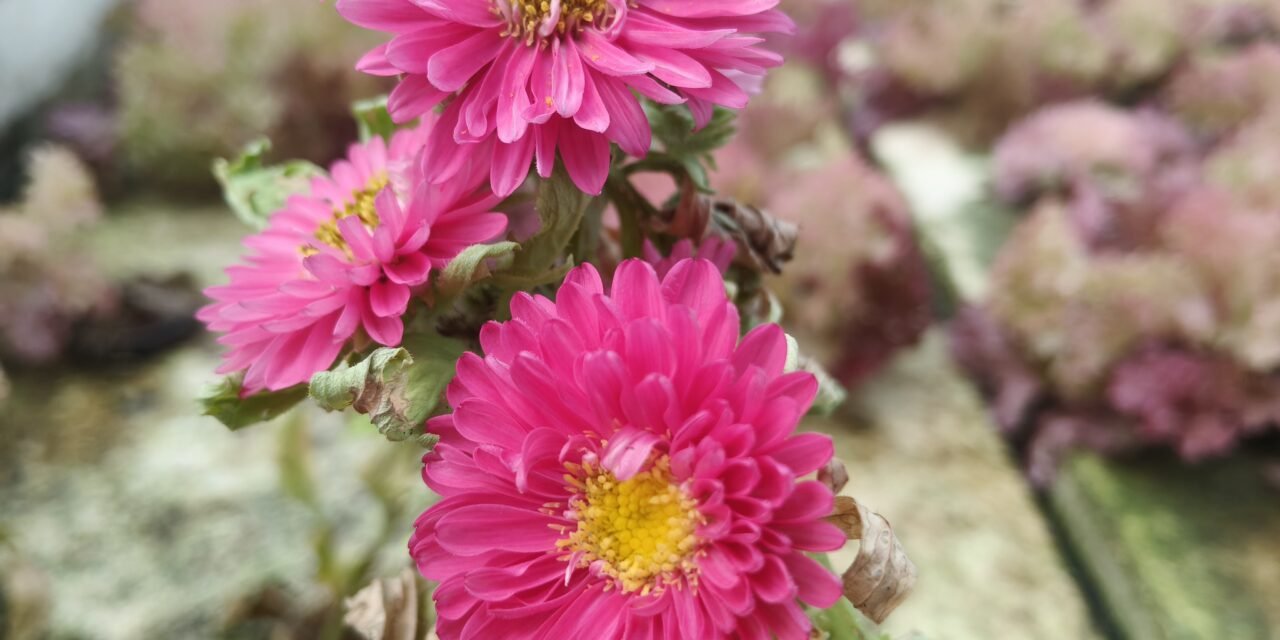
28 September 2025
I had a discussion with Dixit Sir. In that discussion, it was decided that after spinach, we will grow Aster plants in the hydroponic system. For this, I need to find out which type of hydroponic system is suitable for Aster plants. Also, documentation has to be prepared on Aster plants, and after that, the next discussion will be held .
The link below refers to the Aster document :
Aster
- Botanical Name: Callistephus chinensis
- Common Name: Aster
- Family: Asteraceae
- Type: Annual ornamental flowering plant
- Origin: Native to China, widely cultivated globally for cut flowers and garden decoration.
Aster is popular for its vibrant, daisy-like flowers that come in a variety of colors such as purple, pink, red, white, and blue. It is highly valued in floriculture due to its long-lasting blooms and aesthetic appeal.
2. Plant Characteristics :
- Height: Typically 30–90 cm depending on variety and cultivation conditions.
- Leaves: Simple, lance-shaped, arranged alternately on the stem.
- Flowers: Composite flowers with central disc florets and surrounding ray florets.
- Blooming Period: Generally blooms in late summer to autumn (8–12 weeks after planting).
- Life Cycle: Short-lived annual, completing its life cycle in one growing season.
3. Uses:
- Cut Flower Production: Stems are long and sturdy, suitable for bouquets and floral arrangements.
- Ornamental Gardening : Ideal for beds, borders, and containers
- Research Crop: Due to its predictable growth, it is used in floriculture experiments and hydroponic research.
Aster in Hydroponics
- Aster (Callistephus chinensis) is a popular cut-flower crop.
- It grows well in soilless culture, but requires careful nutrient and EC management.
- Hydroponics helps get uniform flower size, better stem length, and controlled flowering.
1. Best Hydroponic Systems for Aster:
- NFT (Nutrient Film Technique): Good for leafy crops, but not ideal for long-term flowering plants like Aster (roots need more stability).
- DWC (Deep Water Culture): Roots may become too waterlogged → fungal risk.
- Drip Irrigation / Dutch Bucket (recommended):Provides stable root support (using cocopeat, perlite, or rockwool). Controlled nutrient supply.Best suited for flowering crops like Aster, Gerbera, Chrysanthemum.
Aster in DWC Hydroponics
Possible
- In DWC, roots stay directly in the nutrient solution → allows fast nutrient uptake.
- Aster can grow if proper aeration is provided.
Challenge:
- Risk of Root Rot – Flowering crops like Aster have a long growth cycle, and since roots remain continuously in water in DWC, the chance of fungal infections (Pythium, Fusarium) is high.
- Plant Support – Aster needs strong stems and support; in DWC, only net pots with Hydroton/coco chips provide support. For large flowering plants, this may be somewhat unstable.
- Nutrient Fluctuation – For long-term crops, maintaining a stable solution is difficult; EC and pH need frequent monitoring.
Precautions if using DWC
- Strong Aeration: 1–2 air stones in tank
- Water Temperature: 20–24 °C (warm water increases disease risk)
- Use Net Pots with Media: Hydroton + cocopeat/perlite mix for stem support.
- Disinfect System Regularly: Use H₂O₂ or other sterilizers for the root zone.
- Change Solution: Every 7–10 days.
Growing media for Aster Hydroponic
| Media | Ratio / Mix | Features | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cocopeat + Perlite | 70:30 | Water retention + aeration balance | Most common and easy to manage |
| Cocopeat + Vermiculite + Perlite | 50:25:25 | Better moisture + oxygen balance | Suitable for seedling to flowering stage |
| Perlite + Vermiculite | 1:1 | Very light & good drainage | Use if system continuously nutrient flow (like NFT or drip) |
| Rockwool | Pure or with perlite | Sterile, pH neutral | Best for nursery but costly |
| LECA (Clay balls) | 100% or with cocopeat (50:50) | Reusable, high aeration | Best for DWC or Dutch bucket system |
Aster – Hydroponic Environmental Requirements :
| Parameter | Ideal Range | Notes |
| pH | 5.8 – 6.2 | Keep stable; check regularly; outside this range nutrient uptake decreases |
| EC (Electrical Conductivity) | 2.0 – 2.5 mS/cm | Too high → leaf burn; too low → poor flowering |
| Young seedlings | 1.8–2.0 mS/cm | |
| flowering plants | 2.3–2.5 mS/cm. | |
| Water Temperature | 20 – 24°C | Cooler water improves root oxygenation; warmer water → disease risk |
| Air Temperature | 18 – 24°C | Aster prefers mild, cool conditions; avoid frost |
| Humidity | 50 – 70% | Too high → fungal infection (Pythium, Fusarium) risk |
| Light | 12–14 hours/day | 200–300 µmol/m²/s (LED or sunlight); sufficient light promotes flowering |
| Other Notes | – | Long photoperiod helps uniform flowering; heat stress >26°C may reduce stem strength and flower quality |
EC (Electrical Conductivity) – 2.0–2.5 mS/cm
1. What EC Means:
- EC measures the total concentration of dissolved salts/nutrients in your hydroponic solution.
- Higher EC = more nutrients; Lower EC = fewer nutrients.
- Units: mS/cm (milliSiemens per centimeter).
- Ideal Range for Aster:
- 2.0 – 2.5 mS/cm is ideal for hydroponic Aster.
- Ensures the plant gets enough nutrients for healthy stem growth, leaf development, and flowering.
3. Effects of Too High EC (>2.5 mS/cm):
- Leaf Burn / Tip Burn: Excess salts cause osmotic stress; water moves out of leaf cells → burning at leaf tips.
- Stunted Growth: Roots may be damaged; nutrient uptake becomes inefficient.
- Reduced Flower Quality: Flower size and stem length may decrease.
4. Effects of Too Low EC (<2.0 mS/cm):
- Nutrient Deficiency: Plant doesn’t get enough macro- and micronutrients (N, P, K, Ca, Mg, Fe).
- Poor Flowering: Stems may be weak, fewer blooms, delayed flowering.
- Leaf Yellowing or Poor Leaf Development: Leaves may turn pale due to nitrogen or iron deficiency .
5. Managing EC in Hydroponics:
- Monitor Daily: Use a reliable EC meter.
- Adjust Nutrients Gradually: Add concentrated nutrient solution to raise EC or dilute with water to lower EC.
- Account for Crop Stage: Young seedlings may need slightly lower EC (1.8–2.0 mS/cm), while flowering plants can handle 2.3–2.5 mS/cm.
- Temperature Factor: Warm water increases nutrient uptake; adjust EC accordingly to avoid over-fertilization.
Aeration in DWC
- In a DWC (Deep Water Culture) system, the plant roots stay directly in the water (nutrient solution).
- If there is no oxygen in the water → the roots will “suffocate” and root rot will occur.
- Therefore, it is essential to maintain dissolved oxygen (DO) in the water.
What is an Air Stone?
- A small porous stone or mesh-like device commonly used in aquariums.
- It is connected to an air pump.
- Air comes from the pump → tiny bubbles come out of the stone.
- These bubbles dissolve oxygen into the nutrient water.
