Dynamic design and Drive train designe for E-vehicle
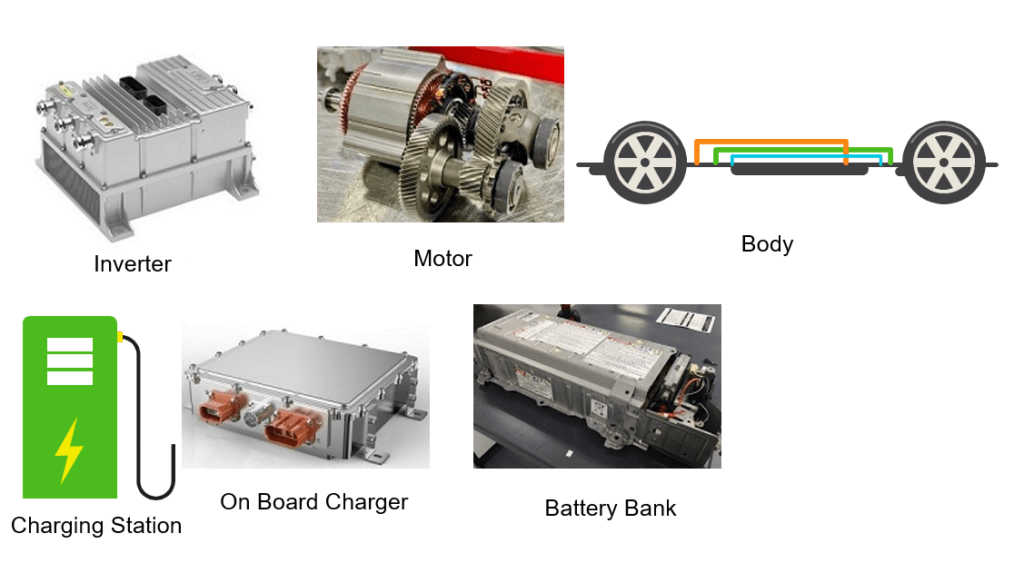
Electric Vehicle Components

EV Parts
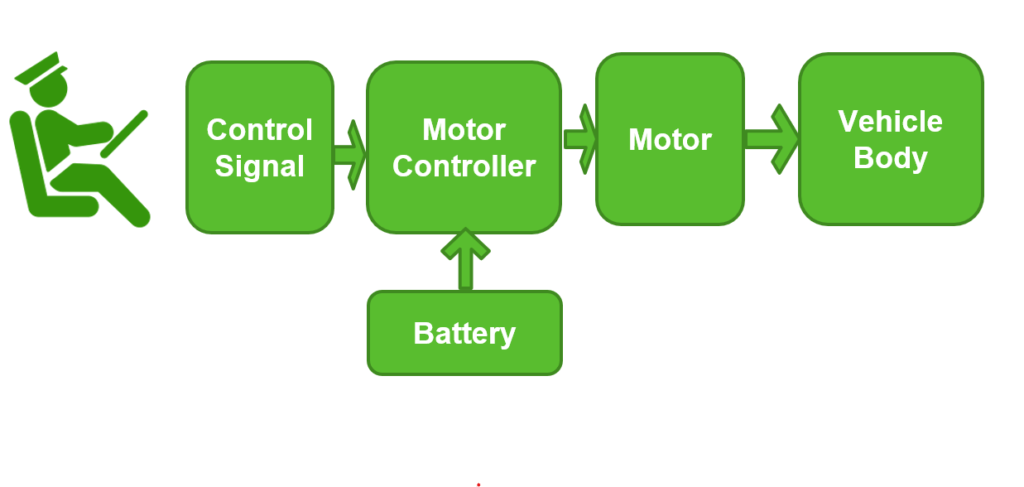
Basic electric vehicle driving flow Block Diagram
Vehicle Design Procedure for EV
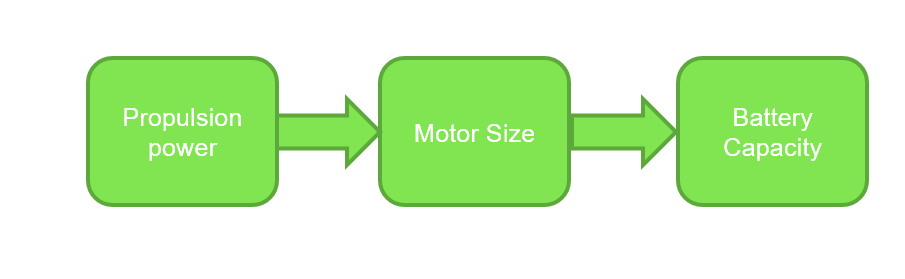
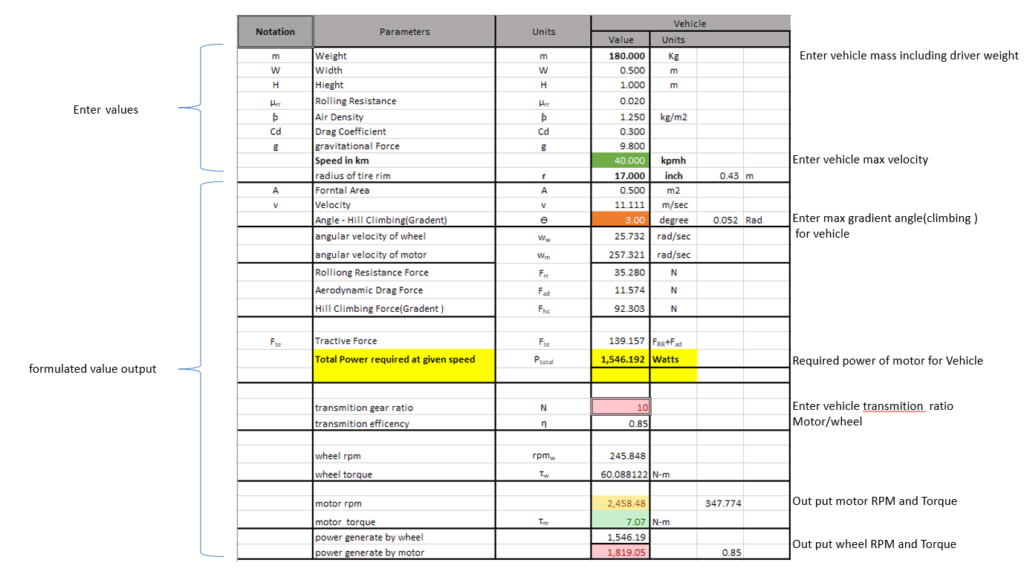
Basic power required to move the vehicle
Power = Total Tractive Force x Velocity of the vehicle
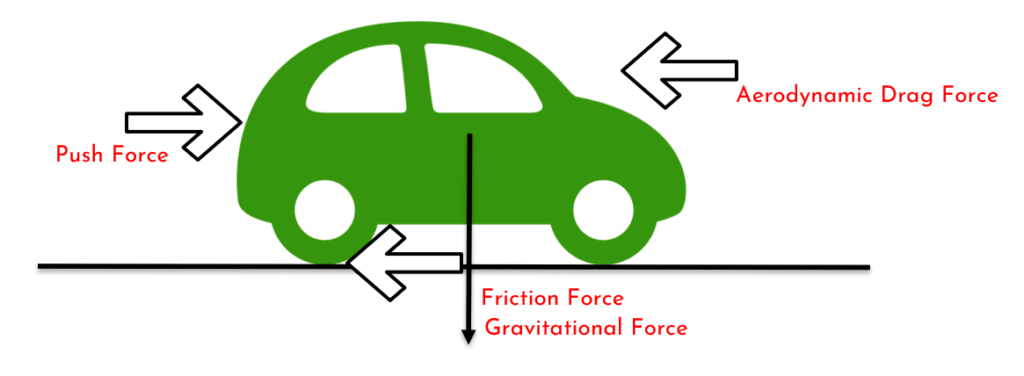
Types of forces on the Vehicle during motion
Total Tractive Force
- Rolling Resistance Force(Frr)
2. Aerodynamic drag force(Faero)
3. Hill climbing Force(Fhc)
