissolve 67.5 g ammonium chloride in 570 mL concentrated ammonium hydroxide, and transfer the solution to a 1-L volumetric flask, let it cool, and bring to volume with DI water.
B. Eriochrome Black Indicator:- Dissolve 0.5 g Eriochrome black with 4.5 g hydroxylamine hydrochloride in 100 mL ethyl alcohol (95%). Prepare a fresh batch every month.
C. Ethylene diamine tetra acetic Acid Solution (EDTA):- 0.01 N Dissolve 2 g ethylene diamine tetra acetic acid, and 0.05 g magnesium chloride (MgCl2) in DI water, and bring to 1-L volume with DI water.
D. Sodium Hydroxide Solution (NaOH):- 2 N Dissolve 80 g sodium hydroxide in about 800 mL DI water, transfer the solution to a 1-L volume, cool, and bring to volume with DI water.
E. Ammonium Purpurate Indicator (C8H8N6O6) :- Mix 0.5 g ammonium purpurate (Murexoid) with 100 g potassium sulfate (K2SO4).
F. Standard Stock Calcium Chloride Solution (CaCl2.2H2O):- 0.01 N Dissolve 0.5 g pure calcium carbonate (CaCO3 dried for 3 hours at 100°C), 31 UAE University in 10 mL 3 N hydrochloric acid and bring to1-L volume with DI water. This can also be prepared by dissolving 0.735 g calcium chloride dihydrate (CaCl2.2H2O) in 1-L volume with DI water.
G. Ammonium acetate solution :- Dissolve 77 grams of ammonium acetate in 80 ml of distilled water and bring volume up to 100 ml .
Preparation of water-
- Weigh 50 ml water and add 200 ml of 40% ethanol to it .
- Filter the mixture and discard the filtrate and add ammonium acetate solution to it
- Incubate the mixture overnight and use it as water extract
A. Calcium
1. Pipette 10 – 20 mL water saturation extract, having not more than 1.0 meq Ca, into 250-mL Erlenmeyer flask.
2. Dilute to 20 – 30 mL with DI water, add 2 – 3 mL 2 N sodium hydroxide solution, and about 50 mg ammonium purpurate indicator.
3. Titrate with 0.01 N EDTA. The color changes from red to lavender or purple. Near the end point, EDTA should be added one drop every 10 seconds since the color change is not instantaneous.
4. Always run a blank containing all reagents but no soil, and treat it in exactly the same way as the samples; and subtract the blank titration reading from the readings for all samples
B. Calcium plus Magnesium :-
1. Pipette 10 – 20 mL water saturation extract, having not more than 1.0 meq Ca, into 250-mL Erlenmeyer flask. saturation extract into a 250-mL flask, dilute to 20 – 30 mL with DI water. Then add 3 – 5 mL buffer solution. And a few drops of eriochrome black indicator.
2. Titrate with 0.01 N EDTA until the color changes from red to blue.

Calculations :-
Ca or Ca + Mg (meq/L) = (V – B) × N × R × 1000 \ Wt
Mg (meq/L) = Ca + Mg (meq/L) – Ca (meq/L)
Result:-
Calcium in given sample was 300 ppm and magnesium was 170 ppm.
Date – 09/09/2021
LOSS ON DRYING ( LOD ) OF KALE SAMPLE :-
- A method commonly used for moisture content determination is the loss-on-drying method,
- LOD on the other hand, measures the total change in weight of a material as a result of drying.
- For some products, components such as alcohol or fat evaporate with the water. Therefore, the LOD method measures both the water and volatile impurities.
- Temperature – 105 degree Celsius for 3 hrs.
CALCULATONS :-
Initial weight – 64.67 gm ( before washing )
initial weight – 56.23 gm ( after washing )
final weight – 15.190 gm
empty plate weight – 43.422 gm
Formula :-
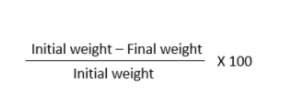
Hence , LOD of kale sample is 88.24 %
Date :- 13/10/2021
Estimation of COD ( chemical oxygen demand ) from given sample :-
In Environmental chemistry, the chemical oxygen demand (COD) is an indicative measure of the amount of oxygen that can be consumed by reactions in a measured solution.
It is commonly expressed in mass of oxygen consumed over volume of solution which in SI units is milligrams per litre (mg/L).
A COD test can be used to easily quantify the amount of organics in water.
The most common application of COD is in quantifying the amount of oxidable pollutants found in surface water (e.g. lakes and rivers or wastewater.
Reagents :-
- 0.25 M Ferrous Ammonium Sulfate (FAS) :- Dissolve 98 gm Ferrous Ammonium Sulfate + 800 ml distilled water +20 ml Sulfuric acid and make it up to 1000 ml with distilled water.
- 0.25 N K2Cr2O7 :- Dissolve 12.25 gm K2Cr2O7 in 1000 ml volumetric flask and fill Distilled water up to mark.
- Potassium hydrogen phthalate (KHP) :- 0.425 gm Dried powder KHP in 1000ml D/W.
- Mercuric Sulfate.
- Ferroin Indicator.
- Samples to checked ( Phenol )
Procedure :-
1. Take 0.4 HgSO4 ( Mercuric Sulfate) in COD test tube.
2. Add 20 ml phenol sample and add 20 ml D/W in it, Mix well. Run Blank with D/W simultaneously.
3. Add 2-3 cumic stones or glass beads in it.
4.Add 10 ml 0.25 N K2Cr2O7 solution.

Add 30 ml of H2SO4.After addition of H2SO4, If color changes to green then it goes up to limit of our COD apparatus so we add know quantity of K2Cr2O7 or we make dilution of test sample. And keep tubes for reflux at 150 degree for 2 hours . Take out COD tubes for cooling.

7.After cooling ,Take all solution in conical flask and add 150 ml D/W and add 5 drops of ferroin indicator. and titer against FAS.
8. Add drop by drop FAS up to color changes from yellowish orange to brick red color. Note down reading. and calculate.

| solution | Burette reading | COD ( mg /lit ) |
| Blank | 9.8 ml | – |
| Phenol ( 1:50 ) | 7 ml | 1000 mg /lit |
| phenol (1:100 ) | 9 ml | 28000 mg /lit |
| Phenol ( 1:20) | 9.6 ml | 5600 mg /lit |





