Title- To study reduce the clogging of drip with the help of chemigation process.
Introduction
Lime softening, also known as Clark’s process, is a type of water treatment used for water softening which uses the addition of limewater (calcium hydroxide) to remove hardness(calcium and magnesium) ions by precipitation.Lime softening was first used in 1841 to treat Thames River water. The process expanded in use as the bactericidal effect of the process was discovered. Lime softening greatly expanded in use during the early 1900s as industrial water use expanded. As lime in the form of limewater is added to raw water, the pH is raised and the equilibrium of carbonate species in the water is shifted. Dissolved carbon dioxide (CO2) is changed into bicarbonate and then carbonate. This action causes calcium carbonate to precipitate due to exceeding the solubility product. Additionally, magnesium can be precipitated as magnesium hydroxide in a double displacement reaction.In the process both the calcium (and to an extent magnesium) in the raw water as well as the calcium added with the lime are precipitated. This is in contrast to ion exchange softening where sodium is exchanged for calcium and magnesium ions. In lime softening, there is a substantial reduction in total dissolved solids (TDS) whereas in ion exchange softening, there is no significant change in the level of TDS .Lime softening can also be used to remove iron, manganese, radium and arsenic from water.
Objectives
- To study the root cause of clogging problems into drip irrigation.
- To find find out the preventive methods for clogging problem.
- To design and suggest preventive treatment for Vigyan Ashram drip irrigation system.
- To document a SOP (Standard Operating Procedure) for above system.
29/03/2022
Firstly I’m checked the total hardness, permanent hardness and temporary hardness of water.

To estimate the amount of total hardness present in the given sample of water by EDTA ( Ethylenediamine Tetra Acid) titration method.
Apparatus required:
50 ml Burette, 20 ml Pipette, 250 ml Conical flask, 100 ml Beaker, 250 mlbeaker, Glass funnel.
Reagents:
EDTA solution, Standard CaCO3 solution, Eriochrome BlackT indicator, Buffersolution.
Theory:
EDTA (Ethylenediamine tetra acetic acid) forms colorless stable complexes with Ca2+and Mg2+ions present in water at pH = 9-10. To maintain the pH of the solution at 9-10, buffersolution (NH4Cl + NH4OH) is used. Eriochrome Black-T (E.B.T) is used as an indicator.The sample of hard water must be treated with buffer solution and EBT indicator which formsunstable, wine-red colored complex s with Ca2+ and Mg2+ present in water .

Procedure:
1. Standardization of EDTA
(i) Pipette out 20 ml of standard hard water into a conical flask.
(ii) Add 5 ml of buffer solution and few drops of Eriochrome Black-T. The indicator, which is
originally blue color would acquire a wine-red color.
(iii) Titrate with EDTA solution taken in the burette, till the wine red color changes to blue
which is the end point. Let the burette reading of EDTA be V2 ml.
2. Determination of Total hardness
Repeat the above titration method for sample hard water instead of standard hard water. Let the
burette reading of EDTA be V3 ml.
3. Determination of Permanent hardness
Take 100 ml of sample hard water in 250 ml beaker. Boil it to remove temporary hardness to
about half of this volume and cool to room temperature. Filter through filter paper to remove
insoluble CaCO3 and MgCO3. Make up the volume to the original 100 ml by adding distilled
water. Now pipette out 20 ml of this solution into a clean conical flask. Then repeat the process
of titration steps as mentioned above. Let the burette reading of EDTA be V4 ml.
Observations :
| Data | Burette Reading ( ml ) |
| V1 ( Volume of standard hard water in conical flask ) | 20 ml |
| V2 ( Volume of EDTA consumed ) | 27.7 ml |
| V3 ( Volume of sample hard water in conical flask) | 3.4 ml |
| V4 (Volume of sample hard water in conical flask ) | 3.1 ml |
- Calculations1: Standardization of EDTA
- M1V1 = M2V2
- Where, M1 = Molarity of standard hard water = 0.002
- V1 = Volume of standard hard water in conical flask
- M2 = Molarity of EDTA = 0.001
- V2 = Volume of EDTA consumed (burette reading)
- Calculation 2: Determination of Total hardness
- M2V2 = M3V3
- Where, M3 = Total hardness of sample water =0.0081
- V1 = Volume of sample hard water in conical flask3.