4. Acceleration Force(Fxi)
1. Linear Acceleration Force, 2. Angular acceleration force
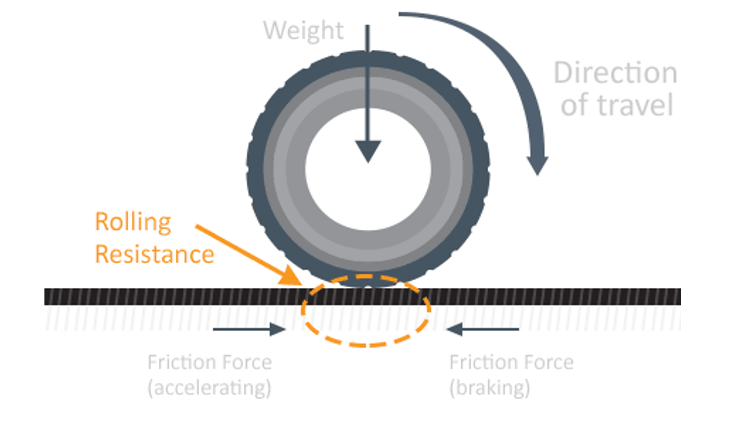
Rolling Resistance Force:
It is one of the forces that act to oppose the motion of a vehicle. It is the force between the wheels of the vehicle and the surface of the road.
The Coefficient, is a function of the Tire material, structure, temp, pressure, tread geometry, road roughness, material, presence & absence of liquids on the road.
Note:
•This value varies with SPEED. •Tire pressure increases its value decreases
Rolling resistance =coefficent of rolling friction*gross Vehicle weight
Frr= µrr m.g
