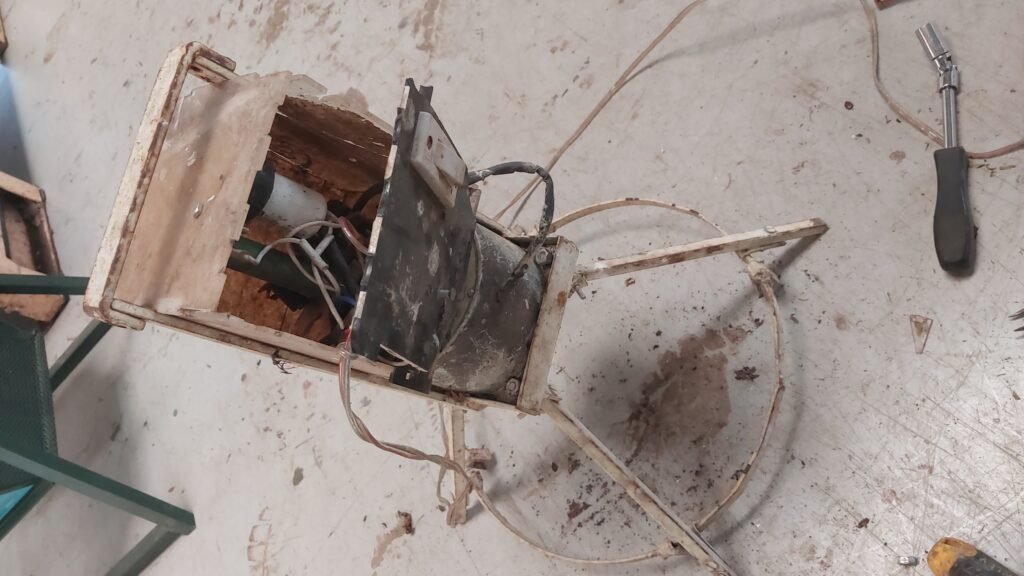

The figure shows the roaster machine, which is used to roast peanuts, semolina, etc.
Date: 18/02/2023
I dismantled all the parts of roaster, separated stirrer, frame, control unit and motor from assembly. Frame is the main part of this assembly which supports to the system, Stirrer blade is used to mix the material. stirrer shaft is connected with motor shaft which rotates and mixes the material present in the utensil. motor’s control is operated by the control unit. control unit changes the direction of motor from clockwise to anti clockwise or wise versa after every 10 minutes.
I checked the total weight of system and weight of the motor. Total weight of system is around 5.366 Kg and only motor’s weight is 2.5 Kg. Frame and other parts weight is nearly 2.8 KG.
After dismantling the motor i saw the the rotor of motor is stuck or jammed due to the rusting of parts. I shown this dismantled motor to Prasad sir,he said it will not work do survey of motors.
date:21/02/2023
As per our requirement i did the survey of high torque and low rpm motor on internet. The weight of previous motor is more , so also tried to find less weight motor. This is the word file of motor survey in that i did both AC and DC motors survey.
Date:22/02/2023
Previous roaster blogs and drawbacks
I also read the blogs of previous roaster in that design, they did so many trials in frame design, in motor selection, in stirrer design and contact between kadai and stirrer.