Standard Nutrient Requirement for Aster :
| Nutrient | Recommended Concentration (ppm) | Target ppm | Role in Aster |
| Nitrogen (N) | 150 – 180 ppm | 165 ppm | Vegetative growth, stem length |
| Phosphorus (P) | 40 – 50 ppm | 45 ppm | Root growth, bud initiation |
| Potassium (K) | 180 – 220 ppm | 200 pm | Strong stems, flower color & size |
| Calcium (Ca) | 140 – 160 ppm | 150 ppm | Cell wall strength, disease resistance |
| Magnesium (Mg) | 40 – 60 ppm | 50 ppm | Chlorophyll, prevents interveinal yellowing |
| Sulfur (S) | 50 – 70 ppm | 60 ppm | Protein synthesis, flower quality |
| Iron (Fe) | 2.0 – 3.0 ppm | 2.5 ppm | Prevents chlorosis |
| Manganese (Mn) | 0.5 – 1.0 ppm | 0.7 ppm | Enzyme activity |
| Zinc (Zn) | 0.05 – 0.1 ppm | 0.1 ppm | Hormone regulation, leaf expansion |
| Copper (Cu) | 0.05 ppm | 0.005 ppm | Enzyme activation |
| Boron (B) | 0.3 – 0.5 ppm | 0.4 ppm | Flower & seed development |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | 0.05 ppm | 0.05 ppm | Nitrogen metabolism |
Nutrient Requirement
- Vegetative stage: Higher nitrogen for leaf and stem growth.
- Flowering stage: Higher potassium and phosphorus for bud formation & flower quality.
- Micro-nutrients like Fe, Mn, Zn, B, Mo are essential for color and petal formation .
Link of Nutrient Source for Aster : https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1rqk6-aB_zssgVop405Xy473vgkeZ4Lzb/edit?usp=sharing&ouid=113141058233737100131&rtpof=true&sd=true
Aster Hydroponics Dosing
| Fertilizer | 1 L | 10 L | 20 L |
| Calcium Nitrate | 0.904 | 9.04 | 18.08 |
| Potassium Nitrate 13 : 00 : 45 | 0.382 | 3.82 | 7.64 |
| Monopotassium Phosphate 00:52:34 | 0.188 | 1.88 | 3.76 |
| Magnesium Sulphate | 0.478 | 4.78 | 9.56 |
| Rexolin Combi II (Micronutrient) | 0.05 | 0.5 | 1.0 |
8 Oct 2025 :
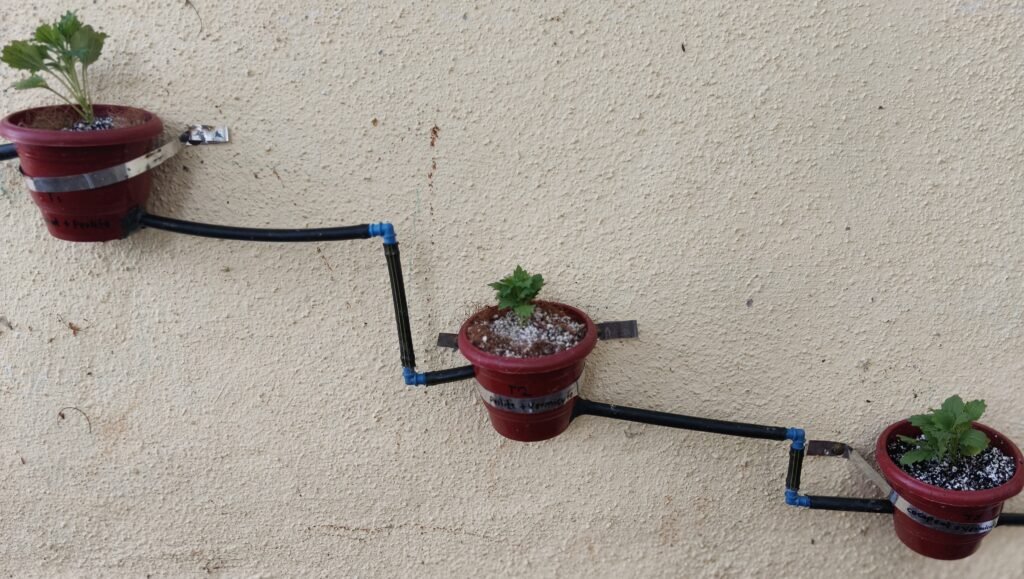
On 8th October, during the discussion with Dixit Sir, we talked about which hydroponic system should be prepared for Aster, which growing media should be used, and that the hydroponic system should be run on the wall. So, for our Aster setup, it was decided to have 4 pots on the wall in a zig-zag or decorative pattern, with continuous water flow through them and a growing media suitable for the plant in each pot. I have started working on that .

19 Oct 2025
On 19th October, there was a detailed discussion with Dixit Sir regarding the Aster hydroponic project. During the meeting, it was decided to conduct trials using a 3-layer NFT (Nutrient Film Technique) system, testing three different EC (Electrical Conductivity) ranges to observe their effects on plant growth and nutrient uptake.
For my part, I have set up a vertical 3-pot hydroponic system on the wall. In this system, I plan to test different combinations of growing media to determine which mix provides the best conditions for Aster growth. The growing media under consideration are Perlite, Cocopeat, and Vermiculite.
