I.Introduction :
The word hydroponics has been derived from the Greek word “water working”. Hydro means “water” and ponic means “working” and it is a technology of sprouting grains or growing plants without soil, but only with water or nutrient rich solution. However, hydroponics fodder can be well produced with the use of fresh water only.
It is one of the most important agricultural techniques currently in use for green forage production in many countries especially in arid and semi-arid regions environmentally control houses .A shade net house is a framed or inflated structure covered with a transparent or translucent material in which the crops could be grown under the conditions at least partially controlled environment and which is large enough to permit a person to work within it to carry out cultural operations.
Hydroponic growing green fodder has high feed quality, rich with proteins, fibres, vitamins, and minerals effects on animals. The growth of the fodder crop mainly depends on moisture, temperature, RH and irrigation. Hydroponic Green fodder is the natural diet for livestock. Hydroponic green fodder consists of grass with grains, roots, stems and leaves which are highly nutritious and provide sustainable fodder production and conserve water take 8 days to develop seed to green fodder.
It’s production to meet current demand has become a greatest challenge among livestock farmers, Due to temperature, humidity and contamination on the seed and fodder are restrict the optimum growth of fodder. Amount of yield and quality of fodder is influenced by grain quality, grain variety and treatments and growing environmental.
Green fodder production crisis serious problems which are contamination of seeds that effect germination, and plant growth. This contamination further takes to fungus and mould infection which are not healthy for livestock animals. Temperature, relative humidity is also parameter to increase and decrease the fungus and mould infection.
Hydroponic farming means growing of plants without soil by using nutrients water at desired temperature and humidity. Through hydroponics it is easy and quick to produce nutritive green fodder.
Advantages of Hydroponic Technology :
- It requires less area
- Saving of water also water can be recycled by nutrient film technique.
- It can be grown throughout the year.
- Less harvesting period.
- Saves labor , energy and time.
II. Review of Literature
In this chapter the reviews are explain about hydroponic fodder production, Dry mass determination and fungus control treatments.
Rachel Jemimah, (et al), studied on rural friendly low-cost hydroponic device to produce 15 – 30 kg of fodder daily. In which yellow maize, horse gram, jowar were used for hydroponic fodder. In which they studied nutritional composition of different stages of growth, growth rate and biomass of hydroponic fodder, for fungal attack they used organic fungicide treatments.
Tamilee Nennich, (et al), gives methods of dry matter determination of hydroponic fodder which are provided to animals. The DM content of feed provides a measure of the amount of particular feed that is required to supply a set amount of nutrients. Force air oven. Microwave, vortex dryer was used to determination of dry mass.
Ghazi n. (et al), They studied on evaluate forage crops for green fodder production and water use efficiency. The experiment conducted under controlled temp (24°c). The results show that green forage can be produced in 8 days of period in hydroponic unit. They concluded that hydroponic fodder production can be done with less water consumption. P.K.Naik (et al), Studied on low cost hydroponic device. The hydroponic fodder production under different types of greenhouses. They concluded that Hydroponic fodder can be grown to low cost greenhouses with locally available or home-grown grains. Production of hydroponic fodder in low cost greenhouse is an effective solution for fodder scarcity and is very promising technology for sustainable livestock production in different regions in India
In Hydroponic fodder production there is so many problems which are methods of production of fodder production, poor grains quality, germination rate of grains, uncontrolled environment, poor drainage of water from tray which conditions are helping to increase the fungus and mould infection.
III.Problem Definition :
The contamination was starts from the seeds. When seeds were soak for 24 hours in water there was problem of fermentation and because of that the fermented odour take place to the seeds which are resulted the fungus infection. After soaking the seeds, the seeds were placed into gunny bags at dark rooms for sprouting this resulted increase in fermentation odour. Sprouted seeds when placed into the hydroponic or office tray water sprayed to the seeds were for 2 minutes which are 1liter/min and because of that the maize seeds had higher amount of water which are not suitable for fodder and the water are not well drained from the trays this causes increase in fungus infection.
Uncontrolled environment was also helping to increasing the fungus infection if there is temperature is greater than 35 °c and humidity higher than 70 to 80 % the fungus and mould infection were increases. Also, the proper fumigation is important.
IV.Problem Solution :
Seed selection and germination rate of seeds are important parameters because contamination is started from the seeds and if the seeds are not get germinated than this unterminated seeds are influence the other sprouted seeds and this tends to increase contamination, for this seed selection is very important. After that the soaking time is essential so fermentation of seeds get control.
To control fungus infection and to conserve water the water requirement of maize is find out by evaporation loss and water holding capacity so odour on fodder also decrease. Seed treatments is used for fungus control i.e Trichoderma and salt test.
Cleaning of seeds with potassium permanganate are used for disinfection. Also the replacement for gunny bags cotton bags are used for sprouting to maintain aeration on bags so the stickiness of seed are get decreased. Cleaning of trays and unit also important. Formahalyde are used to disinfected the unit.
Controlled environment are important solutions because the temperature , relative humidity and wind velocity, solar radiation effect the plant growth.
Objective
- To Remove fungus and mold infection from fodder .
V.Workdone
5.1.1Trial 1
In this experimentation set up the maize seeds were soaked into normal tap water which have 23 °c temperature.
5.1.1.1Materials Required:
| Sr. no | Material | Quantity |
| 1. | Maize grains | 100 gm |
| 2. | Weighing balance | 1 |
| 3. | vessel | 1 |
| 4. | sieve | 1 |
5.1.1.2Methodology:
1.Take 100 gm maize grains.