- Determination of Permanent hardness
- M2V2 = M4V4
- Where, M4= Permanent hardness of sample water = 0.0089
- V4 = Volume of sample hard water in conical flask.
- Calculation 3 : Determination of Temporary hardness
- Temporary hardness = Total hardness – Permanent hardness = 0.0081 – 0.0089 = 0.0008 x 10 5 = 80 ppm
- Result: The hardness of the given water sample
- Total hardness = 81 ppm
- Permanent hardness = 89 ppm
- Temporary hardness = 80 ppm
12/04/2022-17/04/2022
In Clark’s water softening method, hard water is treated with Ca(OH)2 (slaked lime). Calcium hydroxide is Clark’s reagent. It removes the hardness of water by converting bicarbonates into carbonate. Water softening by Clarke’s process uses calcium hydroxide (lime)
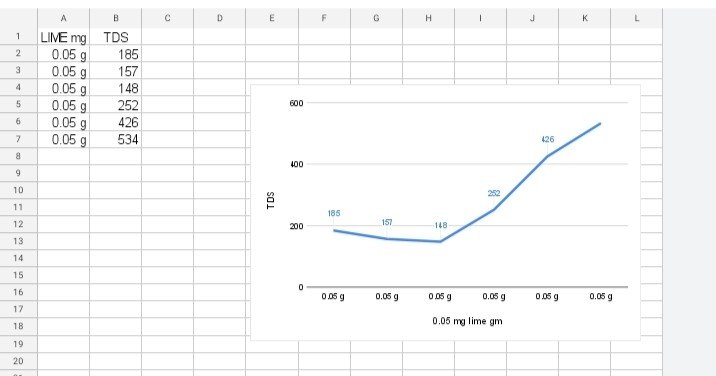
TDS check by each 10 min by using 0.05g of LIME (Calcium Hydroxide) and created graph from it.
| Time | LIME (Calcium Hydroxide) in g of mg | TDS |
| 11:55AM-12:05PM | 0.05g | 185 |
| 12:05PM-12:15PM | 0.05g | 157 |
| 12:15PM-12:25PM | 0.05g | 148 |
| 12:25PM-12:35PM | 0.05g | 252 |
| 12:35PM-12:45PM | 0.05g | 426 |
| 12:45PM-12:55PM | 0.05g | 534 |
Then boil water and check the TDS of tap/ normal water.
TDS before boiling – 182ppm
TDS after boiling –176ppm
15/04/2022
Then checked the TDS of the water in the well is as follows:
TDS before boiling –205ppm
TDS after boiling –200ppm
20/04/2022
TDS meter calibration procedure:
1PPM=1mg=0.001gm
1000PPM=1000mg=1gm
1gm of Nacl for l lit of distilled water
For 342PPM = 342mg =0.0342gm of Nacl
For 500PPM = 500mg =0.05gm of Nacl
For 1000PPM = 1000mg =0.1gm of Nacl
For 1500PPM = 1500mg =0.15gm of Nacl
For 2000PPM = 2000mg =0.2gm of Nacl
Readings of calibration
| Standard solution | Reading |
| 342PPM | 336PPM |
| 500PPM | 457PPM |
| 1000PPM | 846PPM |
| 15000PPM | 1450PPM |
| 2000PPM | 1897PPM |
According to the above data, the graph is as follows:
Observations:
After calibrating the TDS meter, the TDS of the sample water is as follows:
Hardwater TDS is also 401PPM.
Well water TDS is 314PPM.
ASK Group water sample TDS is 1830×2=3660PPM.
