Introduction
Soil organic carbon is a key indicator of fertility because it controls nutrient availability, microbial activity, and soil structure. In our recent testing, few farmland soil samples were analyzed using both soil testing kits and a laboratory chemical method. The chemical method used was the Walkley & Black rapid titration technique, which gives accurate organic carbon percentage through oxidation and back-titration.
Principal
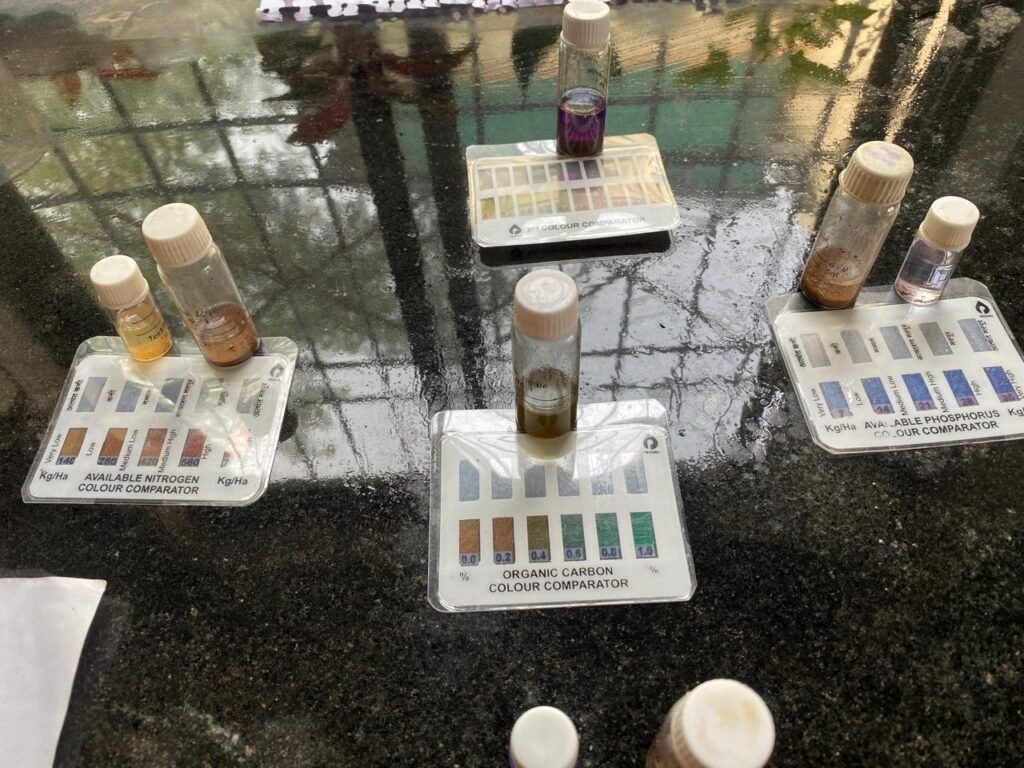
Soil parameters are analyzed using chemical reactions between soil extract and specific reagents. In the Walkley & Black method, organic carbon is oxidized by potassium dichromate in acidic conditions, and the unreacted chemical is measured by titration. In soil testing kits (Prerana & TARA), nutrients like Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium (NPK), along with pH and EC, are estimated by color formation or drop-based comparison with the kit chart. The reaction output is matched to standards to determine soil fertility and carbon content.