2. Add maize grains into the sieve and weight it with weighing balance.

3. Take hollow vessel and placed sieve into it and add water up to maize grains fully immerse.

4. Take weight of grains at one hour of interval up to constant readings were get.
Sample 1
Maize grain = hybrid seed
- Observations:
1.Weight of sieve = 50 gm
2.Weight of maize seeds = 100 gm
3.Weight of sieve + maize seeds = 150 gm
4.Water added = 1000 ml
Table1.1: Following table shows the time and weight of maize
| Time | Weight of maize grains (gm) |
| 0 | 100 |
| 00:30 | 112 |
| 00:60 | 114 |
| 00:90 | 118 |
| 1:00 | 120 |
| 1:30 | 122 |
| 1:60 | 122 |
| 2:00 | 126 |
| 3:00 | 128 |
| 4:30 | 130 |
| 5:00 | 130 |
| 8:30 | 132 |
| 9:30 | 134 |
| 10:30 | 136 |
| 11:00 | 136 |
| 11:30 | 138 |
| 11:30 | 138 |
| 12:00 | 138 |
Sample 2
Maize variety = African tall
1.Weight of maize = 100 gm
2.Weight of sieve = 94 gm
3. Water added = 600 ml
| Time | Weight of maize grains (gm) |
| 0 | 100 |
| 01:30 | 128 |
| 02:30 | 134 |
| 03:00 | 136 |
| 4:30 | 140 |
| 5:30 | 140 |
| 6:30 | 142 |
| 8:30 | 146 |
| 9:30 | 148 |
| 10:30 | 150 |
| 11:30 | 154 |
| 12:30 | 156 |
Sample 3
Maize variety: farm seed
1.Weight of maize= 100 gm
2. Added water = 1000 ml
| Time | Weight of maize (gm) |
| 00:00 | 100 |
| 1:00 | 128 |
| 2:00 | 132 |
| 3:00 | 140 |
| 4:00 | 142 |
| 6:00 | 146 |
| 8:00 | 152 |
| 9:00 | 154 |
| 10:00 | 156 |
| 11:00 | 160 |
| 12:00 | 160 |
5.2.1Trial 2
In this experiment the seeds were soaked on 45°c temperature water in maintain conditions to find out seed soaking time in warm water for this the thermocol box were use as insulation box.
5.2.2Materials required:
| Sr. no | Material | Quantity |
| 1. | Maize seeds | 100 gm |
| 2. | Sieve | 1 |
| 3. | Vessel | 1 |
| 4. | Insulation box | 1 |
| 5. | Thermometer | 1 |
5.2.3Methodology:
1.Take 100 gm of maize seeds.

2. Add maize seeds into the sieve and weight it with weighing balance.

3. Warm the water upto 45°c and added into the vessel where maize seeds and sieve were placed.

4. Vessel place into the insulated box.

5. For maintaining the temperature of water the insulation box (thermocol box) were used. 6.Take readings of one-hour interval till constant readings and also check the temperature of water and if the temperature of water gets decreased than wat was replace by warm water
Observations:
1.Weight of maize = 100 gm
2.Weight of sieve = 94 gm
3. Water added = 800 ml
Table 3. Showing weight of maize seed and temp of water.
| Time | Weigh of maize seeds | Temp of water (°c) |
| 00:00 | 100 | 45 |
| 1:00 | 124 | 45 |
| 2:30 | 140 | 45 |
| 4:30 | 148 | 45 |
| 7:00 | 156 | 45 |
Results and Discussion:
Trial 1
Table 4. Showing results of all varieties of seeds.
| sample | Hybrid seed | African seed | Farm seed |
| Initial weight of maize | 100 gm | 100 gm | 100 gm |
| Final weight of maize | 138 gm | 156 gm | 160 gm |
| Initial amount of Water added | 1000 ml | 600 ml | 1000 ml |
| Final amount of water added | 840 ml | 440 ml | 720 ml |
| Soaking time | 12 hrs. | 12 hrs. | 12 hrs. |
Trial 2
| Initial weight of maize | 100 gm |
| Final weight of maize | 160 gm |
| Initial amount of water | 1000 ml |
| Final amount of water | 890 ml |
| Soaking time | 8 hrs. |
| Water Temp. | 45 °c |
From above table soaking time is 12 hours for any variety of maize seed and when seed soaked in warm water 45°c in maintain conditions so the soaking time is 8 hours. The African tall and farm seeds have more weight than other variety.
Conclusion:
1.Soaking time in tap water with normal temperature (23°c) have 12 hours.
2.In 45 °c water temperature soaking time is 8 hours.
5.2Water holding capacity
Water holding capacity refers to maize seeds capacity to hold the water. In this experiment 4 varieties of maize seeds were taken to calculate water holding capacity.
5.2.1Methodology:
1.Soak seeds for 12 hours.
2.Take 100 gm of soaked seeds.

3. Placed into the oven at 110 °c till constant readings.

4. Water holding capacity were calculated by following formula:
WHC =initial weight- final weight/intial weight × 100
Observations:
In below table shows water holding capacity of maize details observation are in Appendixe I
Table 5.1: following table showing water holding capacity
| Variety | Initial weight | Final weight | WHC (%) |
| Hybrid | 100 | 58.34 | 41.66 |
| African tall | 50 | 30.34 | 39.32 |
| Farm seed | 50 | 32.03 | 35.94 |
Results:

The water holding capacity is higher in hybrid seed i.e. 44.66%.and lower in farm seed 35.94 %.
S:
From above experiment the water holding capacity of maize seeds is 35.94 to 44.66 %.
Seed treatments and its effect on seed germination
Observations:
To control fungus infection seed treatments are given to the seeds in which seeds were soaked in salt water which is 3 % of water amount and Trichoderma 3% for 12 hours after hat its placed into cotton bags for sprouting and calculate germination rate of each treatments and for control normal water is also used.
Observations:
| Control | Salt | Trichoderma | |
| Initial weight (gm) | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Final weight (gm) | 144 | 140 | 144 |
| Added water (ml) | 200 | 200 | 200 |
| Removed water (ml) | 130 | 170 | 150 |
| Germination rate | 86% | 46% | 81% |
To overcome this problem first is to find out the soaking time, water holding capacity and crop water requirements .
Results:
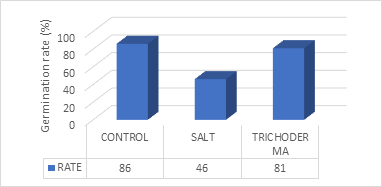
From above graph germination rate is higher in control (86 %) and then Trichoderma test (81%).
Conclusion: From this experiment conclude that salt quantity is affect the germination rate it becomes lower and Trichoderma not affect the germination of seeds and after sprouting there is no fungus were spotted
Water requirement of maize seeds
Water requirement of any crops is basic need of design of irrigation system. Water requirement is the quantity of water required for a crop for its growth. Water requirements include losses due to evapotranspiration.
Evapotranspiration is the sum of two terms transpiration which is water entering to the plants roots and used to growth of plant and evaporation is the loss of water surfaces or plant foliage. So from the evapotranspiration the water requirement can be determine.
- Measurement of evapotranspiration
- Lysimeter experiment
- Field experimental plots
- Soil moisture studies
- Evaporation pan method
All above methods are used to determine the evapotranspiration of crops. In lysimeter method the crop was grown in large tanks and evapotranspiration were determined by weighing of tanks at time interval and observing difference of weight.
Trial 1
Objective: To find out evaporation loss of maize.
In this trial I decided to find out the evaporation losses of the maize at one-hour interval so from these the water will be giving to maize.
- Procedure
- Take soaked maize of 50 gm.
- Maize placed into the tray. (at hydroponic unit)
- Take readings after one hour of interval.
- Take temperature readings.
- Observations
| Time | Weight of maize |
| 11:00 | 50 |
| 11:30 | 42 |
| 12:30 | 40 |
| 1:30 | 38 |
| 2:30 | 36 |
| 3:30 | 36 |
| 5:00 | 34 |
| 6:00 | 32 |
Relative humidity observations
| Time | DBT | WBT | RH (%) |
| 11:00 | 26 | 20 | 58 |
| 11:30 | 35 | 25 | 44 |
| 12:30 | 35 | 22 | 32 |
| 1:30 | 36 | 28 | 54 |
| 2:30 | 34 | 27 | 58 |
| 3:30 | 32 | 25 | 56 |
| 5:00 | 27 | 23 | 71 |
- Conclusion:
In these maize losses its weight by 2 gm. The relative humidity, temperature and wind speed are affecting the evaporation rate. If the 2 gm of water give to the maize so the weight of maize can be maintained and don’t get dry but it is not possible to give the 2 gm of water. Also, the growth of plants the evaporation losses and water requirement also get change. When temperature and wind speed increase the evaporation rate also increases.
Trial 2
This trial was design to find out water requirement of water. In which known amount of maize seeds were soaked and placed to the cotton bag for sprouting after that the sprouts were come and then its take into the growing tray and a fixed amount of water its give to the maize seeds from that water requirement was get known.
Objective : To grow maize fodder.
Methodology:
1.Take 150 gm of maize seeds and wash it from water to cleaning.
2. After cleaning soak in clean water for 12 hours.
3.When seeds get soaked take into cotton bag for approximately 48 hours in hydroponic unit.
4. Sprouting seeds were placed into tray.
5.After one hour of interval give water manually which is 100 ml.
6.Take weight of tray, root and shoot length, temperature and relative humidity readings were taken in daily basis.