Before starting the trials, it is important to measure and calculate the water-holding capacity of each of these media. This will help in deciding the right mix ratio and ensure optimal water and nutrient availability for the plants. This specific point—the water-holding capacity of Perlite, Cocopeat, and Vermiculite—was also highlighted and discussed in the meeting .
24 Oct 2025
Link of Aster EC Maintain sheet :
Three different EC trials have been conducted for the Aster plant in the NFT system, as per the trials below.
| Experiment Trial | EC Range m S/ cm |
| T1 | 1.8 – 2.0 |
| T2 | 2.0 – 2.2 |
| T3 | 2.3 – 2.5 |
Objective of this experiment :
- To study the effect of different EC (Electrical Conductivity) levels of nutrient solution on the growth of Aster Plant in an NFT hydroponic system.
- To determine the optimum EC range for maximum Aster growth .
- To analyze the relationship between EC, nutrient uptake, and physiological responses such as deficiency symptoms or osmotic stress.
25 Oct 2025
Objective :
To determine and compare the water holding capacity (WHC) of different hydroponic growing media — Perlite, Vermiculite, and Cocopeat — in order to identify the most suitable medium or combination for optimal moisture retention and plant growth in hydroponic systems.
Water Holding Capacity (WHC)
The amount of water a medium can hold after being saturated and allowed to drain freely under gravity.
Step-by-Step Procedure
- Take a dry sample:
- Weigh a known amount of oven-dry perlite (W₁).
Example: W₁ = 100 g
- Weigh a known amount of oven-dry perlite (W₁).
- Saturate with water:
- Slowly pour water until all particles are fully wet.
- Avoid floating loss.
- Drain excess water:
- Allow it to drain freely for 30–60 minutes .
- Weigh the wet sample:
- After drainage, weigh again (W₂).
Example: W₂ =
- After drainage, weigh again (W₂).
- Calculate Water Holding Capacity (by weight):
| Media | Dry Weight (g) | Wet Weight (g) | Water Holding Capacity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Perlite | 50 | 104.31 | 108.62% |
| Vermiculite | 50 | 113.44 | 126.88% |
| Cocopeat | 50 | 199.25 | 298.50% |
- Cocopeat retains the most water — nearly 3× its dry weight, ideal for consistent moisture.
- Vermiculite holds moderate water, suitable for seedlings.
- Perlite holds the least but ensures good aeration.
1. Perlite
WHC = Wet wt. – Dry wt. / Dry wt. X 100
= 104.31 – 50 / 50 X 100 = 108.62 %
Perlite WHC = 108.62%
2. Vermiculite
WHC = Wet wt. – Dry wt. / Dry wt. X 100
= 113.44 – 50 /50 X 100 = 126.88 %
Vermiculite WHC = 126.88%
3. Cocopeat
WHC = Wet wt. – Dry wt. / Dry wt. X 100
= 199.25 – 50 /50 X 100 = 298.50 %
Cocopeat WHC = 298.50%
Growing Media :
- Cocopeat + Perlite = 70:30
- perlite + vermiculite = 1:1
- Cocopeat + Vermiculite + Perlite = 50:25:50
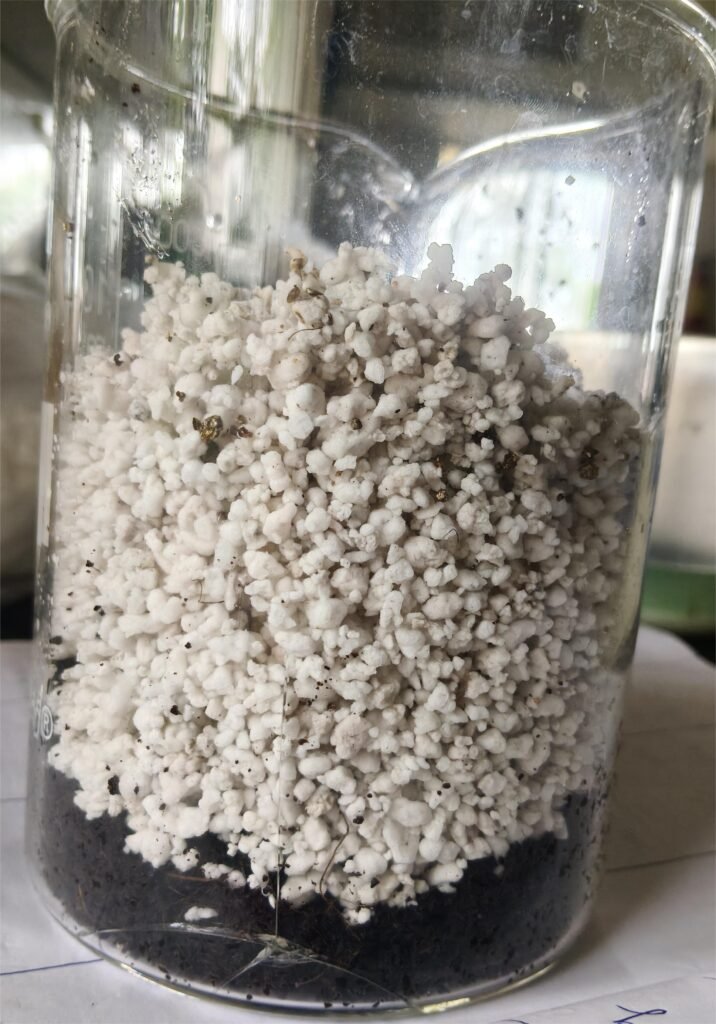
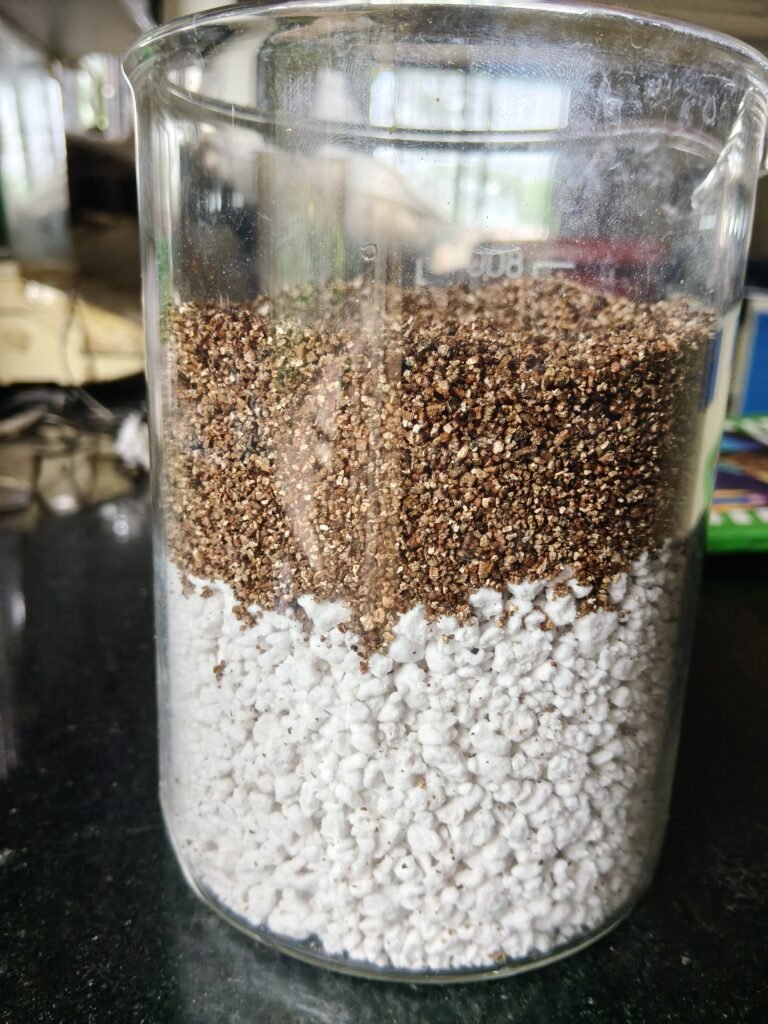
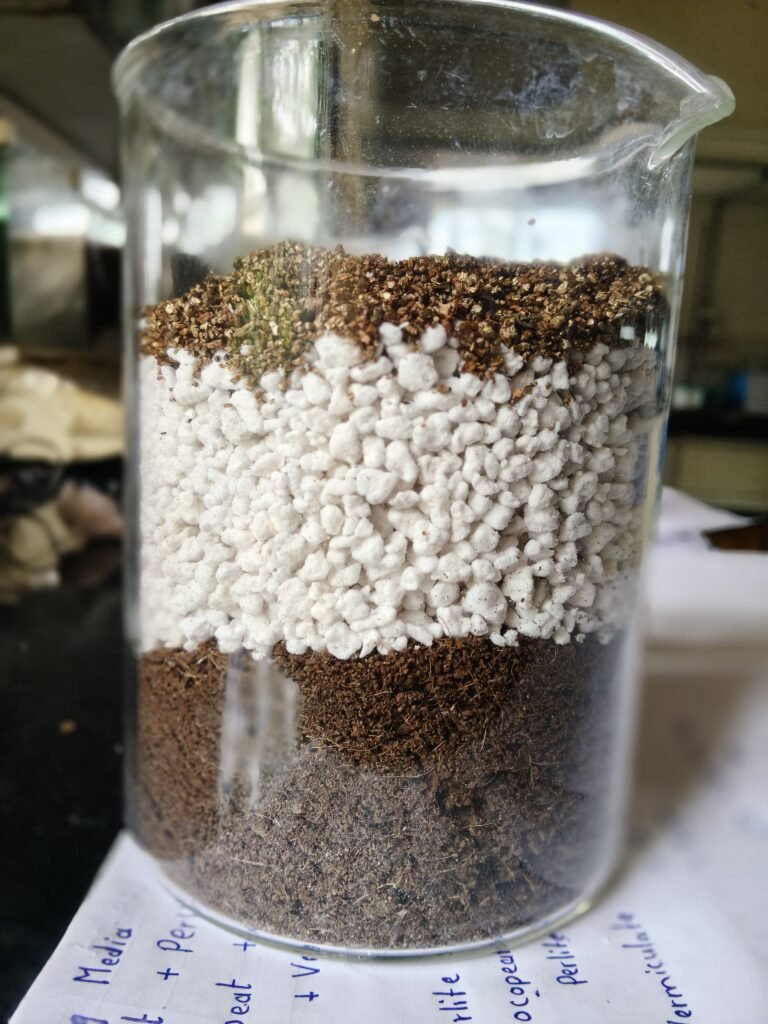




26 Oct 2025 :