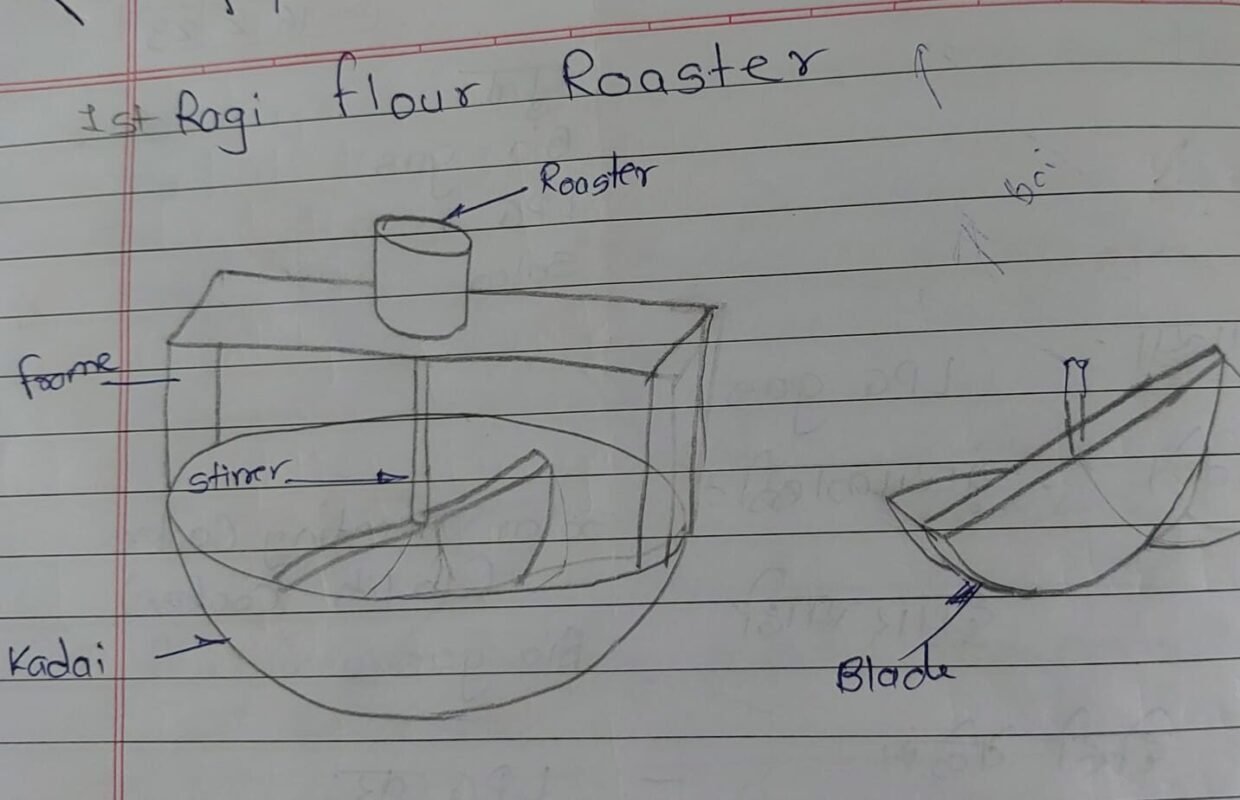

For making these laddoo’s they need to roast ragi flour and continuous movement of flour is needed to avoid burning of ragi, to solve this problem Siddhesh Sakore made one system as shown in above figure. After that Mr. Amol Khamkar has continued this project and developed the final unit. Blog link for final model is:-
1. Initial Design, Development and Trials
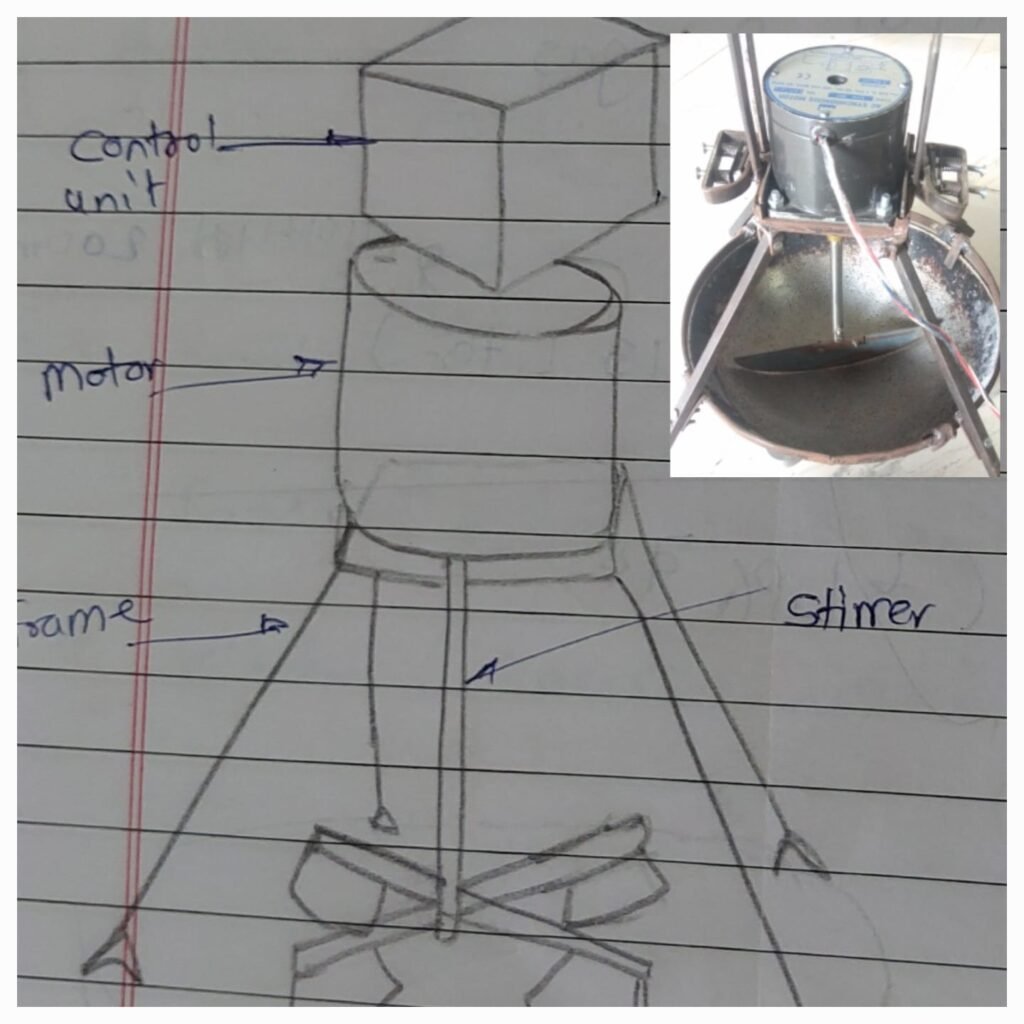
Amol made this machine for Dixit sir, Dixit sir used this machine for one and half year. Dixit sir want some additional modification in that Roaster, so he assigned me this task.
Requirement :
1.Stop material from escaping the kadhai, which occurs due to direction change in stirrer.
2.Reduce weight of product or reduce human work.
3. Stop over heating of motor which occurs due to its position or change the position.