Day 2 
Day 3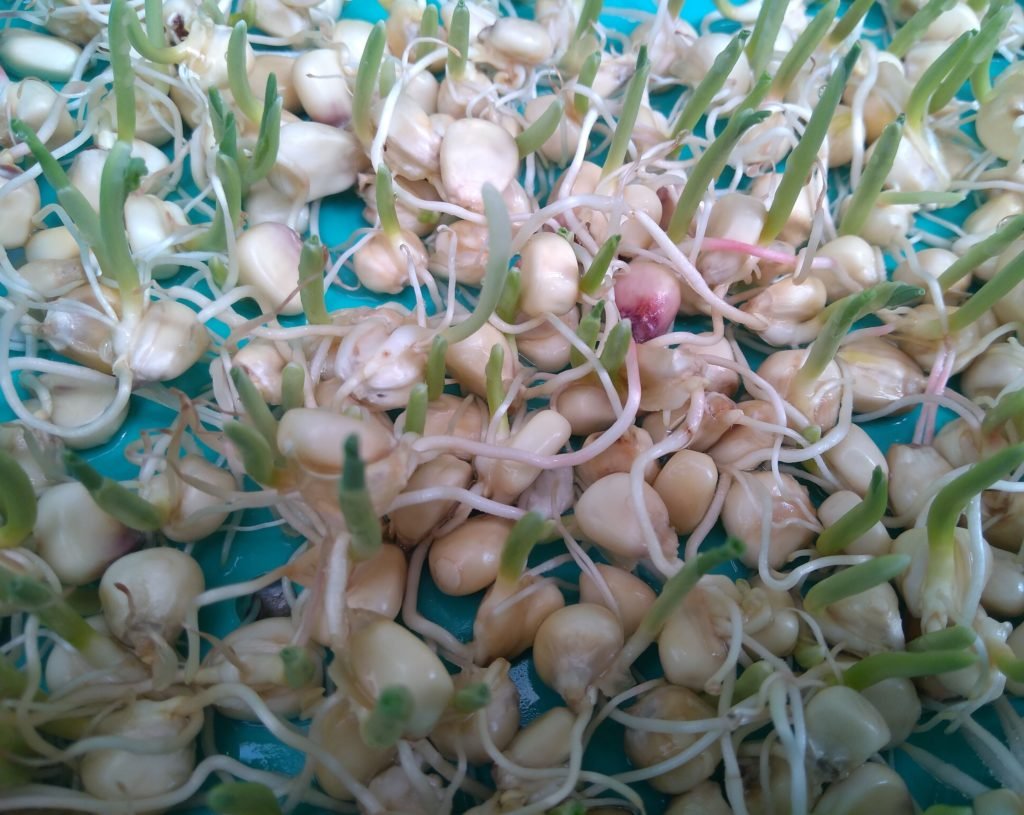 
Day 4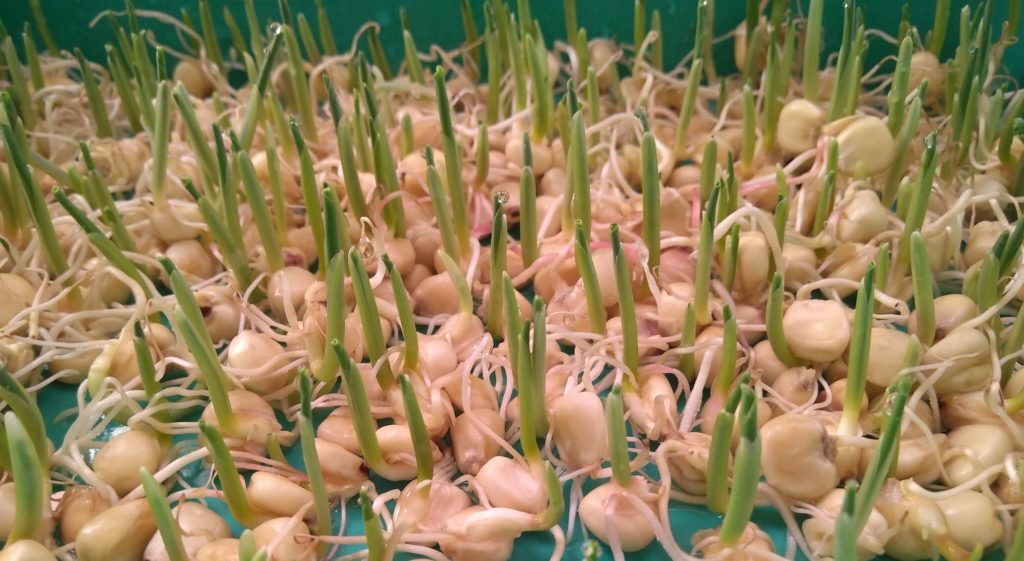 
Day 5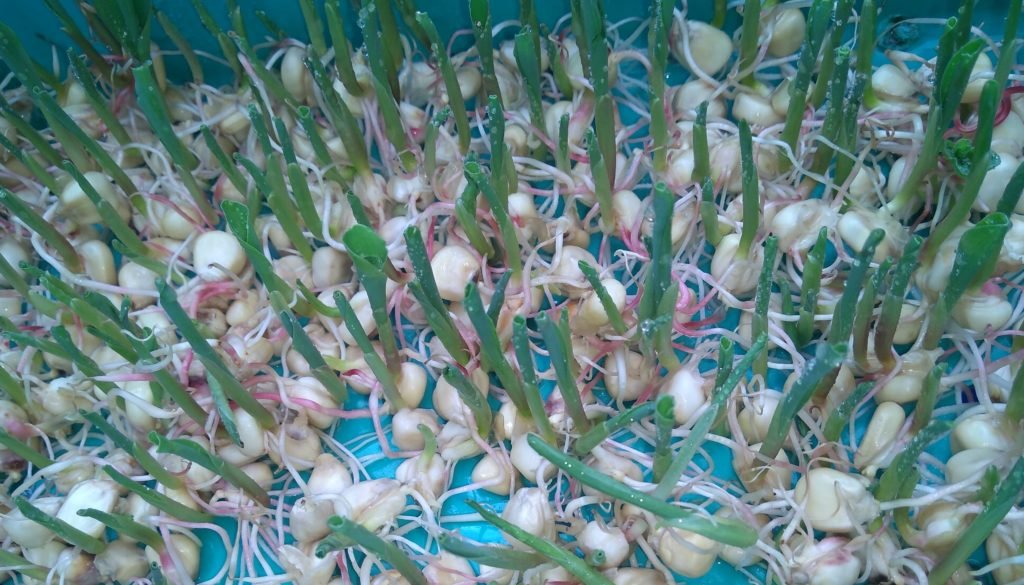 
Day 6 
Day 7
Observations :
1.Weight of maize seeds = 150 gm
2. Water added for soaking seeds = 200 ml
3.Soaked maize seeds =lenght of root and height of shoot
| Day | Weight (gm) | Root (cm) | Shoot (cm) | Temp. (°c) | Humidity (%) |
| 1 | 164 | 0.24 | 0 | 35 | 74.9 |
| 2 | 180 | 0.62 | 0.24 | 37 | |
| 3 | 188 | 1.64 | 0.53 | 32 | 55 |
| 4 | 190 | 3.74 | 1.91 | 31 | 50 |
| 5 | 208 | 0.316 | 2.44 | 29 | 44 |
| 6 | 220 | 3.68 | 4.12 | 37 | 50 |
| 7 | 234 | 7.3 | 6.83 | 37 | 28 |
Following table showing a root and shoot lengh per day
day 2
| 0.5 |
| 1 |
| 0.3 |
| 0.7 |
| 0.7 |
| 0.5 |
| 0.3 |
| 0.6 |
| 0.9 |
| 0.6 |
Day 3
| Length of roots | Height of shoot |
| 3 | 1 |
| 1.3 | 0.5 |
| 2.5 | 0.6 |
| 1.6 | 0.4 |
| 2.1 | 0.6 |
| 1.7 | 0.4 |
| 2.3 | 0.3 |
| 0.4 | 0.5 |
| 1.5 | 0.5 |
| 1.6 | 0.5 |
Day 4
| Length of roots | Height of shoot |
| 2 | 2.5 |
| 3.5 | 1.6 |
| 2.2 | 0.7 |
| 4 | 3.5 |
| 2.9 | 1.8 |
| 1.9 | 1.6 |
| 2.6 | 1.5 |
| 2.2 | 1.6 |
| 3.9 | 2.1 |
| 10.6 | 0.3 |
Day 5
| Length of roots | Height of shoot |
| 3.6 | 4.5 |
| 5.5 | 2.6 |
| 2.3 | 2.4 |
| 6.3 | 2.1 |
| 3.1 | 2.2 |
| 11.6 | 0.6 |
| 3.7 | 2.6 |
| 3.9 | 2.8 |
| 1.3 | 2.6 |
| 6.3 | 2.2 |
Day 6
| Length or root | Height of shoot |
| 2.2 | 5.4 |
| 2.5 | 2.9 |
| 5.5 | 5.9 |
| 10.1 | 5 |
| 2.5 | 3.4 |
| 3.6 | 5.4 |
| 3.8 | 4.6 |
| 1.6 | 2.9 |
| 2.9 | 2.1 |
Day 7
| Length of root | Height of shoot |
| 4.9 | 6 |
| 7.5 | 7 |
| 2.3 | 6.3 |
| 4.1 | 5.5 |
| 5.9 | 8 |
| 13.9 | 10.1 |
| 9.0 | 6.3 |
| 10.6 | 4.5 |
| 3.5 | 5 |
| 9.5 | 9.5 |
2. Relative humidity
Day 3
outside
| Time | DBT | WBT | RH |
| 10:00 | 27 | 16 | 30 |
| 11:00 | 32 | 16 | 15 |
| 12:00 | 35 | 19 | 20 |
| 2:00 | 37 | 20 | 59 |
| 4:00 | 36 | 20 | 32 |
| 8:00 | 27 | 16 | 30 |
Inside
| Time | DBT | WBT | RH |
| 10:00 | 32 | 26 | 62 |
| 11:00 | 40 | 28 | 40 |
| 12:00 | 37 | 26 | 42 |
| 2:00 | 39 | 25 | 32 |
| 4:00 | 36 | 22 | 30 |
| 8:00 | 23 | 16 | 48 |
Day 4
outside
| Time | DBT | WBT | RH (%) |
| 11:00 | 32 | 22 | 41 |
| 12:00 | 34 | 23 | 39 |
| 1:00 | 35 | 26 | 48 |
| 2:00 | 37 | 21 | 22 |
| 3:00 | 36 | 24 | 36 |
| 4:00 | 34 | 29 | 68 |
| 5:00 | 33 | 20 | 29 |
Inside
| Time | DBT | WBT | RH (%) |
| 11:00 | 32 | 25 | 55 |
| 12:00 | 33 | 25 | 49 |
| 1:00 | 45 | 26 | 21 |
| 2:00 | 46 | 28 | 25 |
| 3:00 | 46 | 26 | 20 |
| 4:00 | 42 | 26 | 25 |
| 5:00 | 41 | 24 | 23 |
Day 5
Outside
| Time | DBT | WBT | RH |
| 8:30 | 22 | 17 | 60 |
| 9:30 | 26 | 19 | 51 |
| 10:30 | 30 | 21 | 44 |
| 11:30 | 33 | 21 | 33 |
| 12:30 | 38 | 24 | 30 |
| 1:30 | 39 | 21 | 17 |
| 2:30 | 36 | 22 | 28 |
| 3:30 | 36 | 22 | 28 |
| 5:00 | 33 | 20 | 29 |
Inside
| Time | DBT | WBT | RH |
| 8:30 | 24 | 19 | 62 |
| 9:30 | 31 | 23 | 50 |
| 10:30 | 35 | 24 | 39 |
| 11:30 | 36 | 24 | 36 |
| 12:30 | 42 | 24 | 21 |
| 1:30 | 43 | 25 | 22 |
| 2:30 | 45 | 26 | 21 |
| 3:30 | 43 | 27 | 28 |
| 5:00 | 36 | 21 | 25 |
Day 6
outside
| Time | DBT | WBT | RH |
| 9:00 | 25 | 18 | 50 |
| 10:00 | 30 | 20 | 39 |
| 11:00 | 31 | 19 | 31 |
| 12:00 | 35 | 22 | 32 |
| 1:00 | 35 | 22 | 36 |
| 2:00 | 37 | 22 | 25 |
| 3:00 | 36 | 22 | 28 |
| 5:00 | 32 | 17 | 19 |
Inside
| Time | DBT | WBT | RH |
| 9:00 | 30 | 21 | 44 |