where,
-µrr – Rolling Resistanceααα Constaαnt
-m – Mass of the Vehicle
-g – Gravitational acceleration constant

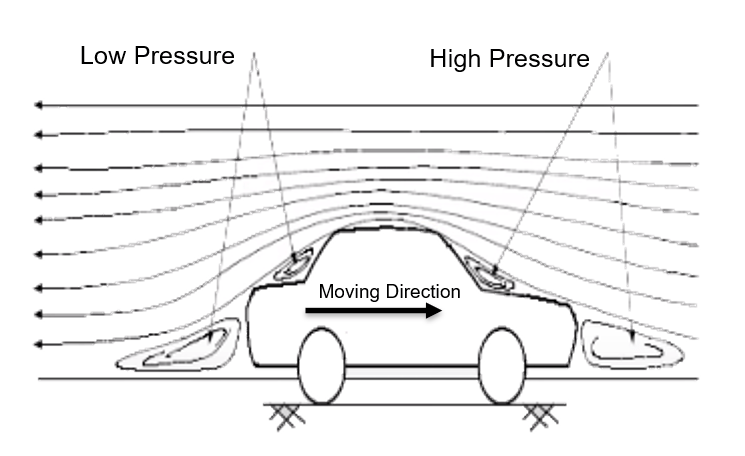
Aerodynamic Drag Force:
•The force on an object that resists its motion through the air is called Aerodynamic drag force.
Aerodynamic drag force α square of the velocity of the vehicle
Fad = ½ρCdAv2 Newtons
where,
ρ – Air Density kg/m3
A – Frontal Area m2
Cd – Drag Coefficient
v – Velocity of the Vehicle m/s
for more details:-
https://info.simuleon.com/blog/how-to-calculate-drag-coefficient-for-motorcycle
Excel Sheet for EV motor Selection base on above Calculations