27/04/2022-30/04/2022
| sr.no | Time | TDS |
| 1 | 5:10PM-5:25PM | 240PPM |
| 2 | 5:55PM-6:10PM | 194PPM |
| 3 | 6;25PM-6:40PM | 170PPM |
| 4 | 10:15AM-10:30AM | 55PPM |
| 5 | 11:25AM-11:40AM | 50PPM |
| 6 | 12:10PM-12:25PM | 278PPM |
| 7 | 12:40PM-12:55PM | 480PPM |
| 8 | 1:25PM-1:40PM | 790PM |
03/052022
Collection of the water samples and determine the TDS-
| Sr.no | Water sample | TDS |
| 1. | Kitchen tap water | 208PPM |
| 2. | Well water | 211PPM |
11/05/2022
Determination of hard water tds
Initial TDS – 1145PPM
pH – 7.24
| Sr. no | Time | TDS |
| 1. | 3.55 PM – 4.10PM | 1046PPM |
| 2. | 4.15 PM – 4.30PM | 963PPM |
| 3 | 4.35 PM – 4.50PM | 929PPM |
| 4. | 4.55 PM – 5.10 PM | 1370PPM |
| 5. | 5.15 PM -5.30PM | 1739PPM |
| 6. | 5.45PM – 6.00PM | above 2000PPM |
12/05/2022
Shubham Shembade, an old student of Vigyan Ashram in Pabal, met Dixit sir and told him about the hard water in his house.
And the water taps in the house are choked due to hard water of borewell.
Then Dixit sir gave me an idea about it.
Then I started working on it. First I took a water sample and measured the TDS.
Then I checked the LOD ( loss of drying) of that water and checked that TDS comes from it.
After removing the LOD, it came to 587g, from which came 1174ppm TDS.
Then I checked the hardness is as follows,
Permanent Hardness- 668 PPM.
Temporary Hardness- 652 PPM.
Total Hardness- 1320 PPM.
17/05/2022
Checked hardness after applying lime.
Permanent Hardness- 850 PPM.
Temporary Hardness- 150 PPM.
Total Hardness- 1000 PPM.
OBJECTIVE 1: To study the root cause of clogging problems into drip irrigation.
The water in Vigyan Ashram appears to be hard, just as the water level in the well decreases in summer and the increased hardness clogs the drip, so we need to study for that. High amounts of dissolved calcium and magnesium salts can cause scale to form in pipes and appliances, reducing their lifespan.
•Tree roots
•Mineral buildup
•Food waste
•Dirt
•Soap
•Hardness of water
Objective 2: To find find out the preventive methods for clogging problem.
Different methods for reducing hardness and TDS in Water:
1.Reverse Osmosis (R.O.): Reverse Osmosis removes TDS by forcing the water, under pressure, through a synthetic membrane. The membrane contains microscopic pores which will allow only molecules smaller than 0.0001 microns to pass through. As the molecules of dissolved metals and salts are large compared to the water molecules, water squeezes through the membrane leaving the metals and salts behind.
2.Distillation: The process involves boiling water to produce water vapor. The water vapor rises to a cool surface where it is condensed back into the liquid form. The dissolved salts are unable to vaporize and remain in the boiling solution.
3. Deionisation (DI): In this process, water is passed through a positive and negative electrode. The ion-selective membranes enable the positive ions to separate from the water and move towards the negative electrode. The end result is de-ionized water with high purity. However, the water is first passed through a reverse osmosis unit first in order to remove the non-ionic organic contaminants.
4. Lime treatment (Calcium Hydroxide): As compare to others methods, Lime softening, also known as Clark’s process, is a type of water treatment used for water softening which uses the addition of limewater (calcium hydroxide) to remove hardness(calcium and magnesium) ions by precipitation. Lime treatment is a very cheap treatment as compare to other methods.