Date:28/02/2023
for solving above problems we did meeting with dixit sir, Prasad sir. In discussion we talked various things like weight reduction of system, Reducing heating of motor. In above case position of motor is directly above of heating source which cause additional heating of motor in his self heating. Sir suggested me to shift the position of motor at 45 degree so the heating of motor is reduces as shown in figure.
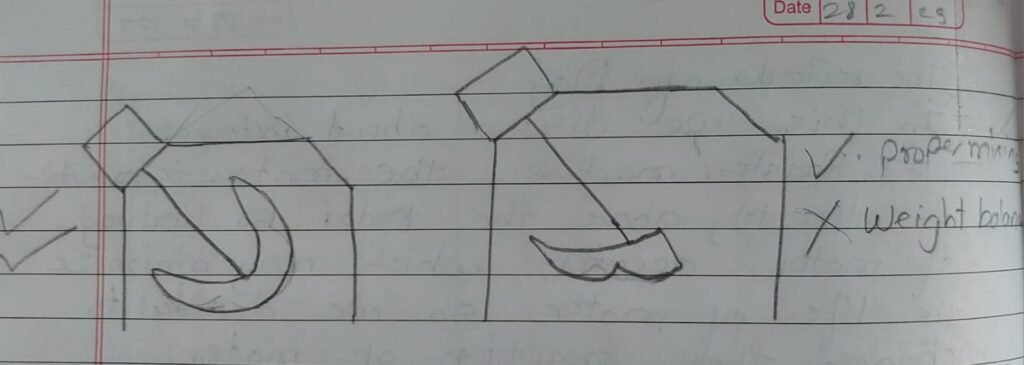
In above figure the motor exposure to hot air is reduced but balancing of system is difficult. All load of motor is shifted towards left which make system unbalance. Another problem in this structure is the movement of stirrer. Half portion of blade is in kadai and half portion is in air, due to this utilization of blade movement is not proper and while mixing process material get escaped out.