During the review meeting held on 26th October with Dixit Sir and Abhijeet Sir, Dixit Sir instructed me to measure the properties of different growing media — Cocopeat, Perlite, and Vermiculite — such as Water Holding Capacity, Density, Porosity/Air Holding Capacity .
28 Oct 2025
Objective:
To evaluate and compare the physical and chemical properties of different growing media based on their air–water ratio, water holding capacity, weight, and electrolyte depletion rate, in order to determine the most suitable medium for optimum plant growth under hydroponic conditions.
1. Air : Water ratio for volume 60:40
→ This refers to the air-to-water ratio in the growing medium by volume.
A 60:40 ratio means 60% air space and 40% water-holding capacity, which is considered ideal for root aeration and moisture balance.
2. Water holding capacity → Higher is better
→ The ability of the medium to retain water. A higher value is beneficial because it ensures water availability to plants between irrigations.
3. Weight of media → Lower is better
→ Lighter media are preferred because they’re easier to handle and provide better aeration.
4. Electrolyte depletion rate
→ This refers to how quickly nutrients (electrolytes) are used up or lost from the growing medium during plant growth. A slower depletion rate indicates better nutrient retention.
Doc. on Growing Media Calculation Link :
| Sr. No. | Property | Cocopeat | Vermiculite | Perlite |
| 1 | Texture | Fine, fibrous, and soft particles | Soft, flaky, and spongy granules | Very light and airy granules |
| 2 | Colour | Brown to dark brown | Golden-brown to silvery-grey | White |
| 3 | Water Holding Capacity | 298.50 % | 126.88% | 108.62% |
| 4 | Bulk Density(g/cm³) | 0.112 | 0.3254 | 0.122 |
| 5 | Particle Density (g/cm³) | 0.428 | 1.5 | 0.375 |
| 6 | Porosity/ Air space/Air Holding Capacity | 73.83 % | 67.47 % | 78.33 % |
| 7 | pH | 5.1 (Slightly acidic) | 6.9 (Slightly Alkaline) | 7.8 (Neutral to slightly alkaline) |
| 8 | EC | 0669 (low) | 1162 | 0528 (very low) |
29 Oct 2025
On 29th October, Dixit Sir checked all the growing media calculations and told me to calculate the void space in the media.
Void space = Air space + Water space
Three different EC trials have been conducted for the Aster plant in the NFT system, as per the trials below.
| Experiment Trial | EC Range m S/ cm |
| T1 | 1.8 – 2.0 |
| T2 | 2.0 – 2.2 |
| T3 | 2.3 – 2.5 |
3 Nov 2025
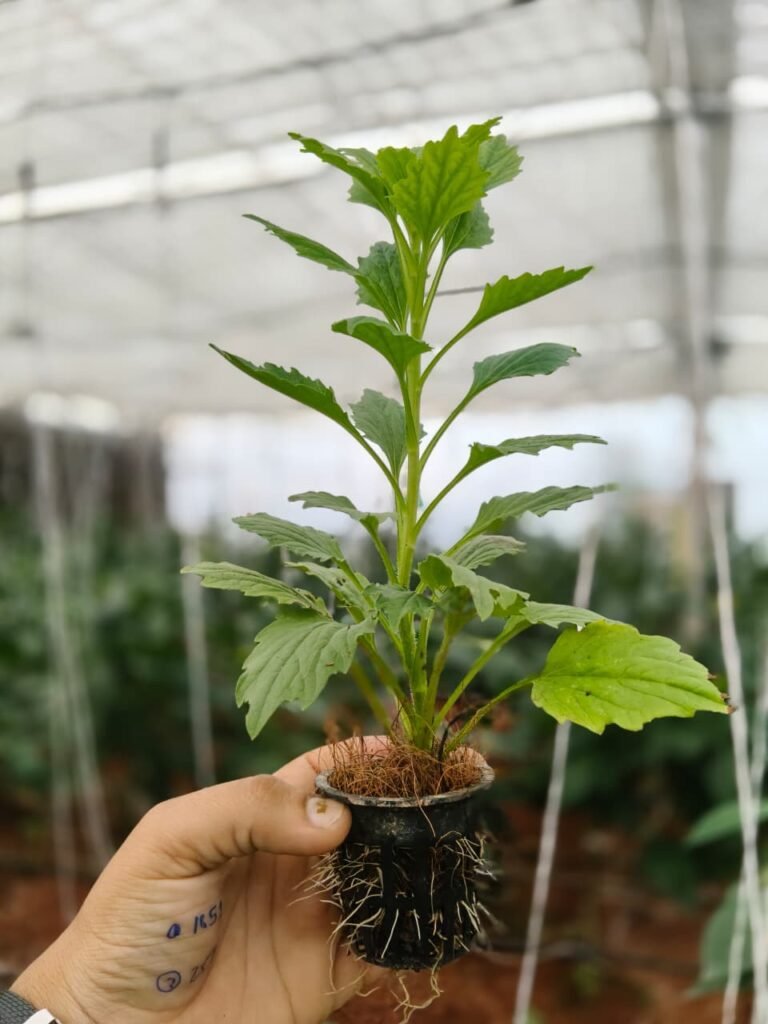
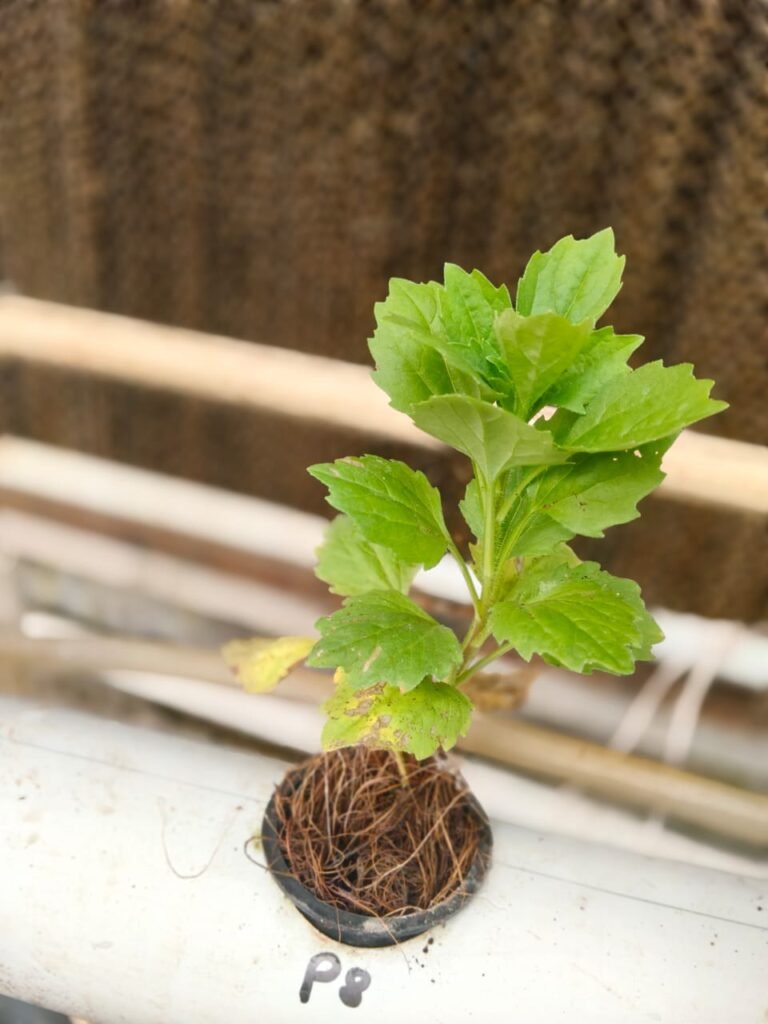
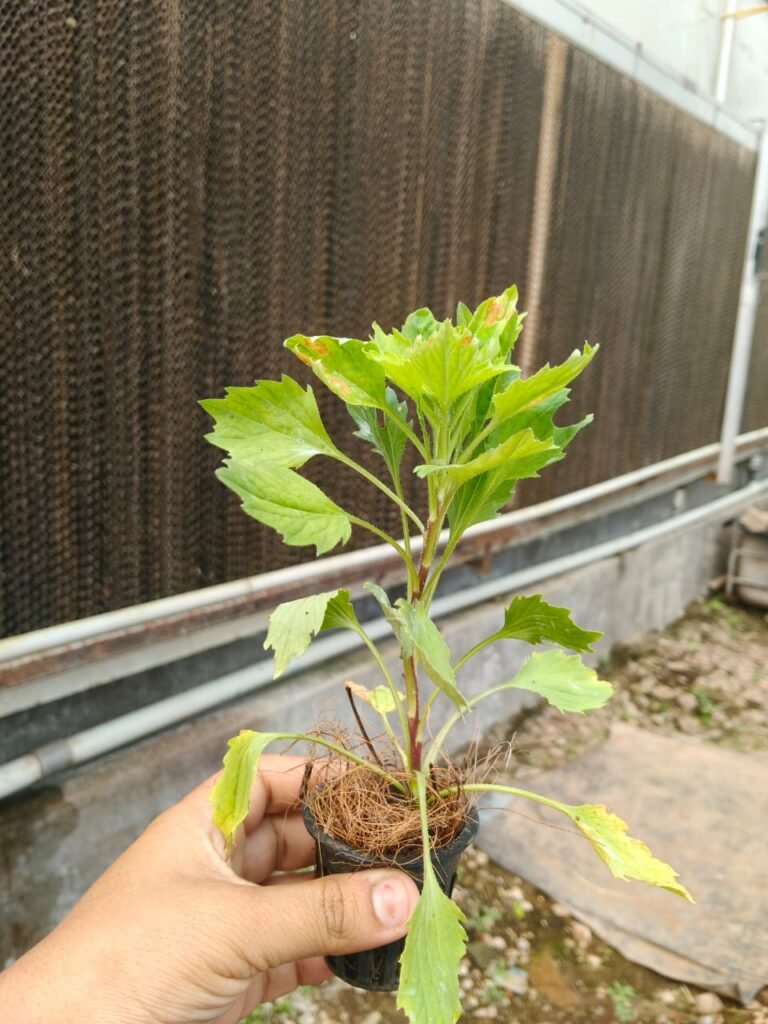
1st observation Of Aster Plant :



15 Nov 2025
2nd Observation Of Aster Plant :
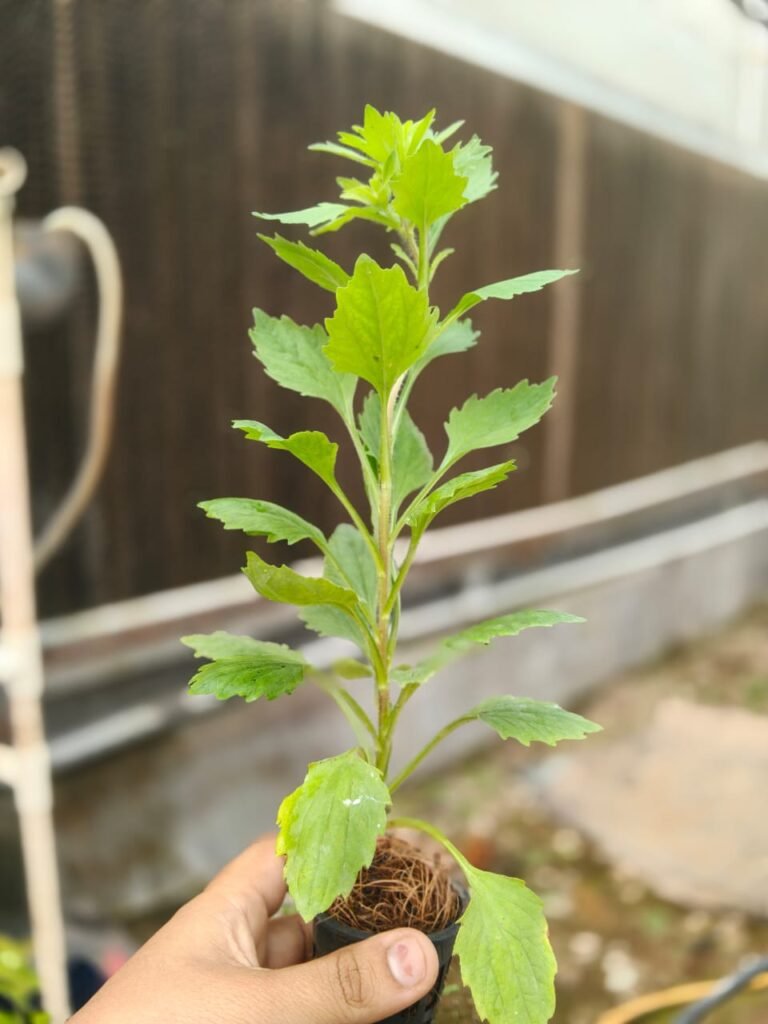
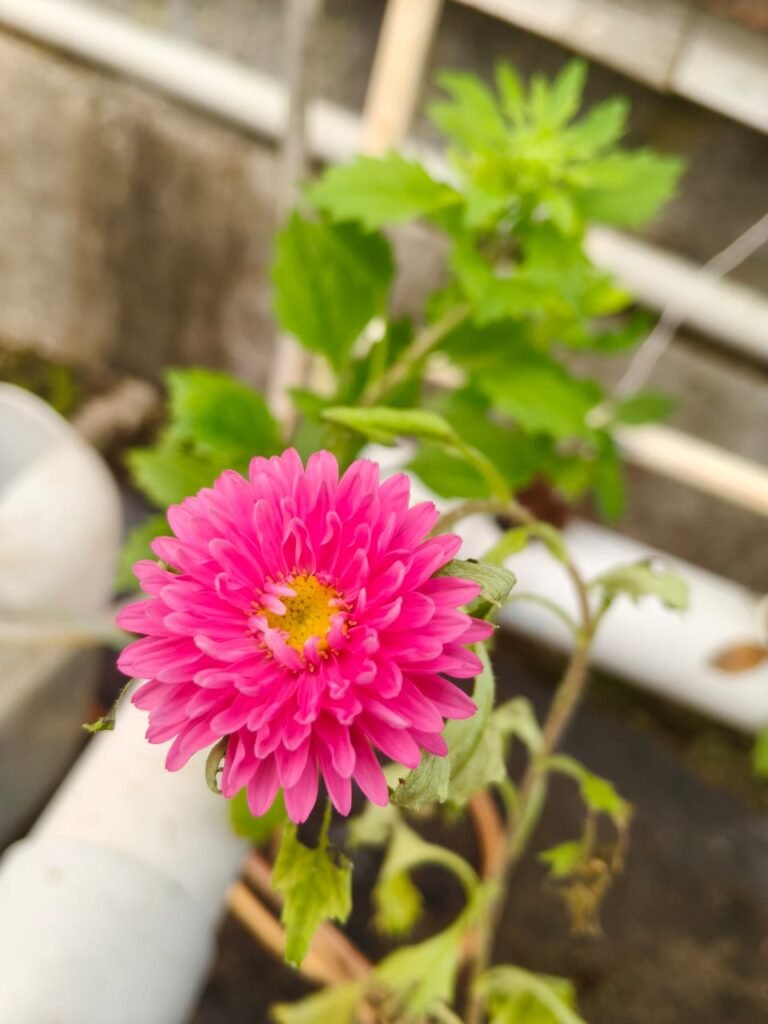


1. EC Range 1.8 m S/cm
Observation:
- Plants show healthy vegetative growth with good leaf color and turgidity.
- Roots are white and fibrous, indicating good oxygen and nutrient balance.
- Flower formation is proper, with bright pink blooms and strong stems.
- No signs of nutrient stress or leaf burn observed.