Chemicals Used
- 1 N Potassium Dichromate (K₂Cr₂O₇)
- Concentrated Sulfuric Acid (H₂SO₄)
- 0.5 N Ferrous Ammonium Sulfate (FAS)
- Ferroin Indicator
- Distilled Water
Apparatus
- Burette
- 10 ml Pipette
- 500 ml Conical Flask
- Digital Weighing Balance
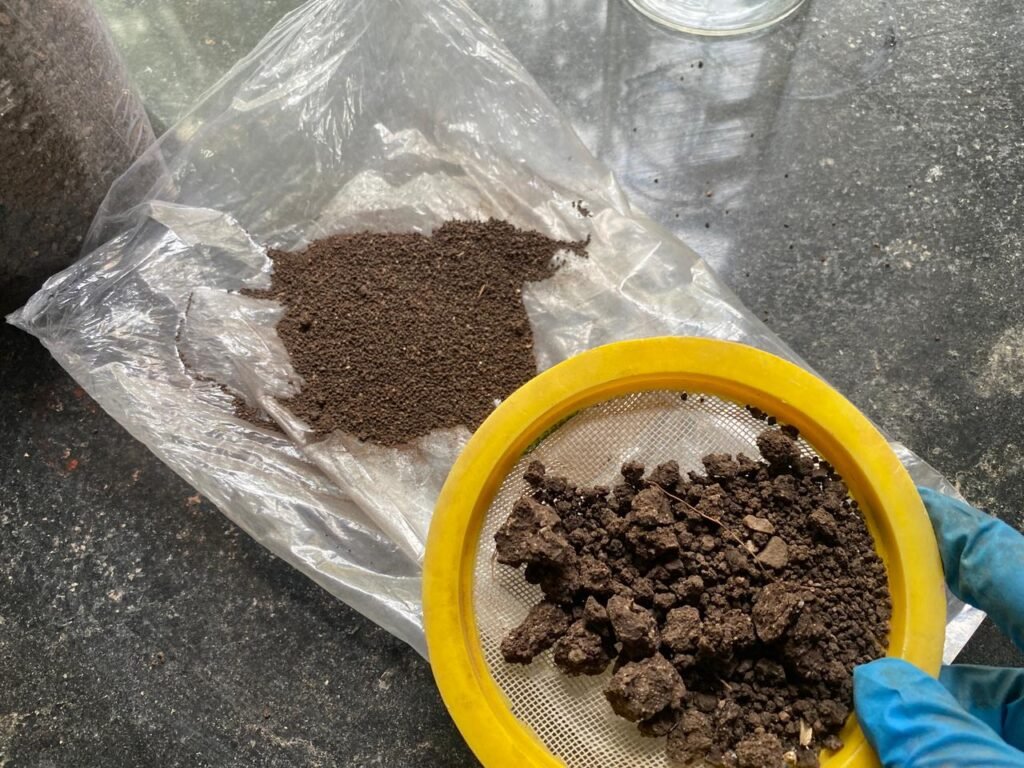
- 0.5 mm Soil Sieve
- Funnel
Procedure
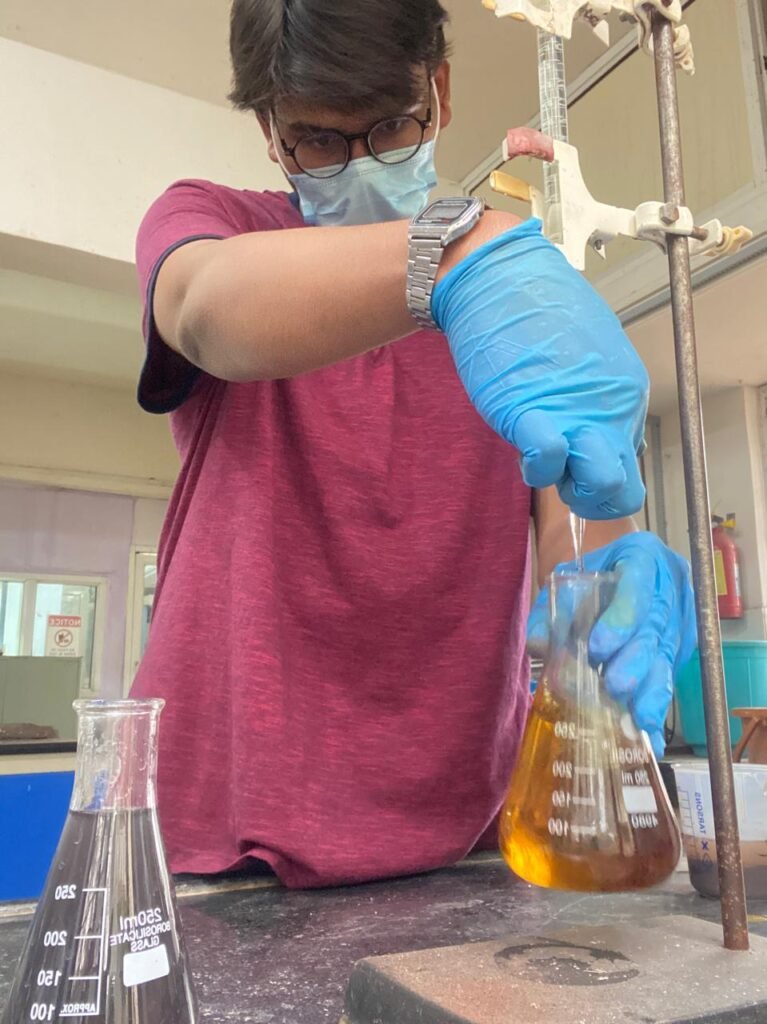
- Take 1 gram of air-dried, sieved soil into a 500 ml conical flask.