Date:01/03/2023
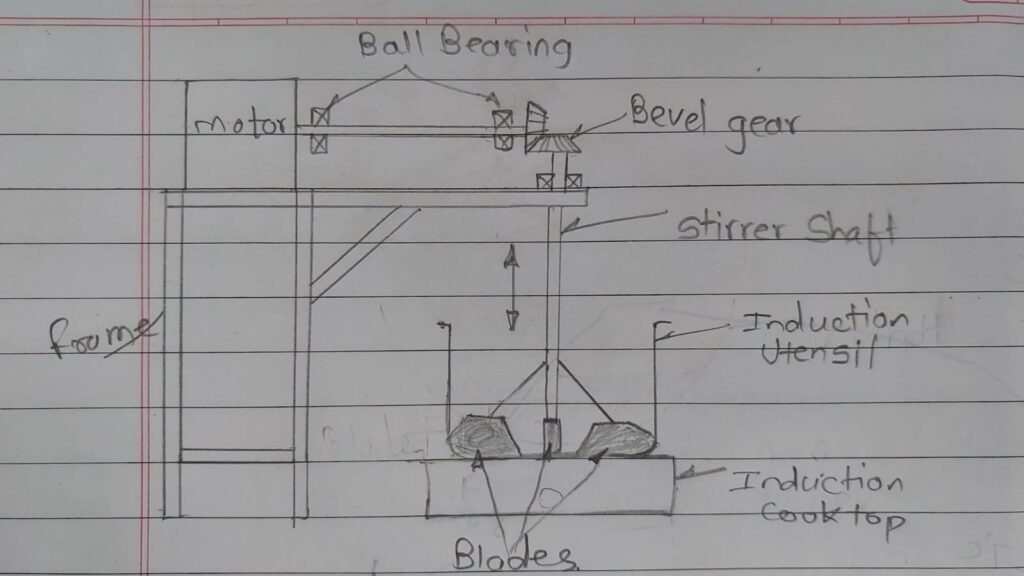
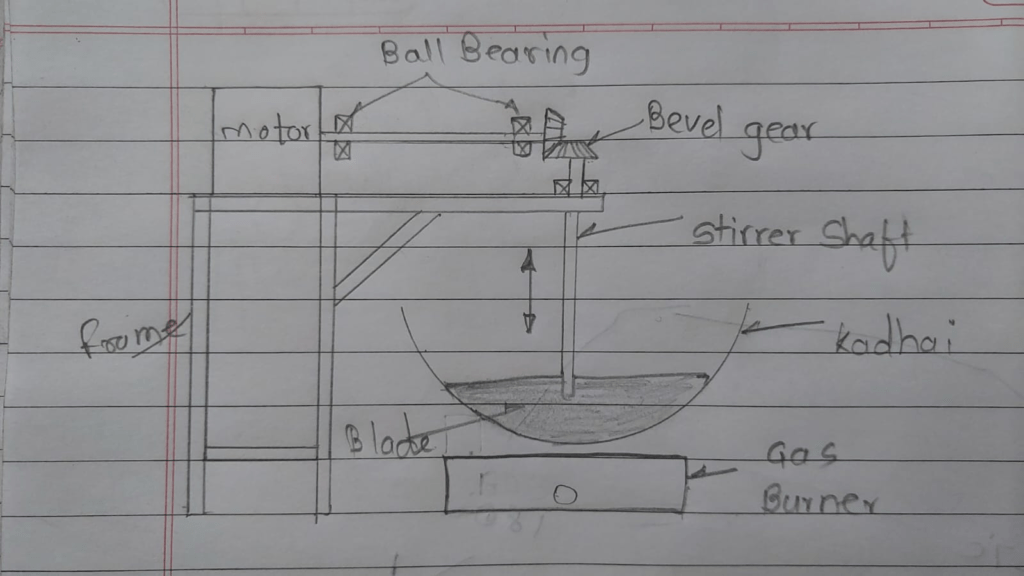
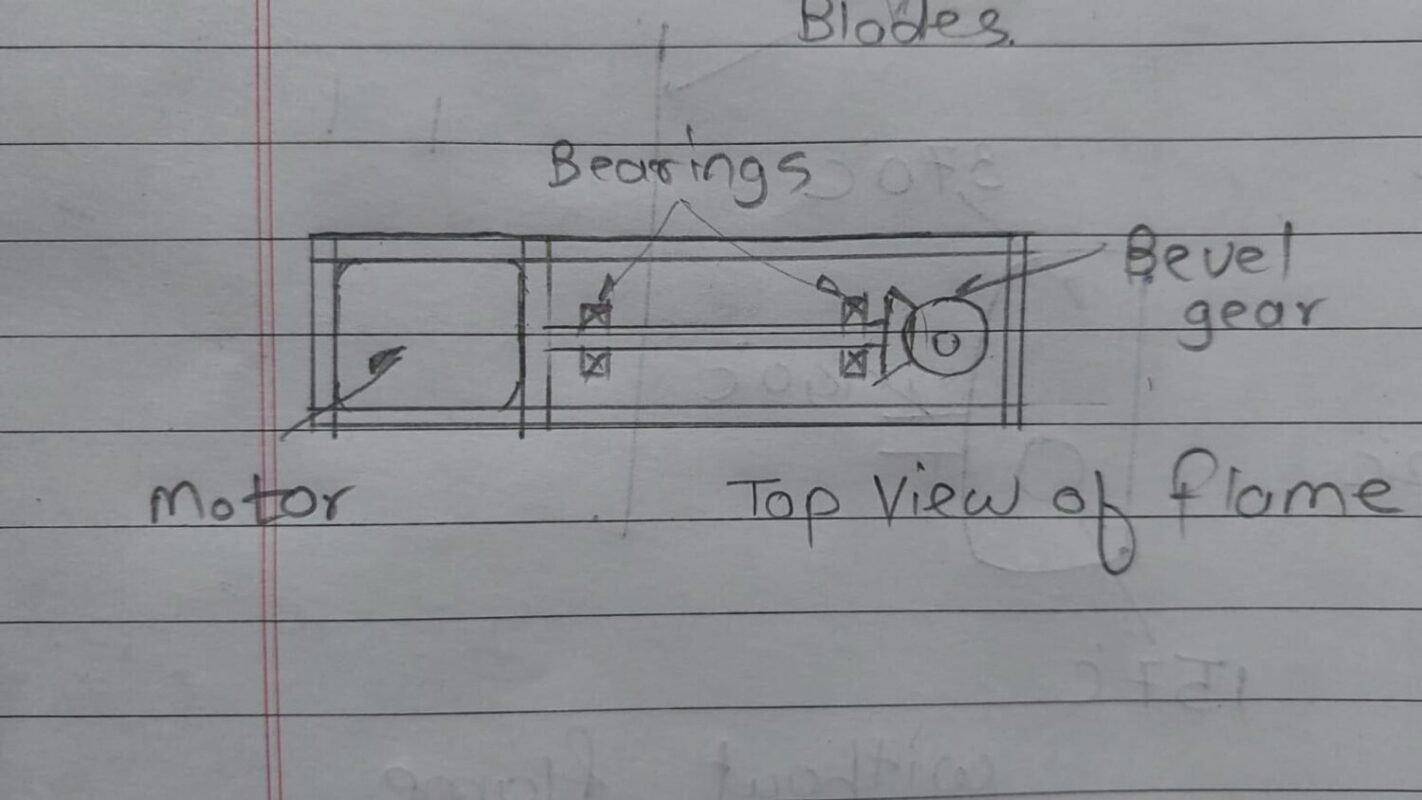
This is a new design made by me.In this I focused on heat reduction of motor for that, I shifted the motor at right same as previous sketck additional to that i also rotated the the position of shaft. Now the motor shaft is parallel to flour.we want shaft position vertical i.e. perpendicular to flour,in between horizontal and vertical shaft bevel gear is provided which transmit the power in 90 degree. The structure of frame is mounted on floor, so the total load of frame is transmitted to floor and minimizes the load on kadhai or gas burner.
Motor selection
Motor Torque calculations
Torque is a measure of a force that can cause an object to rotate in our case object is roasting material in kadai.
T=F*r
Where, T = Torque(N-m)
F= Force(N)
R= radius from Centre axis to force point(m)=0.12m.
Force required for the movement of material is calculated as below,
There are two main resistance to force in stirring operation which we have to overcome,
1.Viscous Force (Fv)