| 10:00 | 34 | 24 | 43 |
| 11:00 | 36 | 24 | 36 |
| 12:00 | 36 | 25 | 52 |
| 1:00 | 37 | 26 | 45 |
| 2:00 | 40 | 29 | 44 |
| 3:00 | 40 | 28 | 40 |
| 5:00 | 40 | 24 | 20 |
Day 7
outside
| Time | DBT | WBT | RH |
| 9:00 | 27 | 18 | 40 |
| 10:00 | 30 | 20 | 38 |
| 12:00 | 34 | 20 | 25 |
| 1:00 | 35 | 22 | 23 |
| 3:00 | 33 | 21 | 28 |
| 4:00 | 33 | 20 | 33 |
| 5:30 | 30 | 19 | 34 |
| 7:00 | 28 | 18 | 61 |
Inside
| Time | DBT | WBT | RH |
| 9:00 | 24 | 19 | 62 |
| 10:00 | 31 | 22 | 45 |
| 12:00 | 38 | 28 | 47 |
| 1:00 | 40 | 29 | 48 |
| 3:00 | 37 | 28 | 50 |
| 4:00 | 34 | 25 | 48 |
| 5:30 | 33 | 22 | 37 |
| 7:00 | 25 | 20 | 76 |
weight of maize
| Day | weight of maize (gm) |
| 2 | 150 |
| 3 | 164 |
| 4 | 180 |
| 5 | 188 |
| 6 | 190 |
| 7 | 208 |
Conclusion :
From above experiment for maize thw water required is 100 ml for 3 days and after that I incresed the amount of water(400ml) so the growth of maize also increses and weight of maize increses day by day .
Final Trial
In this experiment maize seeds of two varieties are taken which are farm seed and African tall which is used for fodder production. The procedure for fodder production is give in below. In this experiment after soaking seed its placed into cotton gunny bags for 24 hours at hydroponic unit. Then 600 gm of seeds were added to tray and 200 ml water are given to maize seeds. Daily weigh of four tray were taken and also the dry mass of every stage is calculated out for both of varieties.
Requirement of hydroponic fodder production:
- Hydroponic unit
- Clean water
- Seed with good germination
- Two labours
Procedure for fodder production:
1.Seed preparation:
- Remove broken seeds and dirt’s from seed.
- Store seeds in dry place.
2.Seed washing:
- Take good quality of seeds.
- Add water
- Wash the seeds with proper scrubbing by hand.
- Remove light weight floating seeds.
- Drain out water.
- Repeat all above steps till dirt and dead seeds are removed completely.
3.Seed cleaning:
- Take 0.1 % potassium permanganate solution for cleaning
- Added solution in water are settling for 5 minutes.
- Drain out water.
4.Soaking of seed:
- Soaking seeds in clean water for 12 hours of interval
- Do not soaked for more than 12 hours because fermentation of seeds gets started.
5.Seed germination:
- Place soaking seeds in dry clean cotton bags.
- Keep the loaded seeds away from direct sunlight.
- Keep for 24 hours to germination.
- Sprinkler water to cotton bags in 5 to 6 hours of interval so cotton bags remains wet.
- After 24 hours remove seed from cotton bags and take weight.
6.Loading seeds in tray:
- Ensure that the trays are clean, wash in potassium permanganate and dirt free.
- Transfer “after germination seeds” on the trays equally and put them in the lower section of unit.
- Shift trays to next level daily so that in move one step ahead in the growth cycle. day
7.Irrigation:
- Water sprayed in to tray at two hours of interval
- 400 ml water per tray are spray manually using sprayer.
8.Relative humidity control:
- For controlling the humidity at unit gunny bag shed is tie up
- Sprayed the gunny bags after half hour of interval to remains wet.
9. Harvesting:
- Trays on 8th day are ready to harvesting.
- Take out fodder mat and weight it.
Wash the trays in water to use for next trial