- Add 10 ml of 1 N K₂Cr₂O₇ solution.
- Carefully add 20 ml concentrated H₂SO₄, swirl gently.
- Let the mixture stand for 30 minutes for complete oxidation.
- Add 200 ml distilled water to dilute the solution.
- Add 2–3 drops of Ferroin indicator, solution turns blue green.
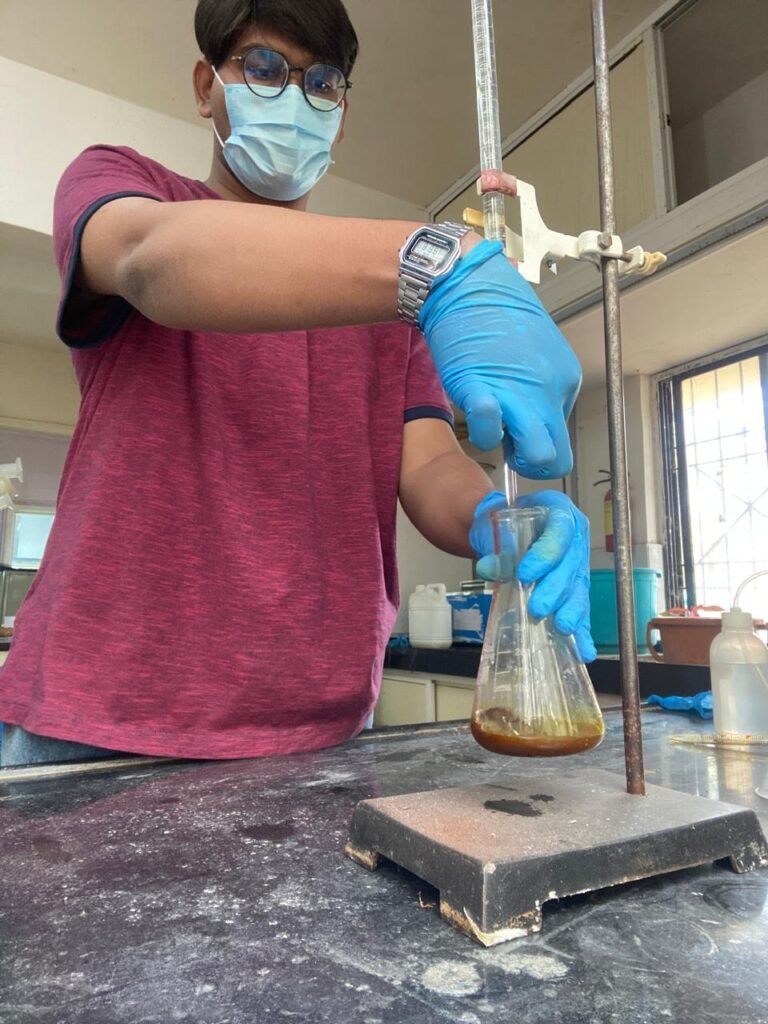
- Titrate with 0.5 N FAS until color changes blue green to reddish brown/ wine red (endpoint).