29/05/2022
From this I suggest design for Vigyan Ashram's drip system
Design for the drip irrigation system :
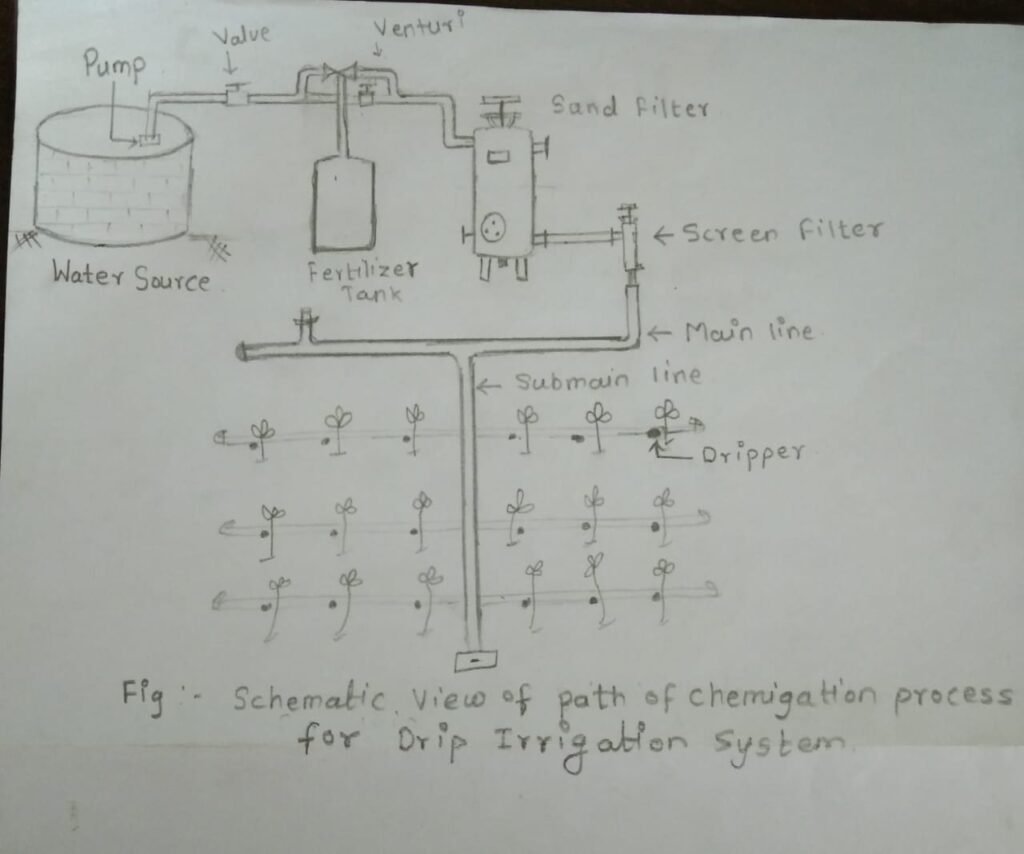
Fig : Appropriate design for Vigyan Ashram drip system.
2D sketch of the system
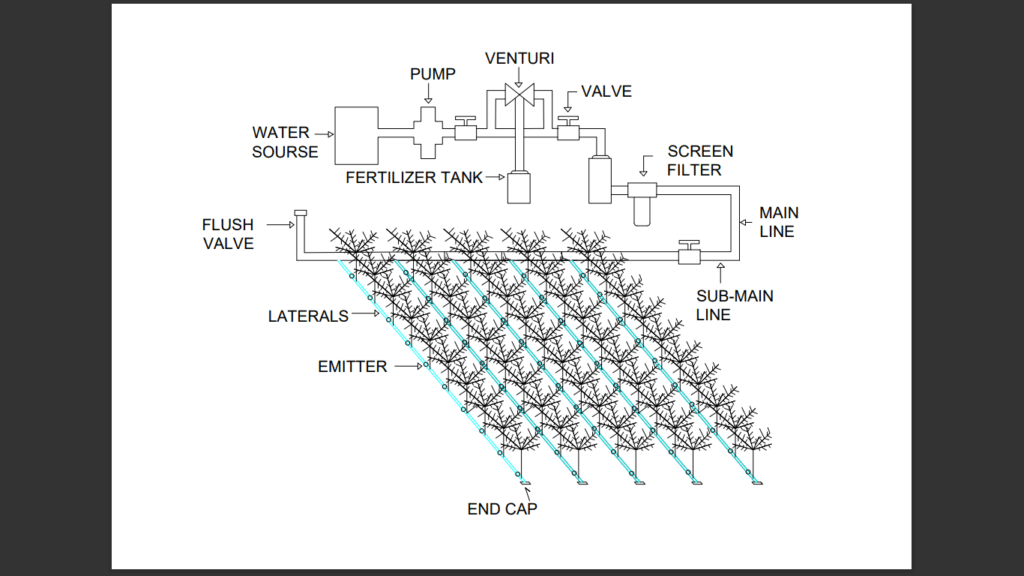
process flow diagram of drip irrigation for chemigation process:
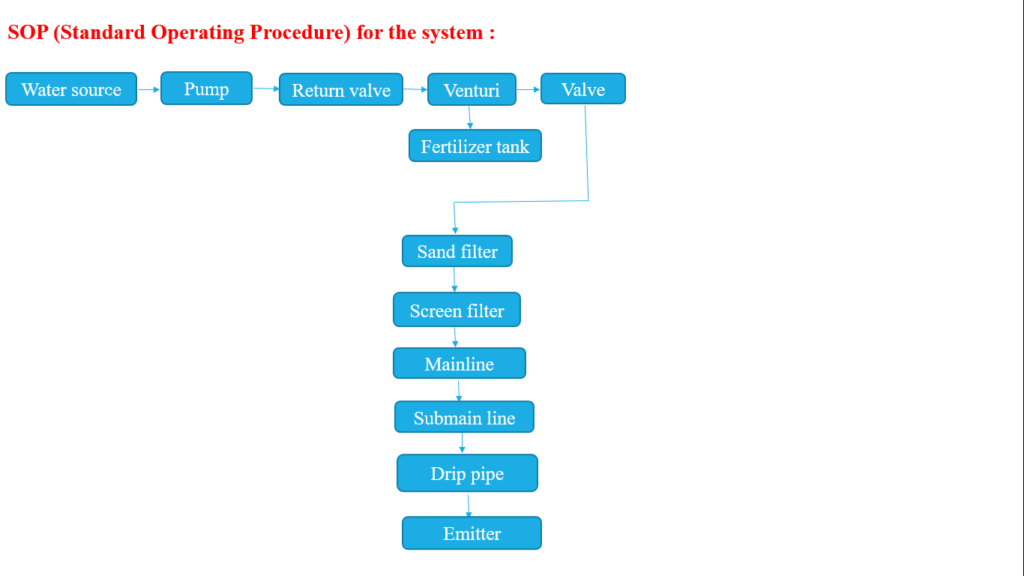
Major Components of Drip Irrigation System For Chemigation Process–
1.Pump
2. Return valve
3.Venturi
4. Fertilizer tank
5.Pressure valve
6. Sand filter
7. Screen filter
8.Main line
9. Submain line
10. Drip pipe
11. Emitter
Working principal of the system component:
Pump:
Pump station takes water from the source and provides the right pressure for delivery into the pipe system.
Return valve:
Control valves control the discharge and pressure in the entire system.
Fertilizer tank / Venturi:
Fertilizer tank/venturi slowly add a measured dose of fertilizer into the water during irrigation. This is one of the major advantages of drip irrigation over other methods.
Sand filter / Screen filter:
Filtration system cleans the water. Common types of filter include screen filters and graded sand filters which remove fine material suspended in the water.
Mainline, submain line, drip pipe:
Mainlines, submains and laterals supply water from the control head into the fields. They are usually made from PVC or polyethylene hose and should be buried below ground because they easily degrade when exposed to direct solar radiation. Lateral pipes are usually 13-32 mm diameter.