- cleaning of seeds.

- Washing of seeds

- Soaking of seeds for 12 hours

- for sproting added to gunny bags for 24 hous

- traying and placed into hydroponic unit.

- Weighing of fodder tray daily

- Take temp. and relative humidity reading.
Loss on Dry
To find out the dry matter of fodder for every vegetative stage the loss on dry method is used in which oven are used and for LOD approximately 34 hours get. From this LOD we can find out the water present in every growth stage of maize.
Methodology for Loss on Dry:
1.Take sample of maize fodder for every growth stage.
2.Weighning 100 gm of wet fodder.
3.placed into to oven at 45°c.
3.Take weight of sample one hour of interval till constant reading.
4.To find out loss on dry following formula use:
LOD =
Initial weight – final weight / final weight × 100

- Initial weight of sample

- Placed into Oven to dry

- Final weight
Observations:
Batch 1
- Farm seeds.
Observations:
weight of maize seed= 6000 gm
weight maize seed of after soaking =8352 gm
water added for soaking =10 lit.
| Day | Weight of Maize |
| 1 | 600 |
| 2 | 871 |
| 3 | 969.5 |
| 4 | 1007.5 |
| 5 | 1108 |
| 6 | 1286 |
| 7 | 1322.5 |
| 8 | 1438 |
| Day | Loss on dry |
| 1 | 38.43 |
| 2 | 46.56 |
| 3 | 48.64 |
| 4 | 70.07 |
| 5 | 71.12 |
| 6 | 74.91 |
| 7 | 75.23 |
| 8 | 75.41 |






2.African tall seeds
- Weight of maize = 5000 gm
- Weight after soaking of seed = 6352 gm
- Water for soaking = 10 lit.
- Weight of yield
| Day | Weight of Maize |
| 1 | 600 |
| 2 | 919.5 |
| 3 | 1161 |
| 4 | 1331 |
| 5 | 1593.5 |
| 6 | 1660 |
| 7 | 1768.5 |
| 8 | 1910 |
- Loss on Dry
| Day | Loss on dry |
| 1 | 43.84 |
| 2 | 52.60 |
| 3 | 63.91 |
| 4 | 68.22 |
| 5 | 73.54 |
| 6 | 80.74 |
| 7 | 76.03 |
| 8 | 64.68 |
Results and discussion:
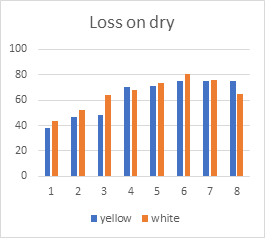