Viscosity, resistance of a fluid to a change in shape, or movement of neighboring portions relative to one another.
Fv= µAu/y
Where,
Fv=Viscous Force (N)
A= Cross sectional area of blade=0.01m2
u/y= Rate of shear deformation
u= Velocity, rpm=60=6.3 rad/s, r=0.12m (radius of blade)
u=0.756m/s
y= distance from Base surface=0.06m
µ=Viscosity (Porridge)=0.45 Pa.s
Fv=0.45*0.01*0.756/0.06
Fv=0.0567 N
2.Friction Force (Ff)
force that resists the sliding or rolling of one solid object over another.
Ff= µmg
In our case friction is occur in between blade material(Teflon) and kadai material (Steel),
Where,
Ff= Friction force(N)
µ=Coefficient of Friction=Teflon and steel=0.2
m= Mass of blade=0.4Kg
g= acceleration due to gravity=9.8 m/s2
Ff=0.2*0.4*9.8
Ff =0.784N
Total Force (F)
F= Fv + Ff
=0.0567 + 0.784
F=0.84N
Let us take safety factor 1.8
F=0.84*1.8
F=1.5 N
Therefore,
T=F*r
=1.5*0.12
T=0.18 N-m
T=1.8 Kg-cm
1.8 Kg-cm torque motor is required.


![Drying Pudina [Mint]](https://vadic.vigyanashram.blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/wp_20170129_16_50_45_pro-440x264.jpg)