Emitters:
Emitters or drippers are devices used to control the discharge of water from the lateral to the plants. They are usually spaced more than 1 metre apart with one or more emitters used for a single plant such as a tree. For row crops more closely spaced emitters may be used to wet a strip of soil. Many different emitter designs have been produced in recent years. The basis of design is to produce an emitter which will provide a specified constant discharge which does not vary much with pressure changes, and does not block easily.
lime treatment
Ca(HCo3)2+Ca(OH)2→2CaCO3+2H2O
The scale on which i took readings is follows:
To get the first readings and check its TDS using calcium hydroxide in 2 liters of sample water as follows:
| Sr. No | TDS |
| 1 | 1060PPM |
| 2 | 975PPM |
| 3 | 900PPM |
| 4 | 835PPM |
| 5 | 1476PPM |
| 6 | 1491PPM |
| 7 | 1532PPM |
From this I realized that 0.2g of Calcium hydroxide is required for 2 liters of sample water and then I calculated how much it is required for 1000 liters.
For 1000 liter 100g calcium hydroxide required
Procedure of adding lime(calcium hydroxide) drip irrigation system for clogging treatment:
- Add 100gm lime in 1000 liter fertilizer tank
- After adding it keep stirring for half hr.
- It holds for 5 hours
- Then drain it after 5-6 hours
- Remove the remaining through valve.
- The bicarbonate will then be converted to carbonate
- Remove calcium and magnesium ions by precipitation





