Hydroponic is the science of growing or the production of plants in nutrient-rich solution instead of soil.
The flood and drain system works on temporarily flooding the grow trays with nutrient solution and then draining the solution back into reservoir.
Components of flood and drain system:
1 Reservoir = 30 litres
2 Drip pipes
3 Tee joints
4. Elbow joint
5. Pots
6. Submersible pump
7. Growing media
We have made a hydroponics (flood and drain) system for brinjal crop for which we have taken a pots of 5 litres and their are total 5 no of pots in the system. Total system is of 25 litres. Approximately 30 litres.
Objectives :
- To study the flood and drain system of hydroponic.
- To make a design and fabricate a system for crops of brinjal
- To study a fertigation for brinjal in hydroponic.
- To take trials on system and analyzing the data with respect to growth patterns.
Hand sketch of system:

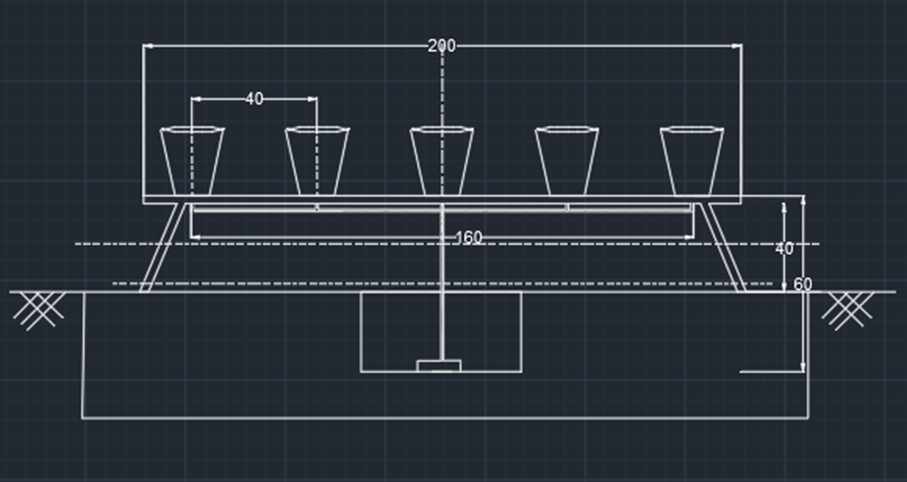
2D CAD Design of System

Dimension:
Length of pot= 21 cm
Diameter of pot = 20 cm
Plant to plant distance = 40 cm
Pot to pot distance = 20 cm
Total length of system = 180 cm
Process Flow Diagram

Material Flow Diagram
1 Pipe System – a) Main line
b) Submain line
c) T joints
d) Elbow joints
f) Grommet
2 Electronic System – a) Timer
b) Wire
3 Crop – Brinjal
4 Pump – Submersible pump 18 watt
5 Growing Media
6 Pots
Pump ON and OFF Timing
The submersible pump of system is connected to timer to start the pump and off the pump.
From 7 am to 7 pm we set a timer at interval of one hour therefore pump start after every one hour from 7 am to 7 pm and turns off after 2 minutes. From 7 pm we set timer at 10 pm, 1 am and 4 am and turns off after 2 minutes.
| SR No | ON | OFF | SR.NO | ON | OFF |
| 1. | 7.00 AM | 7.02 AM | 9. | 3.00 PM | 3.02 PM |
| 2. | 8.00 AM | 8.02 AM | 10. | 4.00 PM | 4.02 PM |
| 3. | 9.00 AM | 9.02 AM | 11. | 5.00 PM | 5.02 PM |
| 4. | 10.00 AM | 10.02 AM | 12. | 6.00 PM | 6.02 PM |
| 5. | 11.00 AM | 11.02 AM | 13. | 7.00 PM | 7.02 PM |
| 6. | 12.00 PM | 12.02 AM | 14. | 10.00 PM | 10.02 PM |
| 7. | 1.00 PM | 1.02 PM | 15. | 1.00 AM | 1.02 AM |
| 8. | 2.00 PM | 2.02 PM | 16. | 4.00 AM | 4.02 AM |
PROCESS
Fabrication
26 – 02 – 2022
Firstly we purchased the pots from shop after that we made a holes of 16 mm in it for making a inlet and outlet of the system with the help of tee and elbow joints.
Then we cut the drip pipe in 35 cm of pieces and connected it with the help of tee and elbow joints and connected it with the growing pots.