Conclusion:
This EC range appears optimum for Aster growth in the NFT system — balanced nutrient uptake and healthy flowering.
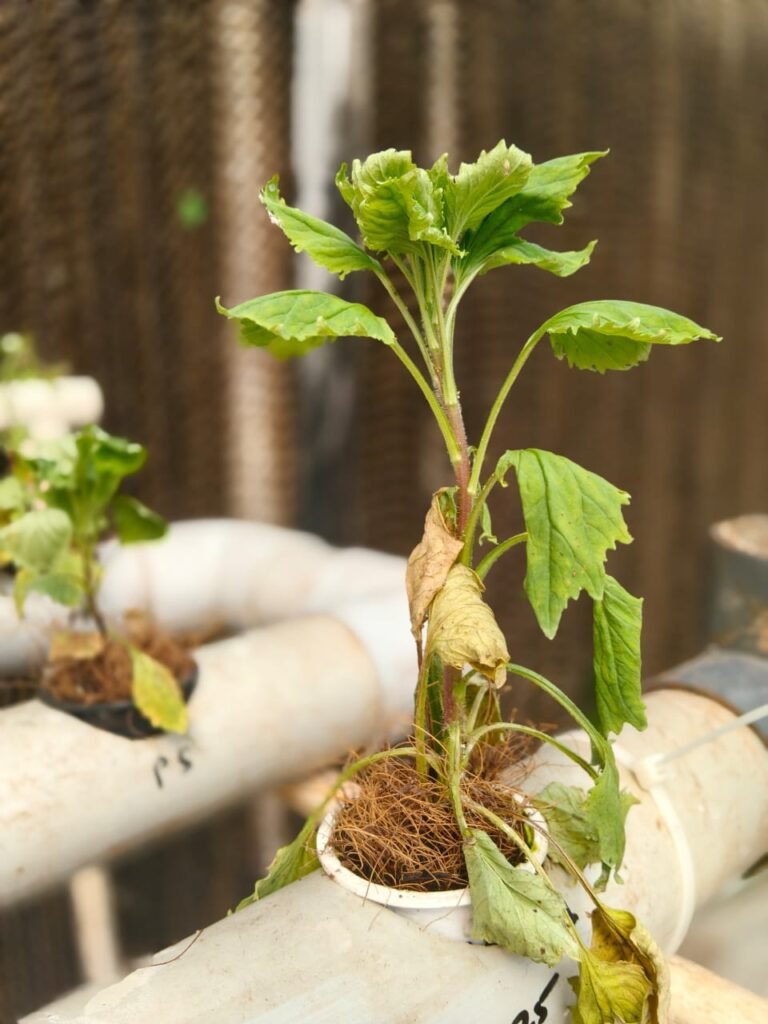


EC Range 2.0–2.2 mS/cm
Observation:
- Plants show moderate growth, but root zone symptoms like slight browning and slimy roots are visible.
- Lower leaves show minor yellowing or tip burn, suggesting early salt stress.
- Flower initiation may still occur, but overall plant vigor is slightly reduced.
Conclusion:
This EC range causes mild stress to the plants. Nutrient concentration may be slightly higher than optimal.
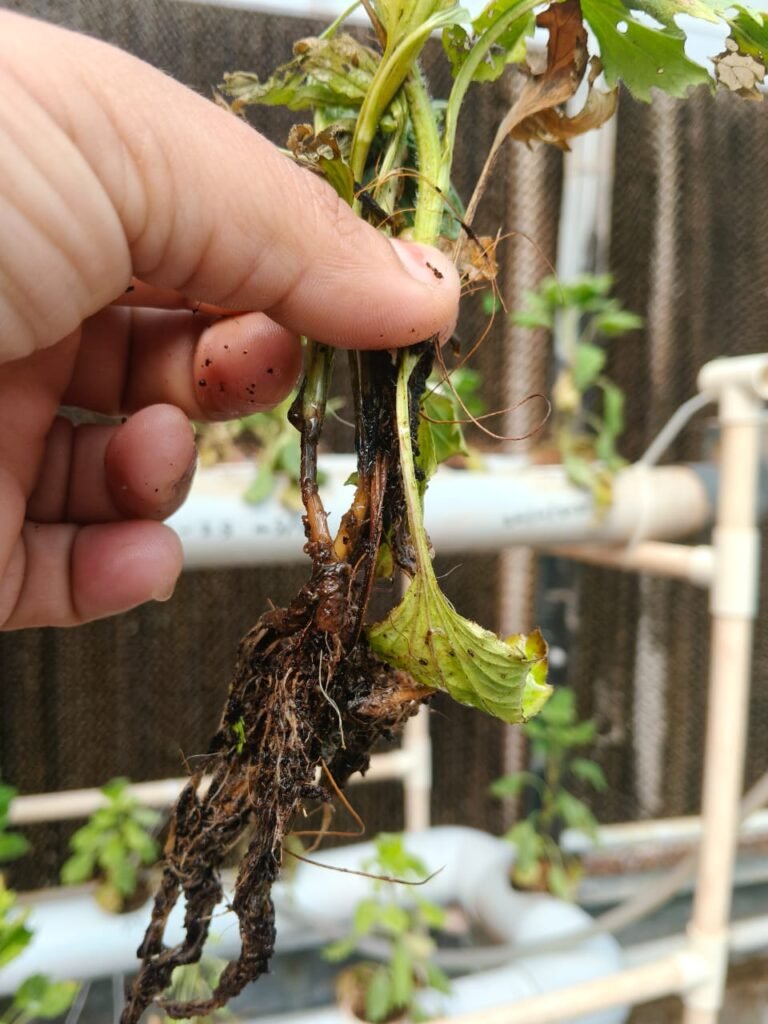
EC Range 2.3–2.5 m S/cm
Observation:
- Plants show visible stress symptoms — reduced leaf size, yellowing, and root rot or blackening as seen in the image.
- Root health is poor, with darkened and decaying roots.
- Growth is stunted and flower development is weak or delayed.
Conclusion:
This EC range is too high for Aster in NFT hydroponics. High salt concentration likely caused root damage and nutrient imbalance. - Detailed Observation – EC 2.3–2.5 m S/cm (High EC Stress)
- Root Condition:
- Roots appear dark brown to black, with slimy or decayed portions, indicating root rot.
- The root tips have stopped elongating, showing restricted growth and oxygen deficiency.
- The high nutrient concentration (EC above 2.3 m S/cm) has likely caused osmotic stress, reducing water uptake.
- Stem Condition:
- The lower stem region is blackened and soft, suggesting onset of fungal infection (possibly Pythium or Fusarium) favored by high salt and moisture stress.
- The stem base appears weak, leading to poor nutrient transport to upper parts of the plant.
15 Nov 2025
To check whether the plants grown under high EC conditions (2.0–2.5 m S/cm) show any improvement, I reduced the EC level to 1.5 m S/cm to observe whether the plants recover and show positive changes in growth and root health .
Expected Effects of Lowering EC to 1.5 m S/cm
- Root Recovery
The root zone stress will reduce because the salt concentration in the nutrient solution will be lower.
Damaged roots may start regenerating fine white roots within 4–7 days if oxygen levels in the NFT system are good.
Root rot progression will slow down, as lower EC improves water uptake and reduces osmotic pressure.
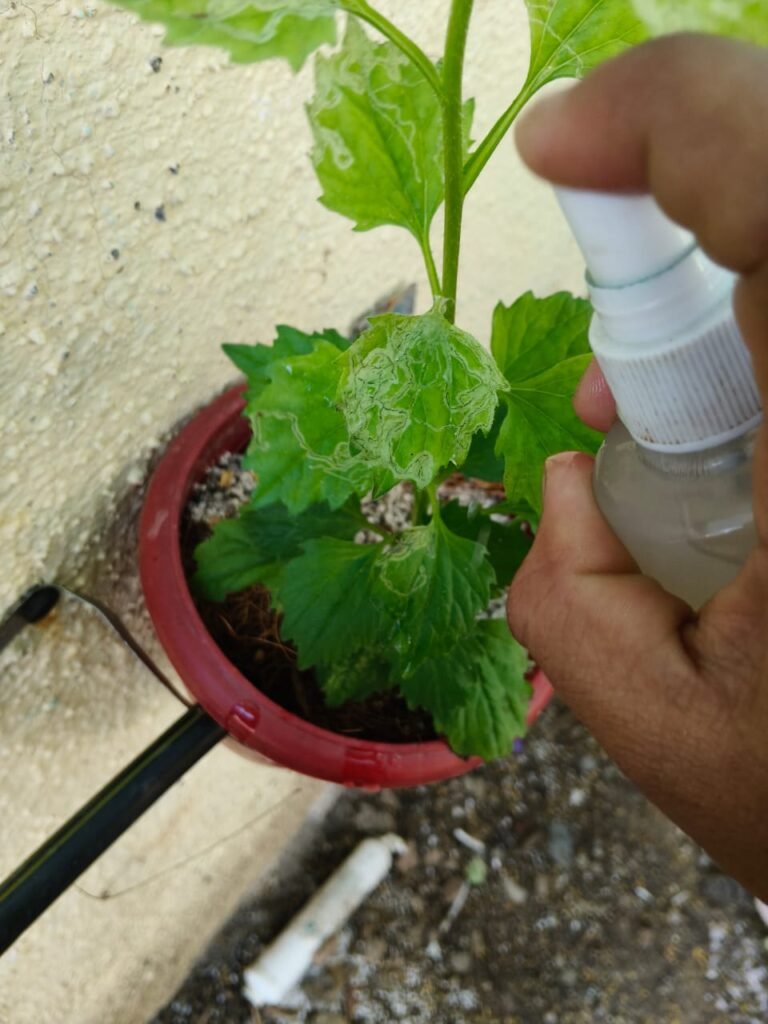
I noticed a leaf miner attack on my Aster plant.
The upper surface of the leaves showed white zig-zag tunnels caused by larvae feeding inside the leaf tissue.
To control the infestation, I sprayed neem oil solution and placed yellow sticky traps near the plant to catch adult insects .