In this final trial the germination rate is higher in African tall variety Because of that in African tall fodder not effected by fungus infection and the water is sufficient to growth of fodder both of varieties. In farm seed there were very low germination rate its causes fungus infection fast in day 6 and 7 and all fodder get infected because of the unterminated seeds. The environment also in controlled conditions but at night there is very high humidity above 80% so the fungus infection increasing fast.
From above graph LOD were shown in which African tall have high loss on dry and yield also higher in African tall.
Conclusion:
1.Seed quality and seed cleaning is essential.
2.Ungerminated seeds causes fungus infection.
3. African tall have high yield.
4. Water use for this trial is sufficient for fodder.
APPENDIX I
| 100 |
| 73.91 |
| 69.15 |
| 66.55 |
| 63.92 |
| 63.05 |
| 62.86 |
| 62.70 |
| 62.50 |
| 62.04 |
| 61.45 |
| 61.39 |
| 61.09 |
| 60.84 |
| 60.81 |
| 60.74 |
| 60.65 |
| 60.55 |
| 59.80 |
| 59.72 |
| 58.61 |
| 58.58 |
| 58.34 |
| 58.34 |
| 58.34 |
Calculations : W.H.C = Initial weight – final weight / Initial weight × 100
= 100 – 58.34 / 58.34 × 100
= 0.4166 × 100 = 41.66 %
.African tall
| Weight of maize (gm) |
| 34.23 |
| 33.10 |
| 32.23 |
| 32.00 |
| 31.91 |
| 31.71 |
| 31.71 |
| 31.68 |
| 31.66 |
| 30.63 |
| 30.54 |
| 30.50 |
| 30.41 |
| 30.35 |
| 30.34 |
| 30.34 |
calculations:
W.H.C = Initial weight – final weight / Initial weight × 100
= 50 -30.34 / 50
= 19.66 / 50 × 100
= 39.32 %
3.farm seed
| Weight of maize |
| 50 |
| 35.33 |
| 33.35 |
| 33.02 |
| 32.75 |
| 32.75 |
| 32.50 |
| 32.47 |
| 32.42 |
| 32.11 |
| 32.08 |
| 32.03 |
W.H.C = Initial weight – final weight / Initial weight × 100= 35.94 %
APPENDIX II
Observations:
Weight of maize
1.Farm seed
| Day | Tray 1 | Tray 2 | Tray 3 | Tray 4 | Average |
| 1 | 600 | 600 | 600 | 600 | 600 |
| 2 | 848 | 896 | 930 | 810 | 871 |
| 3 | 914 | 944 | 1052 | 968 | 969.5 |
| 4 | 1008 | 1000 | 1024 | 998 | 1007.5 |
| 5 | 1082 | 1064 | 1214 | 1072 | 1108 |
| 6 | 1206 | 1266 | 1366 | 1306 | 1286 |
| 7 | 1230 | 1298 | 1396 | 1366 | 1322.5 |
| 8 | 1344 | 1402 | 1514 | 1492 | 1438 |
2.African tall
| Day | Tray 1 | Tray 2 | Tray 3 | Tray 4 | Average |
| 1 | 600 | 600 | 600 | 600 | 600 |
| 2 | 848 | 896 | 930 | 810 | 871 |
| 3 | 914 | 944 | 1052 | 968 | 969.5 |
| 4 | 1008 | 1000 | 1024 | 998 | 1007.5 |
| 5 | 1082 | 1064 | 1214 | 1072 | 1108 |
| 6 | 1206 | 1266 | 1366 | 1306 | 1286 |
| 7 | 1230 | 1298 | 1396 | 1366 | 1322.5 |
| 8 | 1344 | 1402 | 1514 | 1492 | 1438 |
LOD of growing stage observations :
farm seed
| DAY 1 | DAY 2 | DAY 3 | DAY 4 | DAY 5 | DAY 6 | DAY 7 | DAY 18 |
| 100.63 | 100.38 | 100.64 | 100.73 | 100 | 100.55 | 100.32 | 100.38 |
| 69.61 | 62.37 | 61.88 | 61.88 | 33.56 | 62.25 | 33.76 | 36.72 |
| 67.10 | 56.70 | 56.36 | 56.36 | 31.15 | 35.58 | 27.95 | 36.47 |
| 66.90 | 56.09 | 55.22 | 55.22 | 30.63 | 32.11 | 27.50 | 35.98 |
| 65.18 | 56.15 | 53.96 | 53.96 | 30.58 | 30.72 | 26.81 | 35.78 |
| 64.54 | 55.85 | 53.94 | 53.94 | 30.40 | 30.28 | 26.80 | 35.60 |
| 64.45 | 55.62 | 53.74 | 53.74 | 30.12 | 30.19 | 26.44 | 34.91 |
| 63.85 | 54.81 | 53.41 | 53.41 | 30.24 | 30.12 | 26.42 | 34.67 |
| 63.85 | 54.08 | 52.51 | 53.23 | 29.93 | 30.08 | 25.81 | 34.02 |
| 63.33 | 53.79 | 52.19 | 52.51 | 30.04 | 25.79 | 30.55 | |
| 63.23 | 53.68 | 52.11 | 52.19 | 29.96 | 25.41 | 30.17 | |
| 63.20 | 53.64 | 52.05 | 52.11 | 29.78 | 25.09 | 25.22 | |
| 62.45 | 53.64 | 51.81 | 52.05 | 29.67 | 25.09 | 25.09 | |
| 62.19 | 53.64 | 51.77 | 51.81 | 29.68 | 25.09 | 24.97 | |
| 62.13 | 51.77 | 29.50 | 24.97 | ||||
| 61.88 | 51.77 | 29.98 | 24.97 | ||||
| 61.44 | 51.77 | 28.88 | |||||
| 61.95 | |||||||
| 61.95 | |||||||
| 61.95 |
African tall
| Day 1 | Day 2 | Day 3 | Day 4 | Day 5 | Day 6 | Day 7 | Day 8 |
| 100.50 | 91.51 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100.13 | 100.12 | 100.16 |
| 66.56 | 52.16 | 41.02 | 37.71 | 62.48 | 24.54 | 35.31 | 47.56 |
| 62.84 | 46.09 | 37.84 | 33.04 | 34.32 | 20.41 | 35.05 | 39.42 |
| 62.13 | 46.00 | 37.39 | 32.57 | 30.51 | 19.83 | 25.02 | 37.83 |
| 62.67 | 45.64 | 37.14 | 32.26 | 28.19 | 19.70 | 24.80 | 36.69 |
| 61.49 | 45.59 | 36.90 | 31.94 | 27.67 | 19.36 | 24.69 | 36.59 |
| 59.40 | 45.19 | 36.77 | 31.93 | 27.50 | 19.30 | 24.59 | 35.91 |
| 58.33 | 45.02 | 36.74 | 31.84 | 27.46 | 19.29 | 24.34 | 35.85 |
| 58.26 | 44.69 | 36.39 | 31.83 | 27.35 | 19.28 | 24.34 | 35.78 |