For placing a system we needed a platform on which we can place a system properly. Their was a stand which was available but it was 150 cm in length, but our system was 180 cm the stand was short in lenght
With the help of angles we increased the lenght of stand on which we can place the system properly. After that we welded a sheet on stand.
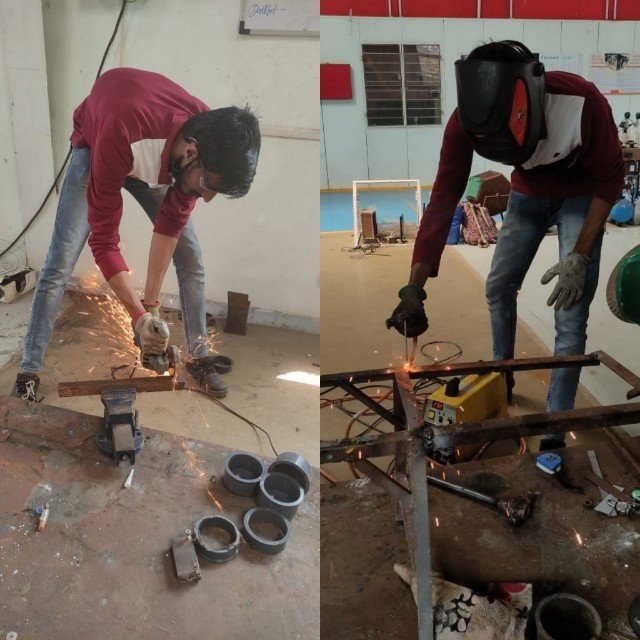

Figure Name – Cutting of L Angles and Welding
Then we dig the pit in the soil and placed the reservoir in the pit which help us to reduce the height of the system from ground level.
After making the set up we connected the timer to the submersible pump and measured the time required to fill the solution in pots, after measuring the time we filled the media in pots and again measured the time required to fill the pots with solution.

PROBLEM FACED DURING TESTING
After filling media in pots the time required to fill solution in pots was about 1.40 minutes but the timer which we have used did not set the time in seconds.
SOLUTION – To tackle this problem we connected a value on mainline after pump and adjusted the valve untill the time required to fill the solution in pot is upto 2 minutes.
08 – 03 – 2022
PLANTATION
We have planted brinjal in pots in growing media.

FINAL SETUP AFTER PLANTATION

Fertigation :
The following are dosing which we have used for the system.
The total system is of 30 litres therefore we made dosing according to 30 litres.
- Ca(NO3)2
Required Nitrogen – 150 ppm
Required Calcium – 139 ppm
N = 150/0.15 = 1000 mg
C = 1000×19/100 = 190 mg
1000 mg × 30 litres = 30 gm.
2. K2SO4
Required Potassium – 216 ppm
K = 216/0.50 = 432 mg
432 × 30 = 12.960 gm
3. MgSO4
Required Magnesium – 47 ppm
Mg = 47×100/9.6 = 489.5 mg
489.5 × 30 = 14.685 gm
4. Humic acid 0.1 ml = 0.1 × 30 = 3 ml
28 – 3 – 22
After few days while testing the EC of nutrient solution it is seen that EC of nutrient solution is deceased so we have made again dosing of nutrient.
Ca(NO3)2 – 8.74 gm
K2SO4 – 3.78 gm
MgSO4 – 4.28 gm
Above nutrient which we used are not showing the growth in brinjal crop and their is lack of phosphorus in the nutrient solution therefore we changed the nutrient pattern as shown below.
1100 gm of brinjal crop requires following nutrient.
Nitrogen – 40 gm
Phosphrous – 4 gm
Potassium – 4 gm
Calcium – 2 gm
Magnesium – 2 gm
Sulphur – 2 gm
- K2SO4
Molecular mass of k2SO4 is 174.25
In 100 gm of k2SO4 there is 45 % of K i,e 45 gm
Plant need 4 gm of K
Now, 45 = 100
4 = x
Therefore 45 * x = 4 * 100
x = 400/45
K = 8.8 gm
In 100 gm of K2SO4 there is 18.40 of S
i,e 18.4 gm
Therefore = 18.40 = 100
x = 8.8
18.40 * 8.8 = 100 * x
x = 18.40 * 8.8 / 100
x = 1.61
2. MgSO4
In 100 gm of MgSO4 there is 26.197 of S
S = 26.19 = 100
2 = x
26.19 * x = 2 * 100
26.19x = 200
x = 200/26.19
S = 7.6 gm
In 100 gm of MgSO4 there is 20.19 %
Mg = 20.19 = 100
x = 7.6
20.19 * 7.6 = 100x
20.19 * 7.6/100 = x
Mg = 1.53 gm
Problems
- Heat Stroke
Due to high temperature plants are suffering from heat stroke
To reduce it we have tigh the shed net over the crop.
2. Snake larvae