17 Nov 2025 – 27 Nov 2025
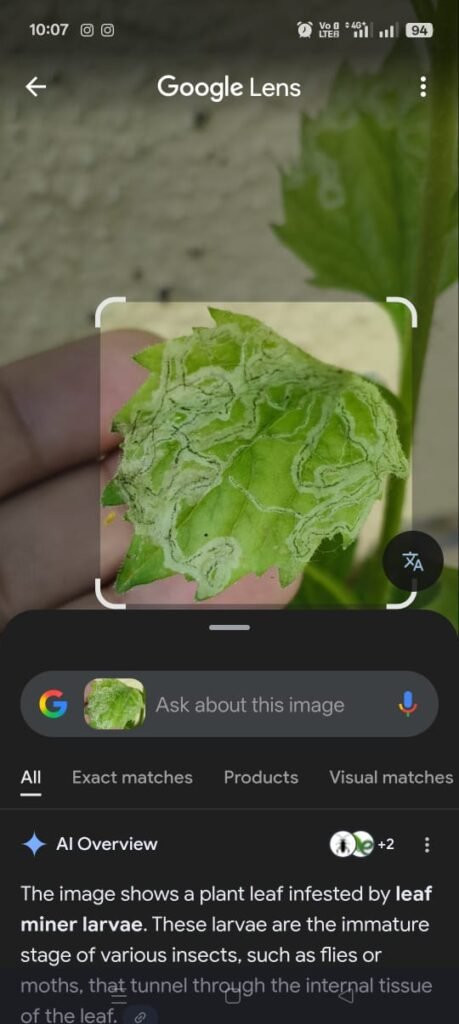

Identification
- The white squiggly trails on the leaf surface are made by leaf miner larvae.
- These larvae live inside the leaf tissue and feed between the upper and lower surfaces.
- Common leaf miners on asters belong to families such as Agromyzidae (leaf miner flies).
Damage
- The mines reduce the leaf’s ability to photosynthesize.
- Heavy infestations can cause yellowing, premature leaf drop, and stunted growth.
Control Measure
1.Neem oil spray (3–5 ml per liter of water) every 5–7 days.
2.Sticky traps (yellow or blue) can catch adult flies that lay eggs.
29 Nov 2025
In the first Aster EC range experiment, the results were not very satisfactory. However, flowering was observed at an EC level of 1.8 mS/cm.
On 29th November, during a discussion with Dixit Sir, it was decided to replant Aster with a lower EC range.
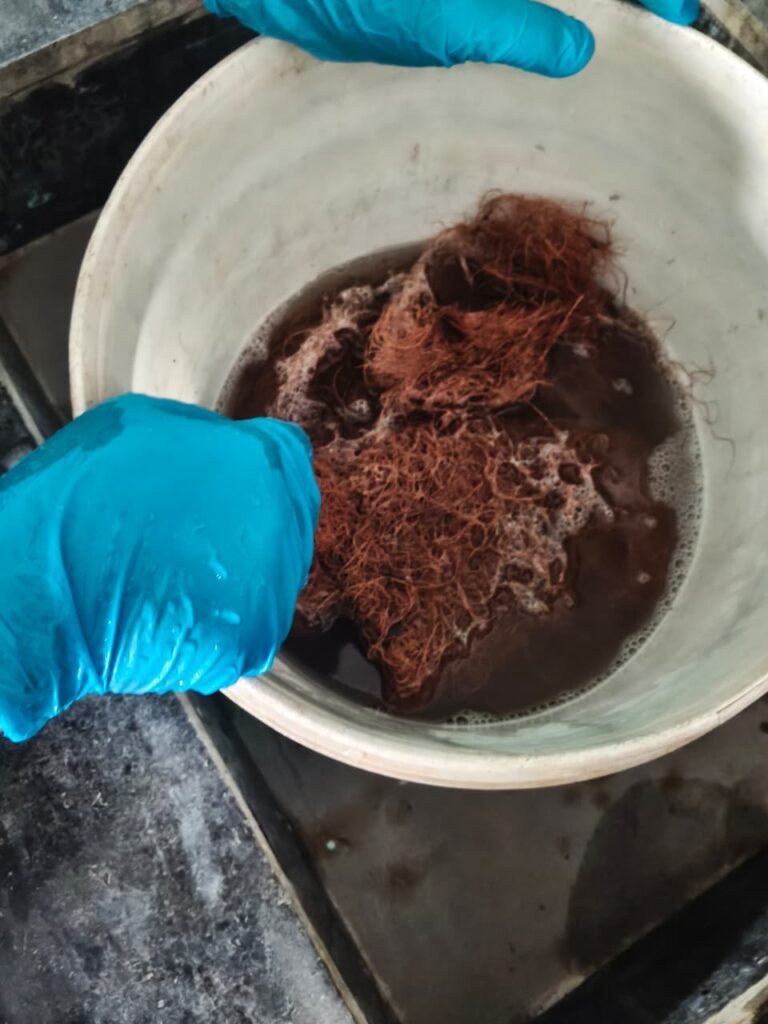
To minimize issues such as root rot and leaf miner attack observed in the first experiment, coco coir will be used as the growing medium. Additionally, 0.1% sodium hypochlorite solution will be used for disinfection, sterilization, and pathogen removal before replanting.
30 Nov – 1 Dec 2025
Sodium Hypochlorite (0.1%) for Coco-Coir Sterilization (NaOCl)
Formula:
Stock = 4%
Desired = 0.1%
Volume = 1 L (1000 ml)
0.1/ 4 X 1000 = 0.025 X 1000 = 25 ml
For 1 L water: add 25 ml NaOCl
Sodium Hypochlorite, It is used for disinfection, sterilization, and removing pathogens. use Sodium Hypochlorite on Coco Coir sometimes contains Fungal spores, Algae, Bacteria Larvae eggs.
Aster Plant – Water Holding Capacity .The Aster plant holds about 70–80% water inside its tissues
1. Aster is a soft, herbaceous, flowering plant.
2. Such plants naturally contain 70–85% water in their leaves and stems.
3. This percentage represents how much water the plant tissues can hold.
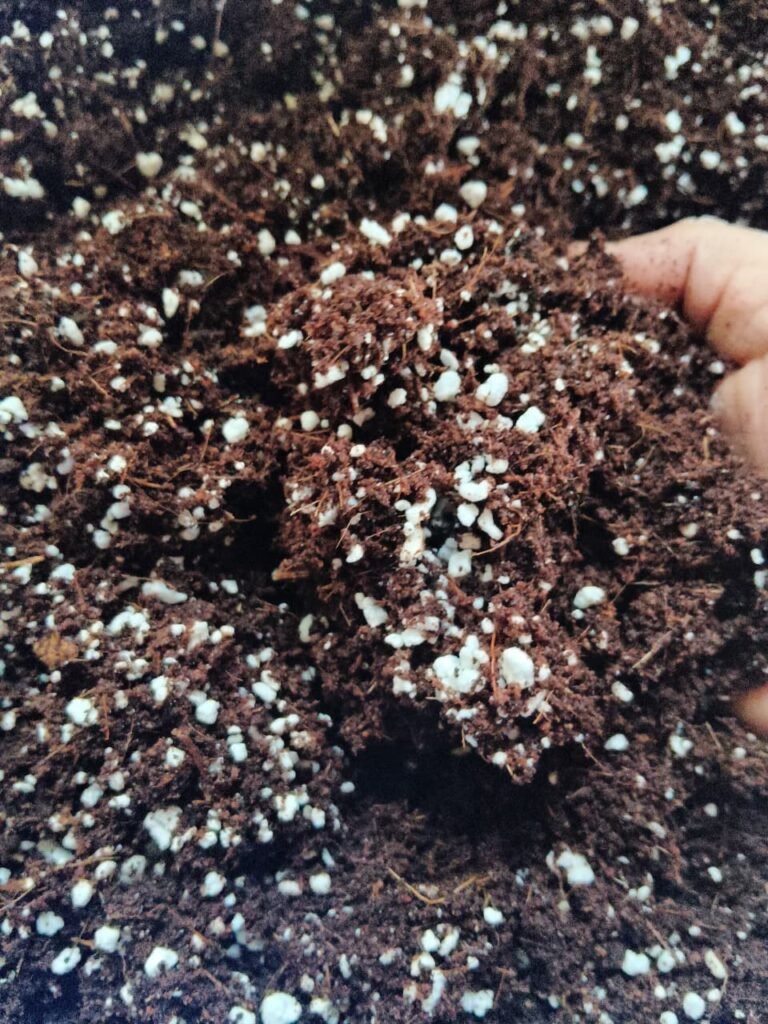
Recommended Media Mix for Aster (Cocopeat : Perlite : Vermiculite = 60 : 30 : 10)
| Why 60% Cocopeat? Cocopeat has: 1. High water-holding capacity 2. Natural aeration 3. Good root support 4. Aster needs consistent moisture (not waterlogging), and 60% cocopeat gives: Enough water for uniform growth Prevents sudden dryness Stable temperature for roots If cocopeat is more than 70%, the medium becomes too wet → risk of root rot. At 60%, moisture remains ideal. | Why 30% Perlite? Perlite provides: 1. Excellent aeration 2. Fast drainage 3. Prevents compaction 4. Aster roots are very sensitive to low oxygen. 30% perlite keeps the medium light, oxygen-rich, and fast-draining | Why 10% Vermiculite? Vermiculite helps by: 1. Holding some moisture 2. Storing nutrients (cation exchange capacity) 3. Releasing nutrients slowly 4. Supporting root tips 5. Aster during flowering requires stable nutrient availability. 6. 10% vermiculite: Improves nutrient distribution Prevents sudden drying of surface Supports early root development More than 15% vermiculite can hold too much water → over-moisture risk. |
60 % Cocopeat → Moisture + root comfort
30 % Perlite → Oxygen + drainage
10 % Vermiculite → Controlled nutrient & moisture holding
Together, this mix provides:
✔ Balanced water retention (matches Aster’s 70–85% tissue water)
✔ High aeration supporting hydroponic
✔ Low risk of fungal/ root rot
3 Dec 2025 – 7 Dec 2025
- In the first Aster EC range experiment, the results were not very satisfactory. However, flowering was observed at an EC level of 1.8 mS/cm.
- On 29th November, during a discussion with Dixit Sir, it was decided to replant Aster with a lower EC range.
- To minimize issues such as root rot and leaf miner attack observed in the first experiment, coco coir will be used as the growing medium. Additionally, 0.1% sodium hypochlorite solution will be used for disinfection, sterilization, and pathogen removal before replanting .