- Run a blank titration without soil for reference.



Formula to calculate Organic Carbon %
The formula used for organic carbon percentage is:
Organic Carbon (%) =
(Blank – Sample) × Normality of FAS × 0.003 × 1.33 × 100 / Weight of soil (g)
Where:
- B = Blank reading
- S = Soil sample reading
- N (Normality of FAS) = 0.5 N
- 0.003 = Carbon equivalent in grams
- 1.33 = Correction factor
Observations
| Date | Soil Sample | pH (Kit) | pH (meter) | EC (µS/cm) | Nitrogen (kg/ha) | Phosphorus (kg/ha) | Potassium (kg/ha) | Organic Carbon(kit) % | Bulk Density (g/cm³) | (B)Blank titration reading(ml) | (S)Soil sample reading(ml) | Organic Carbon% (W&B Titration) |
| 3 Jan 2026 | Sample 1 | 7.5 | 7.32 | 155 | 280 | 7 | 100-150 | 0.4 % | 1.74 | 22.2 | 20 | 0.44 |
| 4 Jan 2026 | Sample 2 | 8.5 | 8.0 | 141 | 140 | 14 | 300 | 0.6 | 1.6 | 22.1 | 19.1 | 0.598 |
| 5 Jan 2026 | Sample 3 | 8.0 | 8.2 | 206 | 280 | 7 | 150-200 | 0.4 | 1.66 | 20.1 | 17.9 | 0.438 |
| 6 Jan 2026 | Sample 4 | 8.0 | 7.77 | 276 | 140 | 14 | 350 | 0.4 | 1.70 | 19.5 | 17.4 | 0.482 |
| 7 Jan 2026 | Sample 5 | 7.5 | 7.02 | 160 | 280 | 14 | 240 | 0.4 | 1.76 | 22.4 | 20.4 | 0.399 |
Calculations
Sample 1 (3 Jan)
Organic Carbon (%) = (22.2 − 20.0) × 0.5 × 0.003 × 1.33 × 100 / 1
= 2.2 × 0.5 × 0.003 × 1.33 × 100
= 0.4389 % ≈ 0.44 %
Sample 2 (4 Jan)
Organic Carbon (%) = (22.1 − 19.1) × 0.5 × 0.003 × 1.33 × 100 / 1
= 3.0 × 0.5 × 0.003 × 1.33 × 100
= 0.5985 %
Sample 3 (5 Jan)
Organic Carbon (%) = (20.1 − 17.9) × 0.5 × 0.003 × 1.33 × 100 / 1
= 2.2 × 0.5 × 0.003 × 1.33 × 100
= 0.4389 %
Sample 4 (6 Jan)
Organic Carbon (%) = (19.5 − 17.4) × 0.5 × 0.003 × 1.33 × 100 / 1
= 2.1 × 0.5 × 0.003 × 1.33 × 100
= 0.41895 % ≈ 0.42 %
Sample 5 (7 Jan)
Organic Carbon (%) = (22.4 − 20.4) × 0.5 × 0.003 × 1.33 × 100 / 1
= 2.0 × 0.5 × 0.003 × 1.33 × 100
= 0.399 %
Conclusion
The soil samples were successfully analyzed for organic carbon content using the Walkley & Black rapid titration method, and the final values were validated with practical readings. The results show low to medium organic carbon percentage, indicating a need for improving soil organic matter for better fertility and structure.