To reduce the effect of snake larvae we have applied neem oil on the plants leaf. 1 ml of neem oil is diluted in 1 lit of water and the applied over the leaf.
3. Deficiency of nutrient

After application of nutrient we have observed that plants leaf are yellowing and drying.
8 – 4 – 2022
To overcome this problem we have added the solution of 10 gm urea and 10 gm of sugar in 10 litres of water and applied it in nutrient solution after 5 days.

13 – 04 – 2022
Application of nutrient solution to the system as recommended above.
20 – 04 – 2022
Application of nutrient solution.
29 – 04 – 2022
Application of nutrient solution to the system.
7 – 5 – 2022
Application of nutrient solution to the system.
13 – 5 – 2022
Application of nutrient solution.
Now we are using soil extract with sugar as nutrient solution. For which we are making another set of hydroponic (flood and drain) for brinjal crop.
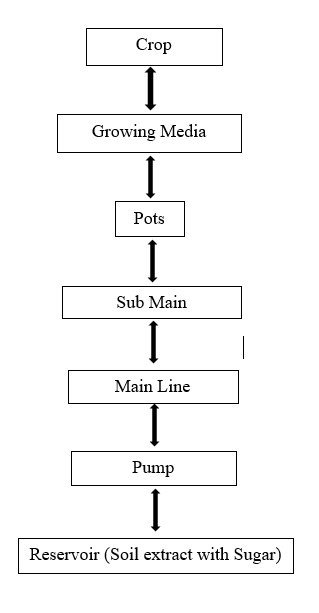
Material Flow Diagram
- Pipe System – a) Drip pipe
b) T and L joints
c) Grommets
2. Submersible pump
3. Pots – 5 litres
4. Reservior = 30 litres
5. Crop – Brinjal
6. Nutrient – Soil extract with sugar
Process Flow Chart:
Material
- Drip pipe – 16 mm
- T and L joint – Plastic – 16 mm
- Reservior – Plastic – 30 litres
- Pots – Plastic – litres
- Grommet – Rubber – 5
16 – 4 – 22
Firstly we calculated the porosity of 1 litres of soil by doing following steps.
- Take a beaker of 1 litre and measures it weight.
- Fill the soil in the beaker upto 1 litre mark and measure the weight.
- Add the water in the beaker slowly slowly untill the water reaches upto to the bottom of beaker (fully saturated ) but make sure water does not comes above the 1 litre mark.
- Add measure the weight of soil + water added in it as final reading.
After doing the above experiment the reading of it are given below.
Weight of beaker – 80 gm
Weight of soil – 992 gm (after adding soil upto 1 litre mark in beaker)
For saturating the 1 litre soil 700 ml of water is added in beaker
Weight of soil after saturation – 1.663 kg
Making of soil extract with sugar
For making the solution we have taken 1 kg of soil and added water of 350 ml in which 1 gm of sugar is diluted and kept in for 5 days in a container and stirring the solution twice a day.
Then we have made 5 cans of soil extract with sugar.
Bill of Material :
20 April 2022
Fabrication:

For placing the hydroponic (flood and drain system) using nutrient solution of soil extract with sugar solution we have made a table using the L angles the length of table was 200 cm and breadth 23 cm and height of 45 cm.
23 April 2022
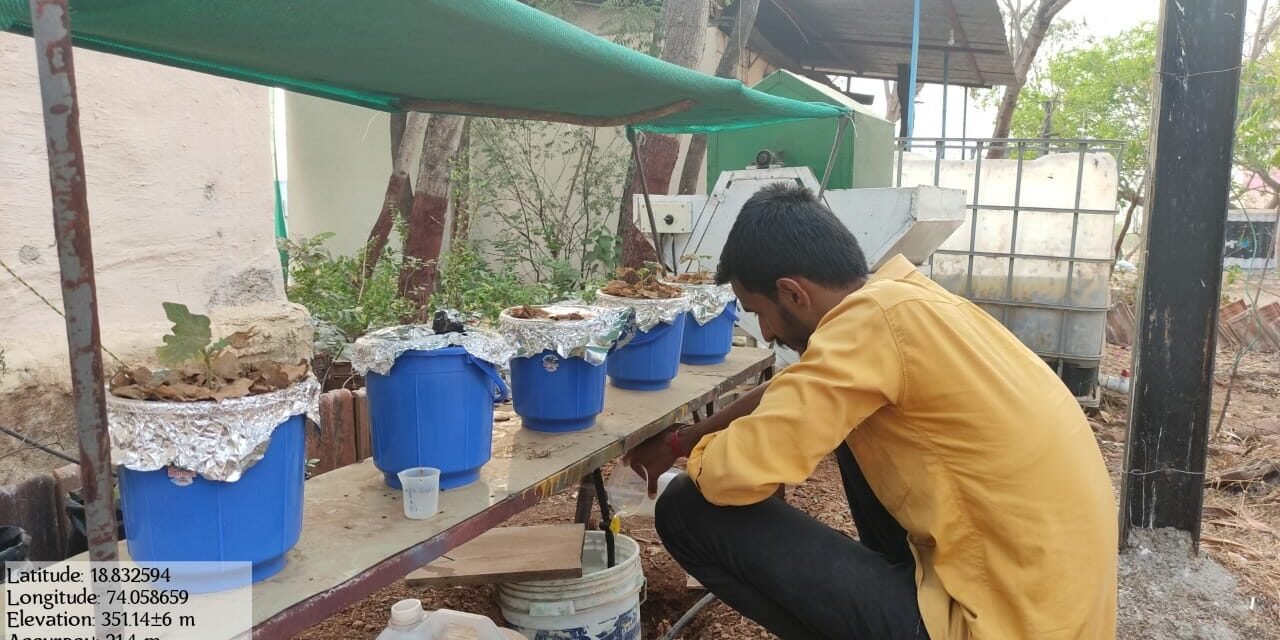
We have planted the brinjal crop in hydroponic (flood and drain) system for which we have used soil extract with sugar as nutrient solution the media used for the system is brick pieces.

24 April 2022
We have applied the soil extract with sugar as nutrient solution in the reservoir

Add the nutrient solution (soil extract with sugar) daily in reservoir.
Process of application of nutrient in reservoir
- Take out 5 litres of water from reservoir.
- Firstly add 2 litres of water in can which contain soil and sugar solution, wait for few minutes.
- Add another 2 and 1 litres of water from reservoir in can and repeat the same process as above.
25 – 04 – 2022 to 29 – 04 – 2022
Repeat the process of making nutrient solution and add the nutrient solution in reservoir daily
Add 1 gm of sugar in the can which have used and repeat the process.
Application of nutrient solution on daily basis.
https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1hgRf-PVMlier3h_rkFHG7CTeOPO3OCjqwvqpf0ocfvo/edit#gid=
Result
- Hydroponic (flood and drain) system is suitable for brinjal crop.
- Through design thinking process we ideate our system and design according to it for 5 crops of brinjal and according to it costing of system is 1733 rupees we locally fabricated the system at vigyan ashram workshop and it is implemented at vigyan ashram.
- Soil extract with sugar is suitable for brinjal (in flood and drain) system as compared to chemical nutrients.
Concluding Note