- Replantation of Aster at two EC range 1.0 – 1.5 m S/ cm and EC range 1.5 – 1.8 m S/cm.
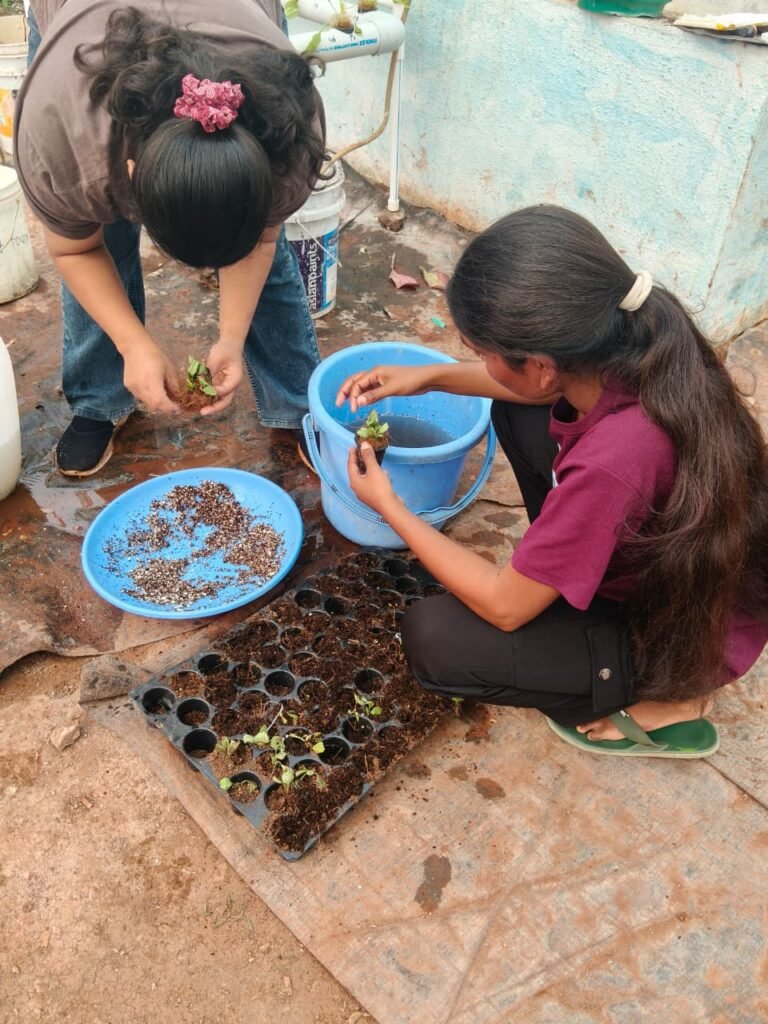
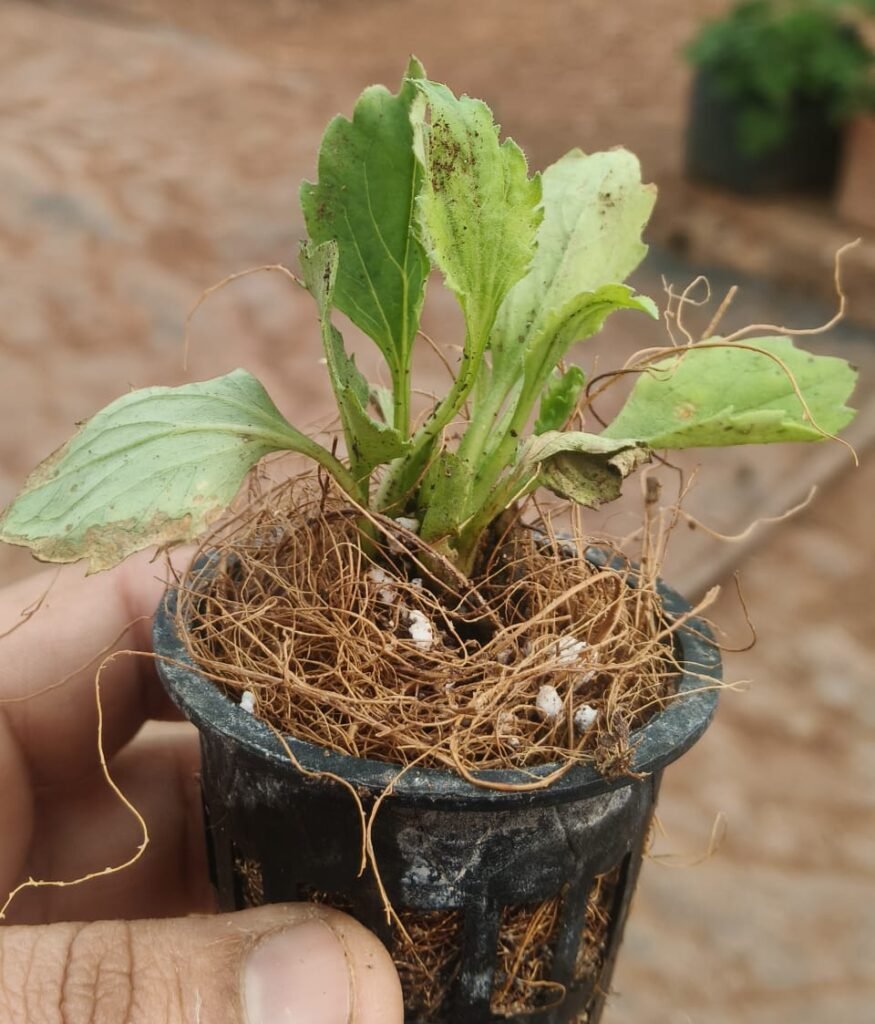
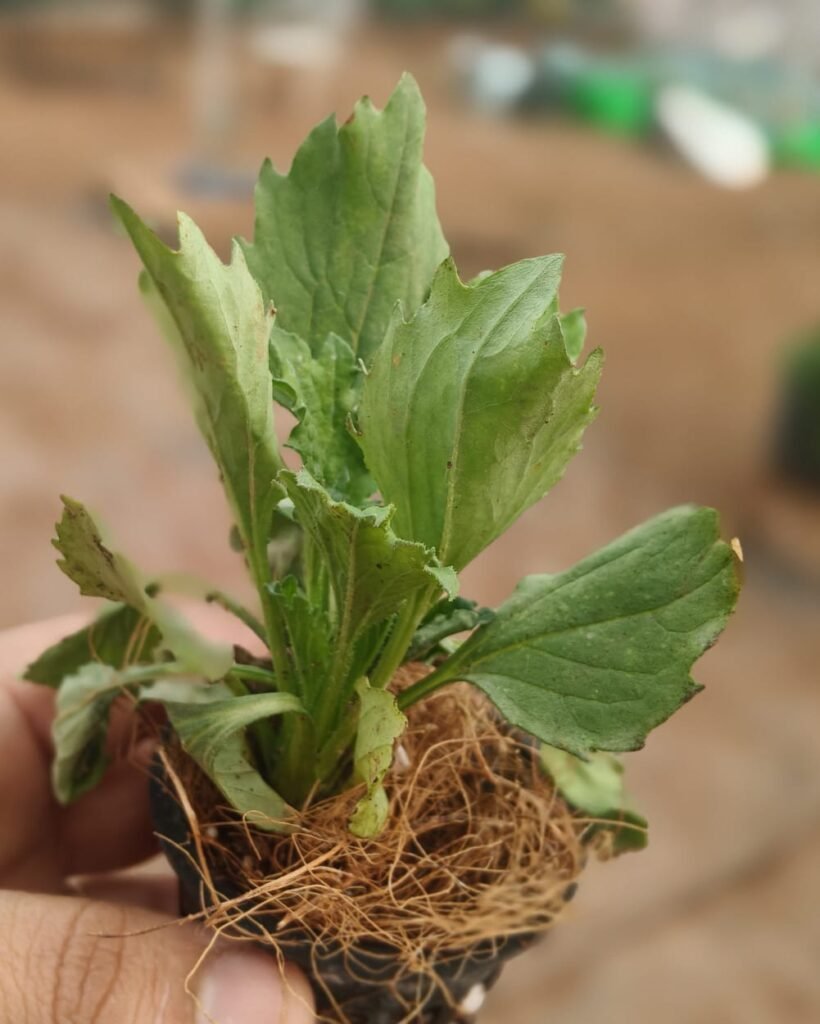





Link of Aster EC Maintain sheet :
20/12/2025
Observation Note:
Aster plants have been successfully planted, and regular dosing and observation work are ongoing. Ranjeet Sir suspected a possibility of root rot in the plants. To verify this, I carefully removed some plants from the net pots for inspection. Upon observation, I did not find any significant symptoms of root rot — approximately 99% of the plants appeared healthy with normal root structure and color.