| 57.38 | 44.53 | 36.32 | 31.78 | 27.04 | 24.27 | 35.74 | |
| 57.38 | 44.39 | 36.09 | 26.96 | 23.99 | 35.70 | ||
| 57.34 | 44.37 | 26.80 | 23.99 | 35.57 | |||
| 57.20 | 43.60 | 26.76 | |||||
| 57.18 | 43.42 | 26.75 | |||||
| 56.44 | 43.38 | 26.41 | |||||
| 56.44 | 43.38 | ||||||
| 43.38 |
Temperature and relative humidity observations
| 16/04/2019 | ||
| Time | DBT | RH % |
| 9:00 | 30 | 72.7 |
| 10:00 | 32 | 56.4 |
| 11:00 | 33 | 62.6 |
| 12:00 | 34 | 68.8 |
| 1:30 | 34 | 56.4 |
| 3:00 | 36 | 59.5 |
| 4:00 | 35 | 53.5 |
| 17/04/2019 | ||
| Time | DBT | RH% |
| 7:00 | 11 | 77.2 |
| 11:00 | 27 | 71.1 |
| 12:00 | 33 | 62.6 |
| 3:00 | 34 | 60 |
| 4:00 | 34 | 40 |
| 5:00 | 34 | 55.6 |
| 19/04/2019 | ||
| Time | DBT | RH% |
| 8:00 | 23 | 78.62 |
| 9:00 | 29 | 43.12 |
| 10:00 | 34 | 38.54 |
| 11:00 | 35 | 40.08 |
| 12:00 | 36 | 43.11 |
| 3:00 | 40 | 33.65 |
| 4:00 | 37 | 44.69 |
| 5:00 | 34 | 23.30 |
| 8:00 | 26 | 61.95 |
| 20/04/2019 | ||
| Time | DBT | RH % |
| 9:00 | 30 | 46.66 |
| 10:00 | 35 | 32.33 |
| 11:00 | 35 | 44.35 |
| 12:00 | 39 | 38.51 |
| 1:00 | 37 | 33.50 |
| 2:00 | 35 | 45 |
| 3:00 | 34 | 60 |
| 4:00 | 34 | 78 |
| 21/04/2019 | ||
| Time | DBT | RH % |
| 9:00 | 31 | 63.98 |
| 10:00 | 34 | 44.77 |
| 11:00 | 33 | 54.43 |
| 12:00 | 36 | 60.95 |
| 1:00 | 38 | 70.02 |
| 2:00 | 40 | 51.00 |
| 4:00 | 35 | 58.40 |
| 22/04/2019 | ||
| Time | DBT | RH % |
| 7:00 | 21 | 82.8 |
| 9:00 | 29 | 65.9 |
| 10:00 | 34 | 47.8 |
| 11:00 | 36 | 54.3 |
| 12:00 | 35 | 58.6 |
| 1:00 | 39 | 61 |
| 2:00 | 42 | 41.5 |
| 3:00 | 39 | 61 |
| 4:00 | 39 | 56.3 |
| 23/04/2019 | ||
| Time | DBT | RH% |
| 9:00 | 29 | 72.2 |
| 11:00 | 30 | 72.7 |
| 12:00 | 35 | 66.9 |
| 1:00 | 37 | 64.5 |
| 2:00 | 32 | 62 |
| 2:30 | 34 | 52.8 |
| 3:00 | 35 | 63.8 |
| 4:00 | 35 | 53.51 |
| 24/04/2019 | ||
| Time | DBT | RH % |
| 9:00 | 31 | 67.1 |
| 11:00 | 32 | 56.4 |
| 11:30 | 34 | 62 |
| 12:00 | 34 | 52.8 |
| 1:00 | 35 | 63.2 |
| 2:00 | 37 | 70.2 |
| 3:00 | 41 | 53 |
| 4:00 | 36 | 75.3 |
Other tasks:
Assignment no 1
Objective: To grow hydroponically wheat grass.
As we know wheat grass is healthy food for animals so I have to grow wheat grass hydroponically in hydroponic unit.
Procedure:
1.Take 1 kg of wheat grains and soaked for 24 hours in tap water.
2. After soaking of water the grains were clean by tap water.
3. Soaked grains were adding to gunny bags and placed into the dome for sprouting for 24 hours.
4.Removed grains from the gunny bags and added to the clean tray 200 gm/tray.
5.Daily spray the water to the grains at one hour of interval.
6.Trichoderma test given to each tray for fungus control. (10 gm/l)
7.Take readings of temperature and humidity.
Observations:
1.Weight of maize = 2000 gm
2.Water added for soaking = 2 litters.
3.weight after soaking = 2307 gm
Following tables showing Temperature and humidity.
| 6/1/2019 | ||
| Time | Temp.(°C) | RH (%) |
| 10:00 | 24 | 84 |
| 12:00 | 27 | 53 |
| 3:00 | 26 | 65 |
| 5:00 | 30 | 67 |
| 8:00 | 24 | 57 |
| 7/1/2019 | ||
| Time | Temp.(°C) | RH (%) |
| 10:00 | 26 | 65 |
| 12:00 | 28 | 79 |
| 3:00 | 25 | 71 |
| 5:00 | 23 | 77 |
| 8:00 | 22 | 70 |
| 8/1/2019 | ||
| Time | Temp.(°C) | RH (%) |
| 10:00 | 23 | 77 |
| 12:00 | 24 | 84 |
| 3:00 | 26 | 51 |
| 5:00 | 22 | 54 |
| 8:00 | 20 | 83 |
| 9/1/2019 | ||
| Time | Temp.(°C) | RH (%) |
| 10:00 | 25 | 64 |
| 12:00 | 28 | 54 |
| 3:00 | 32 | 47 |
| 5:00 | 29 | 44 |
| 8:00 | 20 | 75 |
| 10/1/2019 | ||
| Time | Temp.(°C) | RH (%) |
| 10:00 | 28 | 54 |
| 12:00 | 30 | 45 |
| 3:00 | 35 | 49 |
| 5:00 | 22 | 76 |
| 8:00 | 21 | 75 |
| 11/1/2019 | ||
| Time | Temp.(°C) | RH (%) |
| 10:00 | 26 | 85 |
| 12:00 | 32 | 44 |
| 3:00 | 31 | 68 |
| 5:00 | 22 | 76 |
| 8:00 | 20 | 91 |
| 12/1/2019 | ||
| Time | Temp.(°C) | RH (%) |
| 10:00 | 26 | 58 |
| 12:00 | 28 | 72 |
| 3:00 | 30 | 50 |
| 5:00 | 27 | 47 |
| 8:00 | 24 | 63 |
| 13/01/2019 | ||
| Time | Temp.(°C) | RH (%) |
| 10:00 | 27 | 58 |
| 12:00 | 30 | 61 |
| 3:00 | 30 | 45 |
| 5:00 | 22 | 76 |
| 8:00 | 21 | 75 |
| 14/01/2019 | ||
| Time | Temp.(°C) | RH (%) |
| 10:00 | 22 | 84 |
| 12:00 | 27 | 58 |
| 3:00 | 30 | 45 |
| 5:00 | 22 | 76 |
| 8:00 | 20 | 91 |
| 13/01/2019 | ||
| Time | Temp.(°C) | RH (%) |
| 10:00 | 28 | 54 |
| 12:00 | 32 | 80 |
| 3:00 | 37 | 44 |
| 5:00 | 20 | 91 |
| 8:00 | 20 | 83 |
Result and conclusion:
The fodder was grown in 7 days but there is fungus infection. which is not healthy for animal.