| Parameter | Healthy Roots | Root Rot |
|---|---|---|
| Color | Roots are white to light cream in colour | Roots turn dark brown or black |
| Texture | Roots are firm and fibrous | Roots become soft, slimy, and fragile |
| Smell | No foul smell is observed | Foul or rotten smell is present |
| Strength | Roots do not break easily | Roots break easily |
| New Growth | New root growth is visible | No new root formation |
| Plant Appearance | Plant appears healthy and vigorous | Plant appears weak, wilted, or stunted |
| Water Absorption | Water absorption is normal | Water uptake is poor |
| Indication | Indicates good aeration and drainage | Indicates poor drainage and excess moisture |
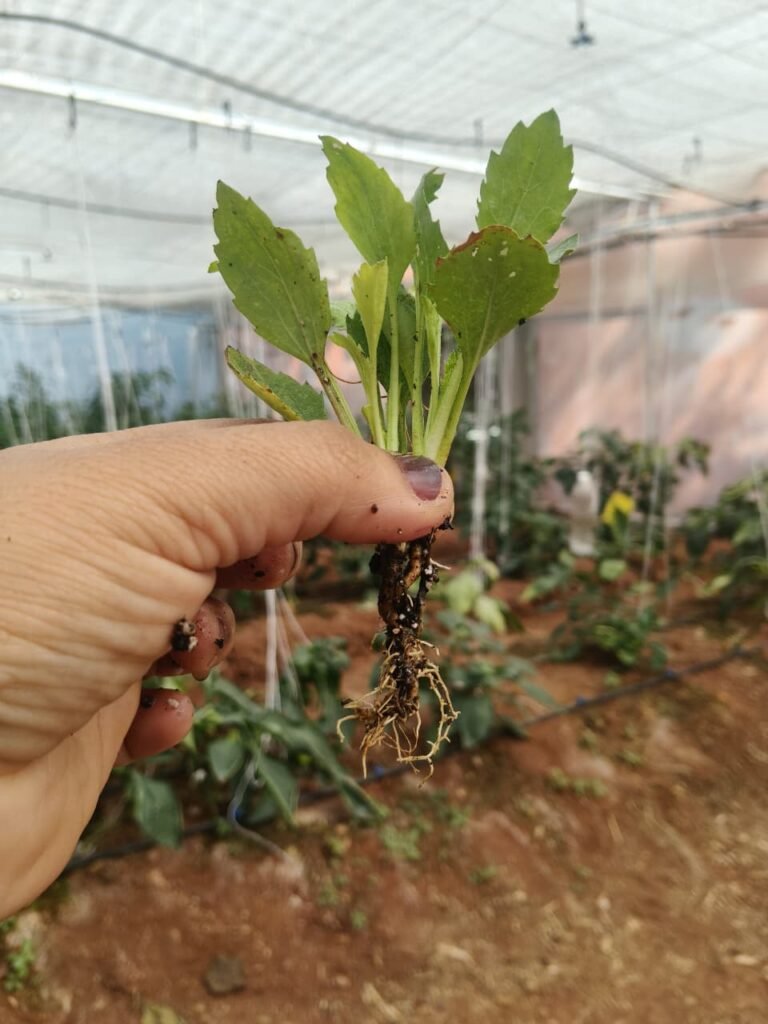

Root Rot Symptoms (Reference)
- Roots turn black or dark brown, soft, or slimy
- Foul odor (rotten smell) from roots
- Roots break easily when touched
- Plants appear suddenly wilted or stunted
Observations from Images
Positive Signs
- Roots appear white to light brown and fibrous
- Roots are firm and turgid, not soft or mushy
- No sliminess or black discoloration observed
- Indicates no active root rot infection
Conclusion:
At the current growth stage, there are no visible signs of root rot infection in the Aster plants. The roots appear healthy and well-developed.
Aster EC Maintenance Sheet :
6 Dec 2026-7 Dec 2026
Aster – Hydroponic NFT System (Winter Vegetative Growth Note)
Initially, the Aster crop showed good vegetative growth in a hydroponic NFT system inside the polyhouse. However, during the winter season,due to low temperature, reduced sunlight, and high humidity inside the polyhouse, further plant growth was adversely affected. Low light intensity and cold . solution reduced root activity, which disturbed vegetative growth.
Considering that open conditions are more suitable for Aster during winter, the hydroponic setup was shifted outside the polyhouse. Under open conditions, with 6–8 hours of direct sunlight, an improvement in vegetative growth is expected.
At present, the crop is still in the vegetative stage, and flowering has not yet occurred. In the next stage, flower induction is planned by controlling nitrogen levels, increasing phosphorus and potassium, and maintaining an appropriate pH (5.8–6.5) and EC (1.5–1.8).
Reasons for Reduced Growth of Aster in Polyhouse During Winter.
During the winter season, the growth of Aster plants in the polyhouse was adversely affected due to several environmental factors. Night temperatures inside the polyhouse often dropped to 10–15°C or even lower, whereas Aster requires an ideal temperature range of 18–25°C during the day and 15–18°C at night.
Low temperatures reduced root metabolic activity, which resulted in poor nutrient absorption and slowed plant growth.In addition, light intensity during winter was low due to shorter day length and frequent fog. The polyhouse covering further reduced light penetration, leading to decreased photosynthesis and sluggish plant growth.High humidity combined with low temperature also affected plant performance. Under such conditions, root respiration was reduced and nutrient uptake became irregular, further disturbing vegetative growth.
The hydroponic NFT system is highly sensitive to temperature fluctuations. During winter, the nutrient solution became too cold, causing root shock. When the temperature of the nutrient solution dropped below 15°C, root activity was significantly reduced, leading to growth stagnation.
Justification for Shifting the Setup Outside the Polyhouse
Shifting the hydroponic NFT setup outside the polyhouse was a correct and practical decision. In open conditions, plants received higher and more uniform direct sunlight, which improved photosynthesis. Daytime temperatures were more balanced compared to the polyhouse during winter, and better air circulation helped reduce humidity stress. As a result, environmental conditions outside were more favorable for maintaining healthy vegetative growth of Aster during the winter season.
14 Jan 2026
Observation of Root and Plant Growth After Shifting to Open Conditions.
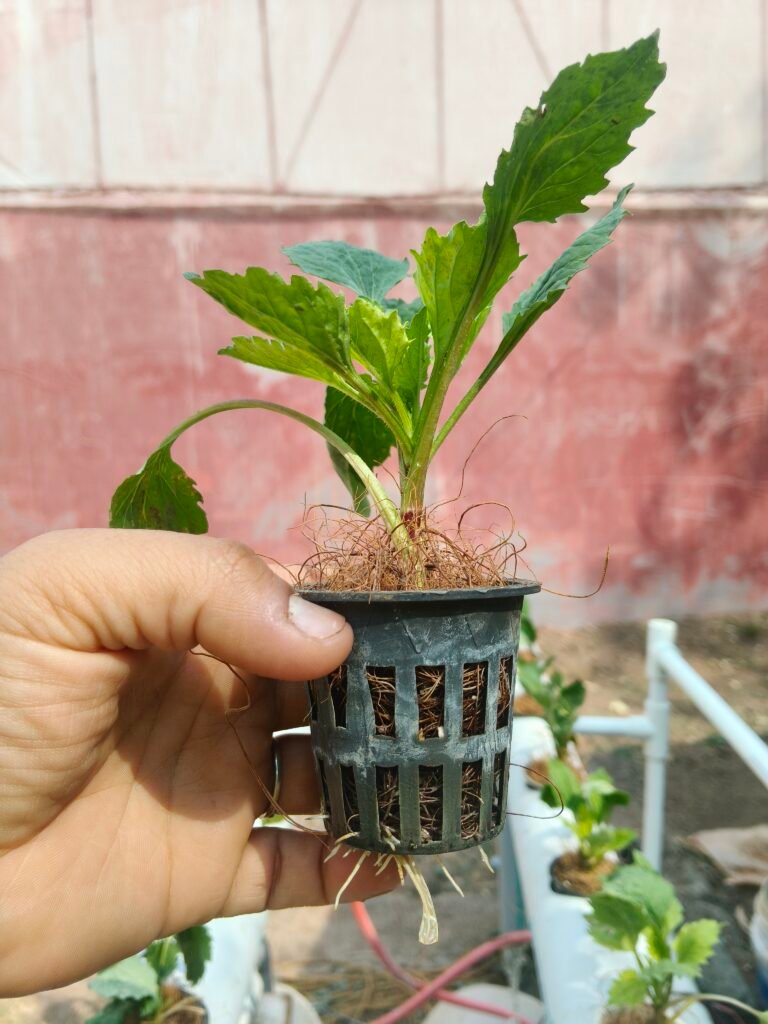
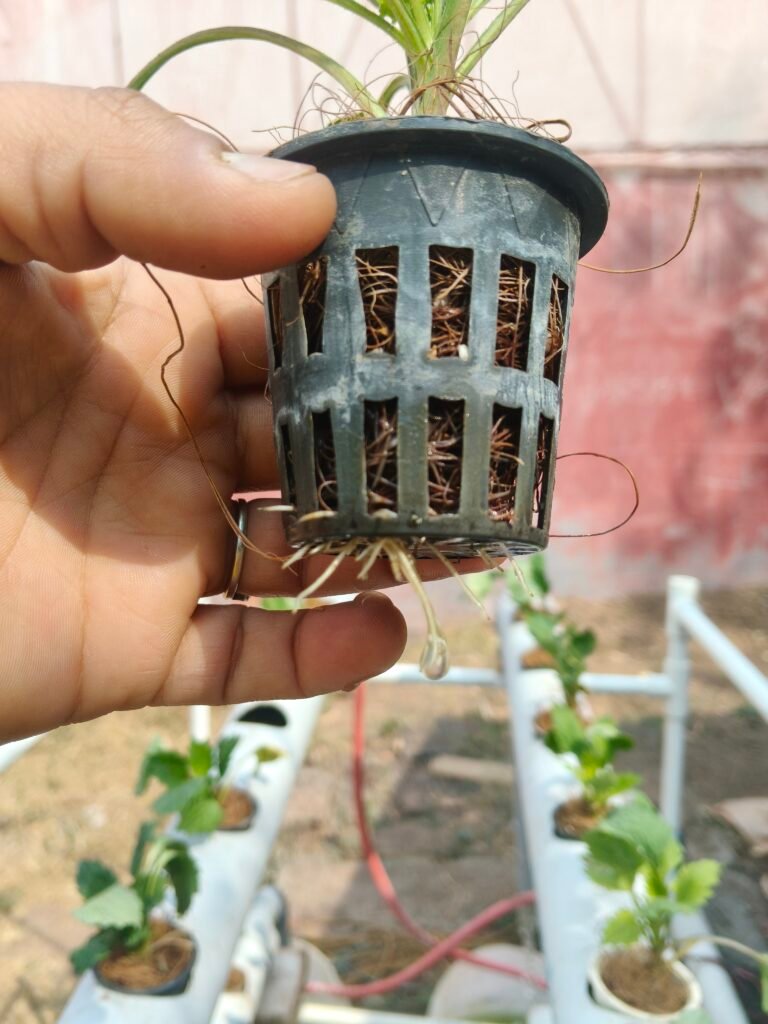
The images clearly show healthy and active root development in the Aster plants after shifting the hydroponic NFT setup outside the polyhouse.
- Roots are white to cream colored, which is a strong indicator of healthy, actively growing roots.
- New root tips are visible emerging from the net pot, indicating resumed root meristem activity.
- Presence of fine feeder roots improved nutrient uptake and oxygen availability.


28 Jan 2026
On 28 January, there was a discussion with Dixit Sir regarding the Aster hydroponics trial. In this season, the Aster plants in the hydroponics system showed issues such as root rot, and the plant growth was not as good as expected. Therefore, the Aster hydroponics trial was paused.





